
Bivalvia, in previous centuries referred to as the Lamellibranchiata and Pelecypoda, is a class of marine and freshwater molluscs that have laterally compressed bodies enclosed by a shell consisting of two hinged parts. Bivalves as a group have no head and they lack some usual molluscan organs like the radula and the odontophore. They include the clams, oysters, cockles, mussels, scallops, and numerous other families that live in saltwater, as well as a number of families that live in freshwater. The majority are filter feeders. The gills have evolved into ctenidia, specialised organs for feeding and breathing. Most bivalves bury themselves in sediment where they are relatively safe from predation. Others lie on the sea floor or attach themselves to rocks or other hard surfaces. Some bivalves, such as the scallops and file shells, can swim. The shipworms bore into wood, clay, or stone and live inside these substances.

Lingulata is a class of brachiopods, among the oldest of all brachiopods having existed since the Cambrian period. They are also among the most morphologically conservative of the brachiopods, having lasted from their earliest appearance to the present with very little change in shape. Shells of living specimens found today in the waters around Japan are almost identical to ancient Cambrian fossils.

Mucrospirifer is a genus of extinct brachiopods in the class Rhynchonellata (Articulata) and the order Spiriferida. They are sometimes known as "butterfly shells". Like other brachiopods, they were filter feeders. These fossils occur mainly in Middle Devonian strata and appear to occur around the world, except in Australia and Antarctica.

Terebratulids are one of only three living orders of articulate brachiopods, the others being the Rhynchonellida and the Thecideida. Craniida and Lingulida include living brachiopods, but are inarticulates. The name, Terebratula, may be derived from the Latin "terebra", meaning "hole-borer". The perceived resemblance of terebratulid shells to ancient Roman oil lamps gave the brachiopods their common name "lamp shell".
The Obolellata are a class of Rhynchonelliform brachiopods with two orders, Obolellida and Naukatida. They are essentially restricted to the lower-middle Cambrian.

Linguliformea is a subphylum of inarticulate brachiopods. These were the earliest of brachiopods, ranging from the Cambrian into the Holocene. They rapidly diversified during the Cambrian into the Ordovician, but most families became extinct by the end of the Devonian.

Lingula is a genus of brachiopods within the class Lingulata. Lingula or forms very close in appearance have existed possibly since the Cambrian. Like its relatives, it has two unadorned organo-phosphatic valves and a long fleshy stalk. Lingula lives in burrows in barren sandy coastal seafloor and feeds by filtering detritus from the water. It can be detected by a short row of three openings through which it takes in water (sides) and expels it again (middle).

The Craniidae are a family of brachiopods, commonly known as lamp shells. Although it belongs to a subdivision called the inarticulata which have shells where the mineral content consist of calcium phosphate, the Craniidae have shells that consist of calcium carbonate. Other special characteristics of this family are that no outgrowths are developed to form a hinge between both valves, nor is there any support for the lophophore. As adults, craniids either lived free on the ocean floor or, more commonly, were attached to a hard object with all or part of the ventral valve. All other brachiopods are supposed to have a stalk or pedicle, at least as an adolescent, but in craniids a pedicle is not known from any development stage.

Strophomenida is an extinct order of articulate brachiopods which lived from the lower Ordovician period to the mid-Carboniferous period. Strophomenida is part of the extinct class Strophomenata, and was the largest known order of brachiopods, encompassing over 400 genera. Some of the largest and heaviest known brachiopod species belong to this class. Strophomenids were among the most diverse and abundant brachiopods during the Ordovician, but their diversity was strongly impacted at the Late Ordovician mass extinction. Survivors rediversified into new morphologies in the Silurian, only to be impacted once again at the Late Devonian mass extinction. They finally died out in the Carboniferous period.

Phoronids are a small phylum of marine animals that filter-feed with a lophophore, and build upright tubes of chitin to support and protect their soft bodies. They live in most of the oceans and seas, including the Arctic Ocean but excluding the Antarctic Ocean, and between the intertidal zone and about 400 meters down. Most adult phoronids are 2 cm long and about 1.5 mm wide, although the largest are 50 cm long.

Brachiopods, phylum Brachiopoda, are a phylum of trochozoan animals that have hard "valves" (shells) on the upper and lower surfaces, unlike the left and right arrangement in bivalve molluscs. Brachiopod valves are hinged at the rear end, while the front can be opened for feeding or closed for protection. Two major categories are traditionally recognized, articulate and inarticulate brachiopods. The word "articulate" is used to describe the tooth-and-groove structures of the valve-hinge which is present in the articulate group, and absent from the inarticulate group. This is the leading diagnostic skeletal feature, by which the two main groups can be readily distinguished as fossils. Articulate brachiopods have toothed hinges and simple, vertically-oriented opening and closing muscles. Conversely, inarticulate brachiopods have weak, untoothed hinges and a more complex system of vertical and oblique (diagonal) muscles used to keep the two valves aligned. In many brachiopods, a stalk-like pedicle projects from an opening near the hinge of one of the valves, known as the pedicle or ventral valve. The pedicle, when present, keeps the animal anchored to the seabed but clear of sediment which would obstruct the opening.

The origin of the brachiopods is uncertain; they either arose from reduction of a multi-plated tubular organism, or from the folding of a slug-like organism with a protective shell on either end. Since their Cambrian origin, the phylum rose to a Palaeozoic dominance, but dwindled during the Mesozoic.
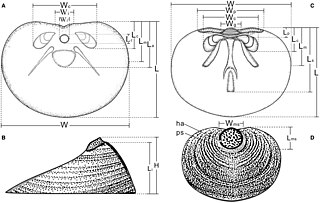
Acrotretida is an extinct order of linguliform brachiopods in the class Lingulata. They lived from the Lower Cambrian to the Middle Devonian. Acrotretida contains the sole superfamily Acrotretoidea. Many acrotretides have a tall and conical ventral valve with a pedicle opening at the apex, while the musculature is simplified relative to other linguliforms. The shell has a rounded outline, and is usually phosphatic like other linguliforms.

The Rhynchonellata is a class of Lower Cambrian to Recent articulate brachiopods that combines orders from within the Rhynchonelliformea with well developed pedicle attachment. Shell forms vary from those with wide hinge lines to beaked forms with virtually no hinge line and from generally smooth to strongly plicate. Most all are biconvex. Lophophores vary and include both looped and spiraled forms. Although morphologically distinct, included orders follow a consistent phylogenetic sequence.

Pentamerida is an order of biconvex, impunctate shelled, articulate brachiopods that are found in marine sedimentary rocks that range from the Middle Cambrian through the Devonian.

Athyridida is an order of Paleozoic brachiopods included in the Rhynchonellata, which makes up part of the articulate brachiopods.

Gigantoproductus giganteus is an extinct species of brachiopods in the family Monticuliferidae, known only from its fossil remains. It was a marine invertebrate found on the seabed in shallow seas. It probably evolved during the Devonian period and it is believed to be the largest brachiopod that has ever existed.

Trimerellida is an extinct order of craniate brachiopods, containing the superfamily Trimerelloidea and the families Adensuidae, Trimerellidae, and Ussuniidae. Trimerellidae is a small but widespread family of warm-water brachiopods ranging from the mid Ordovician (Llandeilo) to late Silurian (Ludlow). Adensuidae and Ussuniidae are monogeneric families restricted to the mid to late Ordovician of Kazakhstan.

Argyrotheca is a genus of very small to minute lampshells. All species share a large pedicel opening, one ridge on the inside of the pedunculate valve, pits in a diamond pattern on the inside of both valves, and without radial ridges that end in tubercles. It occurs in depths between 6 and 1300 m. It is known since the latest Cretaceous.

Kutorginates are early rhynchonelliform brachiopods.



















