
In enzymology, a shikimate dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.25) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a codeinone reductase (NADPH) (EC 1.1.1.247) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a tetrahydroxynaphthalene reductase (EC 1.1.1.252) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 3-keto-steroid reductase (EC 1.1.1.270) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin 2'-reductase (EC 1.1.1.220) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a 2'-hydroxydaidzein reductase (EC 1.3.1.51) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an anthocyanidin reductase (EC 1.3.1.77) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
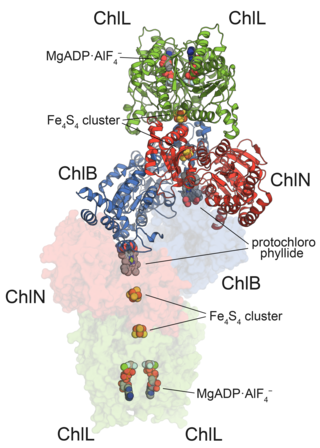
In enzymology, protochlorophyllide reductases (POR) are enzymes that catalyze the conversion from protochlorophyllide to chlorophyllide a. They are oxidoreductases participating in the biosynthetic pathway to chlorophylls.
A glutamyl-tRNA reductase (EC 1.2.1.70) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a ferredoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.2) abbreviated FNR, is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a leucoanthocyanidin reductase (EC 1.17.1.3) (LAR, aka leucocyanidin reductase or LCR) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, an FMN reductase (EC 1.5.1.29) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a NAD(P)H dehydrogenase (quinone) (EC 1.6.5.2) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

Protochlorophyllide, or monovinyl protochlorophyllide, is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of chlorophyll a. It lacks the phytol side-chain of chlorophyll and the reduced pyrrole in ring D. Protochlorophyllide is highly fluorescent; mutants that accumulate it glow red if irradiated with blue light. In angiosperms, the later steps which convert protochlorophyllide to chlorophyll are light-dependent, and such plants are pale (chlorotic) if grown in the darkness. Gymnosperms, algae, and photosynthetic bacteria have another, light-independent enzyme and grow green in the darkness as well.
Geranylgeranyl diphosphate reductase (EC 1.3.1.83, geranylgeranyl reductase, CHL P) is an enzyme with systematic name geranylgeranyl-diphosphate:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalises the following chemical reaction

Chlorophyllide-a oxygenase (EC 1.14.13.122), chlorophyllide a oxygenase, chlorophyll-b synthase, CAO) is an enzyme with systematic name chlorophyllide-a:oxygen 7-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reactions

Magnesium-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (oxidative) cyclase, is an enzyme with systematic name magnesium-protoporphyrin-IX 13-monomethyl ester, ferredoxin:oxygen oxidoreductase (hydroxylating). In plants this enzyme catalyses the following overall chemical reaction
Adrenodoxin-NADP+ reductase (EC 1.18.1.6, adrenodoxin reductase, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate-adrenodoxin reductase, ADR, NADPH:adrenal ferredoxin oxidoreductase) is an enzyme with systematic name adrendoxin:NADP+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

Chlorophyllide a and Chlorophyllide b are the biosynthetic precursors of chlorophyll a and chlorophyll b respectively. Their propionic acid groups are converted to phytyl esters by the enzyme chlorophyll synthase in the final step of the pathway. Thus the main interest in these chemical compounds has been in the study of chlorophyll biosynthesis in plants, algae and cyanobacteria. Chlorophyllide a is also an intermediate in the biosynthesis of bacteriochlorophylls.

Chlorophyllide a reductase (EC 1.3.7.15), also known as COR, is an enzyme with systematic name bacteriochlorophyllide-a:ferredoxin 7,8-oxidoreductase. It catalyses the following chemical reaction








