
Cross-stitch is a form of sewing and a popular form of counted-thread embroidery in which X-shaped stitches in a tiled, raster-like pattern are used to form a picture. The stitcher counts the threads on a piece of evenweave fabric in each direction so that the stitches are of uniform size and appearance. This form of cross-stitch is also called counted cross-stitch in order to distinguish it from other forms of cross-stitch. Sometimes cross-stitch is done on designs printed on the fabric ; the stitcher simply stitches over the printed pattern. Cross-stitch is often executed on easily countable fabric called aida cloth whose weave creates a plainly visible grid of squares with holes for the needle at each corner.

Embroidery is the craft of decorating fabric or other materials using a needle to apply thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as pearls, beads, quills, and sequins. In modern days, embroidery is usually seen on caps, hats, coats, overlays, blankets, dress shirts, denim, dresses, stockings, scarfs, and golf shirts. Embroidery is available in a wide variety of thread or yarn colour. It is often used to personalize gifts or clothing items.

Blackwork, sometimes historically termed Spanish blackwork, is a form of embroidery generally worked in black thread, although other colours are also used on occasion, as in scarletwork, where the embroidery is worked in red thread. Originating in Tudor period England, blackwork typically, though not always, takes the form of a counted-thread embroidery, where the warp and weft yarns of a fabric are counted for the length of each stitch, producing uniform-length stitches and a precise pattern on an even-weave fabric. Blackwork may also take the form of free-stitch embroidery, where the yarns of a fabric are not counted while sewing.

Hardanger embroidery or "Hardangersøm" is a form of embroidery traditionally worked with white thread on white even-weave linen or cloth, using counted thread and drawn thread work techniques. It is sometimes called whitework embroidery.

Drawn thread work is one of the earliest forms of open work embroidery, and has been worked throughout Europe. Originally it was often used for ecclesiastical items and to ornament shrouds. It is a form of counted-thread embroidery based on removing threads from the warp and/or the weft of a piece of even-weave fabric. The remaining threads are grouped or bundled together into a variety of patterns. The more elaborate styles of drawn thread work use a variety of other stitches and techniques, but the drawn thread parts are their most distinctive element. It is also grouped with whitework embroidery because it was traditionally done in white thread on white fabric and is often combined with other whitework techniques.
Needlepoint is a type of canvas work, a form of embroidery in which yarn is stitched through a stiff open weave canvas. Traditionally needlepoint designs completely cover the canvas. Although needlepoint may be worked in a variety of stitches, many needlepoint designs use only a simple tent stitch and rely upon color changes in the yarn to construct the pattern. Needlepoint is the oldest form of canvas work.

Twill is a type of textile weave with a pattern of diagonal parallel ribs. It is one of three fundamental types of weave, along with plain weave and satin. It is made by passing the weft thread over one or more warp threads then under two or more warp threads and so on, with a "step," or offset, between rows to create the characteristic diagonal pattern. Because of this structure, twill generally drapes well.

In the manufacture of cloth, warp and weft are the two basic components in weaving to transform thread and yarn into textile fabrics. The vertical warp yarns are held stationary in tension on a loom (frame) while the horizontal weft is drawn through (inserted) over and under the warp thread. In the terminology of weaving, each warp thread is called a warp end; a pick is a single weft thread that crosses the warp thread, synonymous terms are fill yarn and filling yarn.
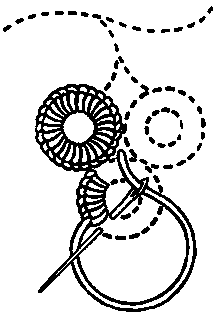
In everyday language, a stitch in the context of embroidery or hand-sewing is defined as the movement of the embroidery needle from the back of the fibre to the front side and back to the back side. The thread stroke on the front side produced by this is also called stitch. In the context of embroidery, an embroidery stitch means one or more stitches that are always executed in the same way, forming a figure. Embroidery stitches are also called stitches for short.

Aida cloth is an open, even-weave fabric traditionally used for cross-stitch embroidery. This cotton fabric has a natural mesh that facilitates cross-stitching and enough natural stiffness that the crafter does not need to use an embroidery hoop.
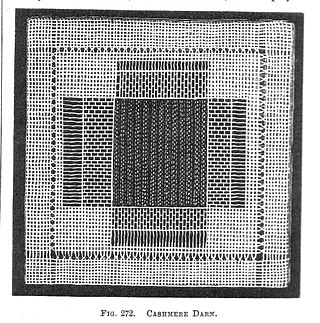
Darning is a sewing technique for repairing holes or worn areas in fabric or knitting using needle and thread alone. It is often done by hand, but using a sewing machine is also possible. Hand darning employs the darning stitch, a simple running stitch in which the thread is "woven" in rows along the grain of the fabric, with the stitcher reversing direction at the end of each row, and then filling in the framework thus created, as if weaving. Darning is a traditional method for repairing fabric damage or holes that do not run along a seam, and where patching is impractical or would create discomfort for the wearer, such as on the heel of a sock.

Textile manufacturing is a major industry. It is largely based on the conversion of fibre into yarn, then yarn into fabric. These are then dyed or printed, fabricated into cloth which is then converted into useful goods such as clothing, household items, upholstery and various industrial products.

A balanced fabric is one in which the warp and the weft are of the same size. In weaving, these are generally called "balanced plain weaves" or just "balanced weaves", while in embroidery the term "even-weave" is more common.

Knitted fabric is a textile that results from knitting, the process of inter-looping of yarns or inter-meshing of loops. Its properties are distinct from woven fabric in that it is more flexible and can be more readily constructed into smaller pieces, making it ideal for socks and hats.
Tent stitch is a small, diagonal needlepoint stitch that crosses over the intersection of one horizontal (weft) and one vertical (warp) thread of needlepoint canvas forming a slanted stitch at a 45-degree angle. It is also known as needlepoint stitch and is one of the most basic and versatile stitches used in needlepoint and other canvas work embroidery. When worked on fine weave canvas over a single warp and weft thread it is known as petit point in contrast to stitches, such as Gobelin, worked over multiple warp and/or weft threads.

A selvage or selvedge is a "self-finished" edge of a piece of fabric which keeps it from unraveling and fraying. The term "self-finished" means that the edge does not require additional finishing work, such as hem or bias tape, to prevent fraying.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.

The Toda Embroidery, also locally known as "pukhoor", is an art work among the Toda pastoral people of Nilgiris, in Tamil Nadu, made exclusively by their women. The embroidery, which has a fine finish, appears like a woven cloth but is made with use of red and black threads with a white cotton cloth background. Both sides of the embroidered fabric are usable and the Toda people are proud of this heritage. Both men and women adorn themselves with the embroidered cloaks and shawls.

Wangkhei Phee is a textile fabric made of white cotton. It is a product which is protected under the GI registration and is made throughout the Indian state of Manipur and is woven by women. The fabric is transparent, has many designs on its body, and is popularly worn by women of Manipur for marriage ceremonies and other festive occasions.

The Game of Thrones Tapestry is a hand-crafted tapestry, woven by hand on a jacquard loom, with additional embroidery. The tapestry tells the entire story of the television show, Game of Thrones. It consists of seven 11-metre-long panels and one 10.5-metre panel. The eight panels depict scenes from each episode and include images of crew at work. The tapestry was commissioned by HBO and Tourism Ireland, the tourism bureau of Northern Ireland where HBO filmed much of the series.




















