Cross-stitch is a form of sewing and a popular form of counted-thread embroidery in which X-shaped stitches in a tiled, raster-like pattern are used to form a picture. The stitcher counts the threads on a piece of evenweave fabric in each direction so that the stitches are of uniform size and appearance. This form of cross-stitch is also called counted cross-stitch in order to distinguish it from other forms of cross-stitch. Sometimes cross-stitch is done on designs printed on the fabric ; the stitcher simply stitches over the printed pattern. Cross-stitch is often executed on easily countable fabric called aida cloth whose weave creates a plainly visible grid of squares with holes for the needle at each corner.

Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on caps, hats, coats, overlays, blankets, dress shirts, denim, dresses, stockings, scarfs, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. It is often used to personalize gifts or clothing items.
Needlepoint is a type of canvas work, a form of embroidery in which yarn is stitched through a stiff open weave canvas. Traditionally needlepoint designs completely cover the canvas. Although needlepoint may be worked in a variety of stitches, many needlepoint designs use only a simple tent stitch and rely upon color changes in the yarn to construct the pattern. Needlepoint is the oldest form of canvas work.

Chain stitch is a sewing and embroidery technique in which a series of looped stitches form a chain-like pattern. Chain stitch is an ancient craft – examples of surviving Chinese chain stitch embroidery worked in silk thread have been dated to the Warring States period. Handmade chain stitch embroidery does not require that the needle pass through more than one layer of fabric. For this reason the stitch is an effective surface embellishment near seams on finished fabric. Because chain stitches can form flowing, curved lines, they are used in many surface embroidery styles that mimic "drawing" in thread.
In everyday language, a stitch in the context of embroidery or hand-sewing is defined as the movement of the embroidery needle from the back of the fibre to the front side and back to the back side. The thread stroke on the front side produced by this is also called stitch. In the context of embroidery, an embroidery stitch means one or more stitches that are always executed in the same way, forming a figure. Embroidery stitches are also called stitches for short.
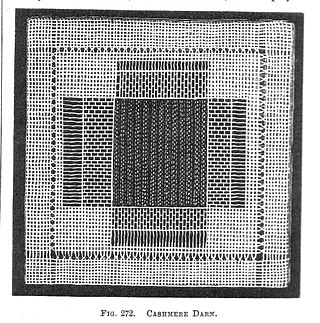
Darning is a sewing technique for repairing holes or worn areas in fabric or knitting using needle and thread alone. It is often done by hand, but using a sewing machine is also possible. Hand darning employs the darning stitch, a simple running stitch in which the thread is "woven" in rows along the grain of the fabric, with the stitcher reversing direction at the end of each row, and then filling in the framework thus created, as if weaving. Darning is a traditional method for repairing fabric damage or holes that do not run along a seam, and where patching is impractical or would create discomfort for the wearer, such as on the heel of a sock.

Backstitch or back stitch and its variants stem stitch, outline stitch and split stitch are a class of embroidery and sewing stitches in which individual stitches are made backward to the general direction of sewing. In embroidery, these stitches form lines and are most often used to outline shapes and to add fine detail to an embroidered picture. It is also used to embroider lettering. In hand sewing, it is a utility stitch which strongly and permanently attaches two pieces of fabric. The small stitches done back-and-forth makes the back stitch the strongest stitch among the basic stitches. Hence it can be used to sew strong seams by hand, without a sewing machine.
Surface embroidery is any form of embroidery in which the pattern is worked by the use of decorative stitches and laid threads on top of the foundation fabric or canvas rather than through the fabric; it is contrasted with canvas work.

Opus Anglicanum or English work is fine needlework of Medieval England done for ecclesiastical or secular use on clothing, hangings or other textiles, often using gold and silver threads on rich velvet or linen grounds. Such English embroidery was in great demand across Europe, particularly from the late 12th to mid-14th centuries and was a luxury product often used for diplomatic gifts.

A balanced fabric is one in which the warp and the weft are of the same size. In weaving, these are generally called "balanced plain weaves" or just "balanced weaves", while in embroidery the term "even-weave" is more common.

In sewing and embroidery, a satin stitch or damask stitch is a series of flat stitches that are used to completely cover a section of the background fabric. Narrow rows of satin stitch can be executed on a standard sewing machine using a zigzag stitch or a special satin stitch foot.

Embroidery thread is yarn that is manufactured or hand-spun specifically for embroidery and other forms of needlework. Embroidery thread often differs widely, coming in many different fiber types, colors and weights.

Embroidery hoops and frames are tools used to keep fabric taut while working embroidery or other forms of needlework.

Cross stitches in embroidery, needlepoint, and other forms of needlework include a number of related stitches in which the thread is sewn in an x or + shape. Cross stitch has been called "probably the most widely used stitch of all" and is part of the needlework traditions of the Balkans, Middle East, Afghanistan, Colonial America and Victorian England.

Featherstitch or feather stitch and Cretan stitch or faggoting stitch are embroidery techniques made of open, looped stitches worked alternately to the right and left of a central rib. Fly stitch is categorized with the featherstitches.

Goldwork is the art of embroidery using metal threads. It is particularly prized for the way light plays on it. The term "goldwork" is used even when the threads are imitation gold, silver, or copper. The metal wires used to make the threads have never been entirely gold; they have always been gold-coated silver or cheaper metals, and even then the "gold" often contains a very low percent of real gold. Most metal threads are available in silver and sometimes copper as well as gold; some are available in colors as well.

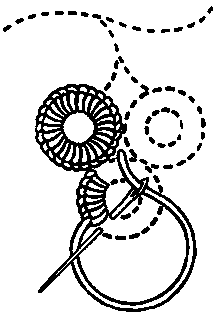
A knotted stitch, also known as knot stitch, is any embroidery technique in which the yarn or thread is knotted around itself. A knotted stitch is a type of decorative embroidery stitches which form three-dimensional knots on the surface of a textile. Common knotted stitches include French knots, coral stitch, and Pekin knot which is sometimes also referred as French knot although there is a difference in techniques between these two stitches. Knotted stitches can be subdivided into individual or detached knots, continuous knotted stitches, and knotted edgings.

The straight or running stitch is the basic stitch in hand-sewing and embroidery, on which all other forms of sewing are based. The stitch is worked by passing the needle in and out of the fabric at a regular distance. All other stitches are created by varying the straight stitch in length, spacing, and direction.

English embroidery includes embroidery worked in England or by English people abroad from Anglo-Saxon times to the present day. The oldest surviving English embroideries include items from the early 10th century preserved in Durham Cathedral and the 11th century Bayeux Tapestry, if it was worked in England. The professional workshops of Medieval England created rich embroidery in metal thread and silk for ecclesiastical and secular uses. This style was called Opus Anglicanum or "English work", and was famous throughout Europe.

Hemstitch or hem-stitch is a decorative drawn thread work or openwork hand-sewing technique for embellishing the hem of clothing or household linens. Unlike an ordinary hem, hemstitching can employ embroidery thread in a contrasting color so as to be noticeable.