Related Research Articles

Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula (C
6H
10O
5)
n, a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall of green plants, many forms of algae and the oomycetes. Some species of bacteria secrete it to form biofilms. Cellulose is the most abundant organic polymer on Earth. The cellulose content of cotton fiber is 90%, that of wood is 40–50%, and that of dried hemp is approximately 57%.

Fiber or fibre is a natural or artificial substance that is significantly longer than it is wide. Fibers are often used in the manufacture of other materials. The strongest engineering materials often incorporate fibers, for example carbon fiber and ultra-high-molecular-weight polyethylene.

Cellophane is a thin, transparent sheet made of regenerated cellulose. Its low permeability to air, oils, greases, bacteria, and liquid water makes it useful for food packaging. Cellophane is highly permeable to water vapour, but may be coated with nitrocellulose lacquer to prevent this.

Rayon, also called viscose and commercialised in some countries as sabra silk or cactus silk, is a semi-synthetic fiber, made from natural sources of regenerated cellulose, such as wood and related agricultural products. It has the same molecular structure as cellulose. Many types and grades of viscose fibers and films exist. Some imitate the feel and texture of natural fibers such as silk, wool, cotton, and linen. The types that resemble silk are often called artificial silk. It can be woven or knit to make textiles for clothing and other purposes.

Pulp is a fibrous lignocellulosic material prepared by chemically, semi-chemically or mechanically producing cellulosic fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemicals or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw material used in papermaking and the industrial production of other paper products.
Synthetic fibers or synthetic fibres are fibers made by humans through chemical synthesis, as opposed to natural fibers that are directly derived from living organisms, such as plants or fur from animals. They are the result of extensive research by scientists to replicate naturally occurring animal and plant fibers. In general, synthetic fibers are created by extruding fiber-forming materials through spinnerets, forming a fiber. These are called synthetic or artificial fibers. The word polymer comes from a Greek prefix "poly" which means "many" and suffix "mer" which means "single units"..

Pulpwood can be defined as timber that is ground and processed into a fibrous pulp. It is a versatile natural resource commonly used for paper-making but also made into low-grade wood and used for chips, energy, pellets, and engineered products.

In biochemistry, cellulose acetate refers to any acetate ester of cellulose, usually cellulose diacetate. It was first prepared in 1865. A bioplastic, cellulose acetate is used as a film base in photography, as a component in some coatings, and as a frame material for eyeglasses; it is also used as a synthetic fiber in the manufacture of cigarette filters and playing cards. In photographic film, cellulose acetate film replaced nitrate film in the 1950s, being far less flammable and cheaper to produce.

Lyocell is a semi-synthetic fiber used to make textiles for clothing and other purposes. It is a form of regenerated cellulose made by dissolving pulp and dry jet-wet spinning. Unlike rayon; which is made by the more common viscose processes, Lyocell production does not use carbon disulfide, which is toxic to workers and the environment. Lyocell was originally trademarked as Tencel in 1982.

The kraft process (also known as kraft pulping or sulfate process) is a process for conversion of wood into wood pulp, which consists of almost pure cellulose fibres, the main component of paper. The kraft process involves treatment of wood chips with a hot mixture of water, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), and sodium sulfide (Na2S), known as white liquor, that breaks the bonds that link lignin, hemicellulose, and cellulose. The technology entails several steps, both mechanical and chemical. It is the dominant method for producing paper. In some situations, the process has been controversial because kraft plants can release odorous products and in some situations produce substantial liquid wastes.
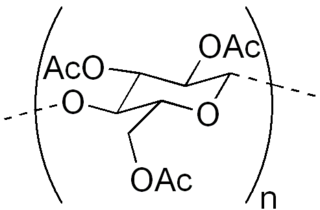
Cellulose triacetate, triacetate, CTA or TAC is a chemical compound produced from cellulose and a source of acetate esters, typically acetic anhydride. Triacetate is commonly used for the creation of fibres and film base. It is chemically similar to cellulose acetate. Its distinguishing characteristic is that in triacetate, at least "92 percent of the hydroxyl groups are acetylated." During the manufacture of triacetate, the cellulose is completely acetylated; whereas in normal cellulose acetate or cellulose diacetate, it is only partially acetylated. Triacetate is significantly more heat resistant than cellulose acetate.

A pulp mill is a manufacturing facility that converts wood chips or other plant fiber sources into a thick fiber board which can be shipped to a paper mill for further processing. Pulp can be manufactured using mechanical, semi-chemical, or fully chemical methods. The finished product may be either bleached or non-bleached, depending on the customer requirements.
N-Methylmorpholine N-oxide (more correctly 4-methylmorpholine 4-oxide), NMO or NMMO is an organic compound. This heterocyclic amine oxide and morpholine derivative is used in organic chemistry as a co-oxidant and sacrificial catalyst in oxidation reactions for instance in osmium tetroxide oxidations and the Sharpless asymmetric dihydroxylation or oxidations with TPAP. NMO is commercially supplied both as a monohydrate C5H11NO2·H2O and as the anhydrous compound. The monohydrate is used as a solvent for cellulose in the lyocell process to produce cellulose fibers.

In industrial chemistry, black liquor is the by-product from the kraft process when digesting pulpwood into paper pulp removing lignin, hemicelluloses and other extractives from the wood to free the cellulose fibers.
Courtaulds was a United Kingdom-based manufacturer of fabric, clothing, artificial fibres, and chemicals. It was established in 1794 and became the world's leading man-made fibre production company before being broken up in 1990 into Courtaulds plc and Courtaulds Textiles Ltd.
The sulfite process produces wood pulp that is almost pure cellulose fibers by treating wood chips with solutions of sulfite and bisulfite ions. These chemicals cleave the bonds between the cellulose and lignin components of the lignocellulose. A variety of sulfite/bisulfite salts are used, including sodium (Na+), calcium (Ca2+), potassium (K+), magnesium (Mg2+), and ammonium (NH4+). The lignin is converted to lignosulfonates, which are soluble and can be separated from the cellulose fibers. For the production of cellulose, the sulfite process competes with the Kraft process which produces stronger fibers and is less environmentally costly.

Bamboo textile is any cloth, yarn or clothing made from bamboo fibres. While historically used only for structural elements, such as bustles and the ribs of corsets, in recent years different technologies have been developed that allow bamboo fibre to be used for a wide range of textile and fashion applications.

Cellulose fibers are fibers made with ethers or esters of cellulose, which can be obtained from the bark, wood or leaves of plants, or from other plant-based material. In addition to cellulose, the fibers may also contain hemicellulose and lignin, with different percentages of these components altering the mechanical properties of the fibers.
In industrial paper-making processes, organosolv is a pulping technique that uses an organic solvent to solubilise lignin and hemicellulose. It has been considered in the context of both pulp and paper manufacture and biorefining for subsequent conversion of cellulose to fuel ethanol. The process was invented by Theodor Kleinert in 1968 as an environmentally benign alternative to kraft pulping.
Red Scar Works was built in 1939 by Courtaulds and produced rayon. It was located in Ribbleton Preston off Longridge Road. The closure of the works was announced in November 1979 and the issue raised in the UK Parliament House of Commons by the constituency MP. At the time of closure approximately 2,600 people were employed there but there were approximately 4,000 at its peak. It was the largest rayon producing site in Britain. Two main products were manufactured with one being tyre cord by a process known as CSPT – Continuous Spinning Process Tenasco. Two main denier of this product were manufactured. The other product was a general textile called Bright. A range of deniers of this were produced in a range of colours. The trade name for the coloured product was Duracol. At the time of closure, one reason given by management for the closure was the rising popularity of steel belt radial tires thus reducing demand for tyre cord.
References
- ↑ Biermann, Christpher J. (1996). "3". Handbook of Pulping and Papermaking (2nd ed.). pp. 72–73. ISBN 978-0-12-097362-0.
- 1 2 3 Sixta, Herbert (2006). "11.3". Handbook of Pulp. Vol. 2. Weinheim, Germany: Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA. pp. 1023–1062. ISBN 978-3-527-30999-3.
- ↑ Aldred, F.C. (December 1967). "Pulping Quality in Plantation Grown Species". The Commonwealth Forestry Review. 46 (4): 270–277. JSTOR 42604765.