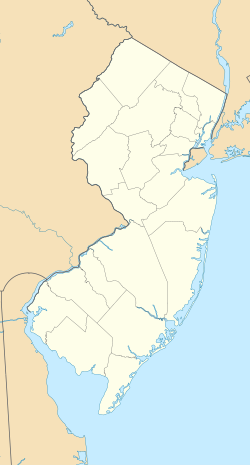
Route 21 is a state highway in northern New Jersey, running 14.35 mi (23.09 km) from the Newark Airport Interchange with U.S. Route 1/9 (US 1-9) and US 22 in Newark, Essex County to an interchange with US 46 in Clifton, Passaic County. The route is a four- to six-lane divided highway known as McCarter Highway on its southern portion in Newark that serves as a connector between the Newark and Paterson areas, following the west bank of the Passaic River for much of its length. It also serves as the main north–south highway through the central part of Newark, connecting attractions in Downtown Newark with Newark Airport. The portion of Route 21 through Newark is a surface arterial that runs alongside the elevated Northeast Corridor rail line through the southern part of the city and continues north through Downtown Newark while the portion north of Downtown Newark is a freeway. Route 21 intersects many major roads including Interstate 78 (I-78), Route 27, and I-280 in Newark, Route 7 in Belleville, and Route 3 in Clifton.

Passaic is a city in Passaic County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 United States census, the city was the state's 16th-most-populous municipality, with a population of 70,537, falling behind Bayonne, an increase of 756 (+1.1%) from the 2010 census count of 69,781, which in turn reflected an increase of 1,920 residents (+2.8%) from the 2000 census population of 67,861. The Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that the city's population was 69,128 in 2022, ranking the city the 546th-most-populous in the country. Among cities with more than 50,000 people, Passaic was the fifth-most-densely-populated municipality in the United States, with more than 22,000 people per square mile.

The Passaic River is a river, approximately 80 miles (130 km) long, in Northern New Jersey. The river in its upper course flows in a highly circuitous route, meandering through the swamp lowlands between the ridge hills of rural and suburban northern New Jersey, called the Great Swamp, draining much of the northern portion of the state through its tributaries.

The Great Falls of the Passaic River is a prominent waterfall, 77 feet (23 m) high, on the Passaic River in the city of Paterson in Passaic County, New Jersey. The falls and surrounding area are protected as part of the Paterson Great Falls National Historical Park, administered by the National Park Service. The Congress authorized its establishment in 2009.

The Society for Establishing Useful Manufactures (S.U.M.) or Society for the Establishment of Useful Manufactures was a private state-sponsored corporation founded in 1791 to promote industrial development along the Passaic River in New Jersey in the United States. The company's management of the Great Falls of the Passaic River as a powersource for grist mills resulted in the growth of Paterson as one of the first industrial centers in the United States. Under the society's long-term management of the falls, the industrialization of the area passed through three great waves, centered first on cotton, then steel, and finally silk, over the course of over 150 years. The venture is considered by historians to have been a forerunner for many public–private partnerships in later decades in the United States.

The Morris Canal (1829–1924) was a 107-mile (172 km) common carrier anthracite coal canal across northern New Jersey that connected the two industrial canals in Easton, Pennsylvania across the Delaware River from its western terminus at Phillipsburg, New Jersey to New York Harbor and New York City through its eastern terminals in Newark and on the Hudson River in Jersey City. The canal was sometimes called the Morris and Essex Canal, in error, due to confusion with the nearby and unrelated Morris and Essex Railroad.

The Augusta Canal is a historic canal located in Augusta, Georgia, United States. The canal is fed by the Savannah River and passes through three levels in suburban and urban Augusta before the water returns to the river at various locations. It was devised to harness the water power at the fall line of the Savannah River to drive mills, to provide transportation of goods, and to provide a municipal water supply. It is the only canal in the US in continuous use for its original purposes of providing power, transport, and municipal water.

Acquackanonk Township was a township that existed in New Jersey, United States, from 1693 until 1917, first in Essex County and then in Passaic County.

Ringwood Manor, located in Passaic County, New Jersey, was the site of an ironworks and home to a number of well-known ironmasters from the 1740s to the late 19th century. The current manor house was not built until 1807.

The Clark Thread Company Historic District, located at 900 Passaic Avenue, East Newark, Hudson County, New Jersey, United States, is a large mill complex. Begun in 1875, it was a major manufacturing site of the Clark Thread Company, the world's leading manufacturer of sewing thread, until 1935. The complex was designated a National Historic Landmark District in 1978 for this association. It now functions as an industrial park housing a diversity of businesses.

North Highlands Dam is a structure on the Chattahoochee River at the northern edge of the Columbus, Georgia, United States. It is approximately 4.2 miles (6.8 km) north of 9th Avenue in downtown Columbus. The dam was built in 1899 to provide power for the former Bibb City Mill. It was one of the first large dams constructed in the South. The North Highlands Dam was owned by the Columbus Electric and Power Company, until that utility was purchased by Georgia Power in 1930.

The 1926 Passaic textile strike was a work stoppage by over 15,000 woolen mill workers in and around Passaic, New Jersey, over wage issues in several factories in the vicinity. Conducted in its initial phase by a "United Front Committee" organized by the Trade Union Educational League of the Workers (Communist) Party, the strike began on January 25, 1926, and officially ended only on March 1, 1927, when the final mill being picketed signed a contract with the striking workers. It was the first Communist-led work stoppage in the United States. The event was memorialized by a seven reel silent movie intended to generate sympathy and funds for the striking workers.

The NX Draw is an out-of-service railroad bridge on the Passaic River between Newark and Kearny, New Jersey. It is the 13th bridge from the river's mouth at Newark Bay and is 6.5 miles (10.5 km) upstream from it. The bascule bridge, built by the Erie Railroad and once part of its Newark Branch, has been abandoned in the raised position.

The Winooski Falls Mill District is located along the Winooski River in the cities of Winooski and Burlington, Vermont, in the United States of America. It encompasses a major industrial area that developed around two sets of falls on the river in the 19th century.

The Belleville Turnpike Bridge is a vehicular moveable bridge spanning the Passaic River in northeastern New Jersey 8.9 miles (14.3 km) from its river mouth at Newark Bay. Also known as Rutgers Street Bridge and Route 7 Bridge, it is the fourth fixed crossing to be built at the location, today the tripoint of the municipal and county lines of Belleville in Essex, Kearny in Hudson, and North Arlington in Bergen. Commissioned by the New Jersey Department of Transportation, which owns and operates it, the vertical lift bridge opened in 2002.

The Monadnock Mills are a historic mill complex in Claremont, New Hampshire. They extend along the southern bank of the Sugar River on both sides of Water Street, between the Broad Street bridge to the east, and the junction of Main and Water Streets in the west, where they abut the industrial area formerly associated with the Sullivan Machinery Company; there also a small number of surviving elements on the north side of the river opposite this area. The complex represents the surviving elements of what was once the largest manufacturing complex in the upper Connecticut River watershed area, and one of its oldest. The mills were listed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1979. Many of its buildings have been repurposed to other uses.

Eighth Street Bridge is a road bridge over the Passaic River in northeastern New Jersey, United States. It connects the City of Passaic in Passaic County with the Borough of Wallington in Bergen County and is jointly owned by both counties. The bridge connects Eighth Street in Passaic with County Route 507 in Wallington.

Gregory Avenue Bridge, earlier known as the Main Avenue Bridge, is road bridge over the Passaic River in northeastern New Jersey, United States. It is the 7th bridge to be built at the river crossing. Originally built in 1905 as a moveable bridge, it has been in a fixed closed position since 1985. A four lane road carries traffic between Passaic & Wallington at the Passaic and Bergen county line.