
Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP, pyridoxal 5'-phosphate, P5P), the active form of vitamin B6, is a coenzyme in a variety of enzymatic reactions. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology has catalogued more than 140 PLP-dependent activities, corresponding to ~4% of all classified activities. The versatility of PLP arises from its ability to covalently bind the substrate, and then to act as an electrophilic catalyst, thereby stabilizing different types of carbanionic reaction intermediates.

In biochemistry, mixed acid fermentation is the metabolic process by which a six-carbon sugar is converted into a complex and variable mixture of acids. It is an anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) fermentation reaction that is common in bacteria. It is characteristic for members of the Enterobacteriaceae, a large family of Gram-negative bacteria that includes E. coli.
The hisB gene, found in the enterobacteria, in Campylobacter jejuni and in Xylella/Xanthomonas encodes a protein involved in catalysis of two step in histidine biosynthesis, namely the bifunctional Imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase/histidinol-phosphatase.

Colitose is a mannose-derived 3,6-dideoxysugar produced by certain bacteria. It is a constituent of the lipopolysaccharide. It is the enantiomer of abequose.

The acetolactate synthase (ALS) enzyme is a protein found in plants and micro-organisms. ALS catalyzes the first step in the synthesis of the branched-chain amino acids.
The methylglyoxal pathway is an offshoot of glycolysis found in some prokaryotes, which converts glucose into methylglyoxal and then into pyruvate. However unlike glycolysis the methylglyoxal pathway does not produce adenosine triphosphate, ATP. The pathway is named after the substrate methylglyoxal which has three carbons and two carbonyl groups located on the 1st carbon and one on the 2nd carbon. Methylglyoxal is, however, a reactive aldehyde that is very toxic to cells, it can inhibit growth in E. coli at milimolar concentrations. The excessive intake of glucose by a cell is the most important process for the activation of the methylglyoxal pathway.
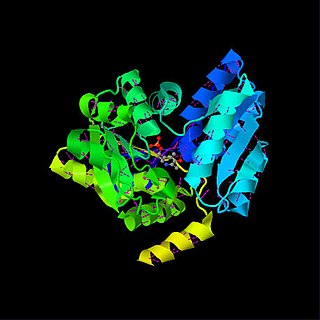
Serine dehydratase or L-serine ammonia lyase (SDH) is in the β-family of pyridoxal phosphate-dependent (PLP) enzymes. SDH is found widely in nature, but its structural and properties vary among species. SDH is found in yeast, bacteria, and the cytoplasm of mammalian hepatocytes. SDH catalyzes is the deamination of L-serine to yield pyruvate, with the release of ammonia.
In enzymology, a D-lactate dehydrogenase (cytochrome) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme lactoylglutathione lyase (EC 4.4.1.5, also known as glyoxalase I) catalyzes the isomerization of hemithioacetal adducts, which are formed in a spontaneous reaction between a glutathionyl group and aldehydes such as methylglyoxal.

The enzyme 3-dehydroquinate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.10) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme dTDP-glucose 4,6-dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.46) catalyzes the chemical reaction

The enzyme imidazoleglycerol-phosphate dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.19) catalyzes the chemical reaction
The enzyme methylglyoxal synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
The glyoxalase system is a set of enzymes that carry out the detoxification of methylglyoxal and the other reactive aldehydes that are produced as a normal part of metabolism. This system has been studied in both bacteria and eukaryotes. This detoxification is accomplished by the sequential action of two thiol-dependent enzymes; firstly glyoxalase І, which catalyzes the isomerization of the spontaneously formed hemithioacetal adduct between glutathione and 2-oxoaldehydes into S-2-hydroxyacylglutathione. Secondly, glyoxalase ІІ hydrolyses these thiolesters and in the case of methylglyoxal catabolism, produces D-lactate and GSH from S-D-lactoyl-glutathione.
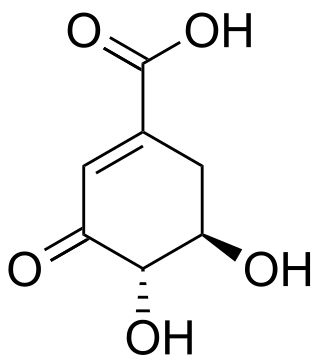
3-Dehydroshikimic acid is a chemical compound related to shikimic acid. 3-DHS is available in large quantity through engineering of the shikimic acid pathway.
3-hydroxydecanoyl-(acyl-carrier-protein) dehydratase (EC 4.2.1.60, D-3-hydroxydecanoyl-[acyl-carrier protein] dehydratase, 3-hydroxydecanoyl-acyl carrier protein dehydrase, 3-hydroxydecanoyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase, β-hydroxydecanoyl thioester dehydrase, β-hydroxydecanoate dehydrase, beta-hydroxydecanoyl thiol ester dehydrase, FabA, β-hydroxyacyl-acyl carrier protein dehydratase, HDDase, β-hydroxyacyl-ACP dehydrase, (3R)-3-hydroxydecanoyl-[acyl-carrier-protein] hydro-lyase) is an enzyme with systematic name (3R)-3-hydroxydecanoyl-(acyl-carrier protein) hydro-lyase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
N-acetylmuramic acid 6-phosphate etherase (EC 4.2.1.126, MurNAc-6-P etherase, MurQ) is an enzyme with systematic name (R)-lactate hydro-lyase (adding N-acetyl-D-glucosamine 6-phosphate; N-acetylmuramate 6-phosphate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
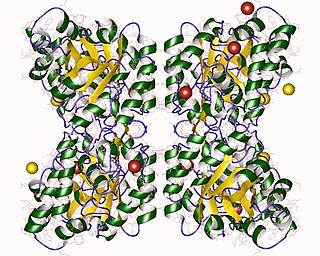
4-Hydroxy-tetrahydrodipicolinate synthase (EC 4.3.3.7, dihydrodipicolinate synthase, dihydropicolinate synthetase, dihydrodipicolinic acid synthase, L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing), dapA (gene)) is an enzyme with the systematic name L-aspartate-4-semialdehyde hydro-lyase (adding pyruvate and cyclizing; (4S)-4-hydroxy-2,3,4,5-tetrahydro-(2S)-dipicolinate-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Manju Ray was an Indian scientist specializing in Molecular Enzymology and Cancer Biochemistry. Her research has contributed significantly to the development of anticancer drugs and understanding the differentiation process of cells. Her interests include tumor biochemistry and molecular enzymology. She was awarded the Shanti Swarup Bhatnagar Prize for Science and Technology in the year 1989, being only the second woman to receive this award in the category 'Biological Sciences'.
The Monovalent Cation:Proton Antiporter-2 (CPA2) Family is a moderately large family of transporters belonging to the CPA superfamily. Members of the CPA2 family have been found in bacteria, archaea and eukaryotes. The proteins of the CPA2 family consist of between 333 and 900 amino acyl residues and exhibit 10-14 transmembrane α-helical spanners (TMSs).










