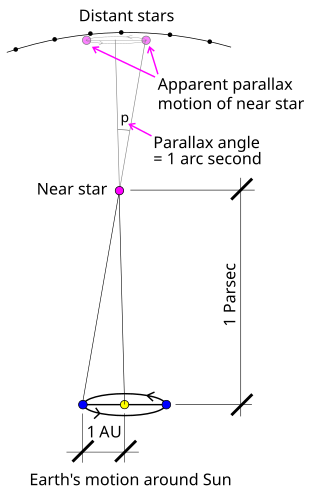
The parsec is a unit of length used to measure the large distances to astronomical objects outside the Solar System, approximately equal to 3.26 light-years or 206,265 astronomical units (AU), i.e. 30.9 trillion kilometres. The parsec unit is obtained by the use of parallax and trigonometry, and is defined as the distance at which 1 AU subtends an angle of one arcsecond. The nearest star, Proxima Centauri, is about 1.3 parsecs from the Sun: from that distance, the gap between the Earth and the Sun spans slightly less than 1/3600 of one degree of view. Most stars visible to the naked eye are within a few hundred parsecs of the Sun, with the most distant at a few thousand parsecs, and the Andromeda Galaxy at over 700,000 parsecs.

A microquasar, the smaller version of a quasar, is a compact region surrounding a stellar black hole with a mass several times that of its companion star. The matter being pulled from the companion star forms an accretion disk around the black hole. This accretion disk may become so hot, due to friction, that it begins to emit X-rays. The disk also projects narrow streams or "jets" of subatomic particles at near-light speed, generating a strong radio wave emission.

Messier 87 is a supergiant elliptical galaxy in the constellation Virgo that contains several trillion stars. One of the largest and most massive galaxies in the local universe, it has a large population of globular clusters—about 15,000 compared with the 150–200 orbiting the Milky Way—and a jet of energetic plasma that originates at the core and extends at least 1,500 parsecs, traveling at a relativistic speed. It is one of the brightest radio sources in the sky and a popular target for both amateur and professional astronomers.

IC 10 is an irregular galaxy in the constellation Cassiopeia. It was discovered by Lewis Swift in 1887 and in 1935 Nicholas Mayall became the first to suggest that the object is extragalactic. Edwin Hubble suspected it might belong to the Local Group of galaxies, but its status remained uncertain for decades. The radial velocity of IC 10 was measured in 1962, and it was found to be approaching the Milky Way at approximately 350 km/s, strengthening the evidence for its membership in the Local Group. Its membership in the group was finally confirmed in 1996 by direct measurements of its distance based on observations of Cepheids; most estimates place the galaxy 2–3 million light years from Earth, with some estimates ranging from 1.5–4.5 million light years. Despite its closeness, the galaxy is rather difficult to study because it lies near the plane of the Milky Way and is therefore heavily obscured by interstellar matter.

Messier 63 or M63, also known as NGC 5055 or the seldom-used Sunflower Galaxy, is a spiral galaxy in the northern constellation of Canes Venatici with approximately 400 billion stars. M63 was first discovered by the French astronomer Pierre Méchain, then later verified by his colleague Charles Messier on June 14, 1779. The galaxy became listed as object 63 in the Messier Catalogue. In the mid-19th century, Anglo-Irish astronomer Lord Rosse identified spiral structures within the galaxy, making this one of the first galaxies in which such structure was identified.

Messier 108 is a barred spiral galaxy about 28 million light-years away from Earth in the northern constellation Ursa Major. It was discovered by Pierre Méchain in 1781 or 1782. From the Earth, this galaxy is seen almost edge-on.

The Circinus Galaxy is a Seyfert galaxy in the constellation of Circinus. It is located 4 degrees below the Galactic plane, and, at a distance of 4.0 Mpc (13 Mly), is one of the closest major galaxies to the Milky Way. The galaxy is undergoing tumultuous changes, as rings of gas are likely being ejected from the galaxy. Its outermost ring is 1400 light-years across while the inner ring is 260 light-years across. Although the Circinus galaxy can be seen using a small telescope, it was not noticed until 1977 because it lies close to the plane of the Milky Way and is obscured by galactic dust. The Circinus Galaxy is a Type II Seyfert galaxy and is one of the closest known active galaxies to the Milky Way, though it is probably slightly farther away than Centaurus A.

NGC 3109 is a small barred Magellanic type spiral or irregular galaxy around 4.35 Mly away in the direction of the constellation of Hydra. NGC 3109 is believed to be tidally interacting with the dwarf elliptical galaxy Antlia Dwarf. It was discovered by John Herschel on March 24, 1835 while he was in what is now South Africa.

NGC 6822 is a barred irregular galaxy approximately 1.6 million light-years away in the constellation Sagittarius. Part of the Local Group of galaxies, it was discovered by E. E. Barnard in 1884, with a six-inch refractor telescope. It is the closest non-satellite galaxy to the Milky Way, but lies just outside its virial radius. It is similar in structure and composition to the Small Magellanic Cloud. It is about 7,000 light-years in diameter.

The Cartwheel Galaxy (also known as ESO 350-40 or PGC 2248) is a lenticular ring galaxy about 500 million light-years away in the constellation Sculptor. It has a D25 isophotal diameter of 44.23 kiloparsecs (144,300 light-years), and a mass of about 2.9–4.8 × 109 solar masses; its outer ring has a circular velocity of 217 km/s.

IC 342 is an intermediate spiral galaxy in the constellation Camelopardalis, located relatively close to the Milky Way. Despite its size and actual brightness, its location behind dusty areas near the galactic equator makes it difficult to observe, leading to the nickname "The Hidden Galaxy", though it can readily be detected even with binoculars. If the galaxy were not obscured, it would be visible by naked eye. The dust makes it difficult to determine its precise distance; modern estimates range from about 7 million light-years (Mly) to about 11 Mly. The galaxy was discovered by William Frederick Denning in 1892. It is one of the brightest in the IC 342/Maffei Group, one of the closest galaxy groups to the Local Group. Edwin Hubble first thought it to be in the Local Group, but it was later determined not to be a member.

IC 1101 is a class S0 supergiant (cD) lenticular galaxy at the center of the Abell 2029 galaxy cluster. It has an isophotal diameter at about 123.65 to 169.61 kiloparsecs. It possesses a diffuse core which is the largest known core of any galaxy to date, and contains a supermassive black hole, one of the largest discovered. The galaxy is located at 354.0 megaparsecs from Earth. The galaxy was discovered on 19 June 1790, by the British astronomer William Herschel.

DDO 169 is an irregular galaxy located in the constellation Canes Venatici. It is a member of the M51 Group of galaxies and measures approximately 5 × 1.5 kiloparsecs. The galaxy's large-scale structure is very unorganized and it has two clusters of stars in its outer portions in addition to the cluster in the center. These clusters make it practically impossible to determine the galaxy's rotation curve and contributes to a large variation in distance figures that are derived with different methods. The exact distance to the galaxy is not known, although a 1998 paper estimated the distance as 8.23 megaparsecs.

ESO 306-17 is a fossil group giant elliptical galaxy in the Columba constellation, about 1.07 million light-years in diameter, and roughly 517 million light-years away.

Malin 1 is a giant low surface brightness (LSB) spiral galaxy. It is located 1.19 billion light-years (366 Mpc) away in the constellation Coma Berenices, near the North Galactic Pole. As of February 2015, it is the largest known spiral galaxy, with an approximate diameter of 650,000 light-years (200,000 pc), thus over six times the diameter of our Milky Way. It was discovered by astronomer David Malin in 1986 and is the first LSB galaxy verified to exist. Its high surface brightness central spiral is 30,000 light-years (9,200 pc) across, with a bulge of 10,000 light-years (3,100 pc). The central spiral is a SB0a type barred-spiral.

ESO 198-13 is a ring galaxy with multiple ring-like structures located about 240 million light-years away in the constellation Eridanus.

ESO 444-46 is a class E4 supergiant elliptical galaxy; the dominant and brightest member of the Abell 3558 galaxy cluster around 640 million light-years away in the constellation Centaurus. It lies within the core of the massive Shapley Supercluster, one of the closest neighboring superclusters. It is one of the largest galaxies in the local universe, and possibly contains one of the most massive black holes known. The black hole's mass is very uncertain, with estimates ranging from as low as 501 million M☉, to as high as 77.6 billion M☉.

Donatiello I, also known as Mirach's Goblin, is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy in the constellation Andromeda, located between 8.1 and 11.4 million light-years from Earth. It is a possible satellite galaxy of the dwarf lenticular galaxy NGC 404, "Mirach's Ghost", which is situated 60 arcminutes away. It is otherwise one of the most isolated dwarf spheroidal galaxies known, being separated from NGC 404 by around 211,000 light-years. The galaxy is named after its discoverer, amateur astrophotographer Giuseppe Donatiello, who sighted the galaxy in a 2016 review of his archival long exposures from 2010 and 2013. Follow-up observations with the Roque de los Muchachos Observatory led to a scientific paper on its discovery being published in December 2018.

ESO 383-76 is an elongated, X-ray luminous supergiant elliptical galaxy, residing as the dominant, brightest cluster galaxy (BCG) of the Abell 3571 galaxy cluster, the sixth-brightest in the sky at X-ray wavelengths. It is located at the distance of 200.6 megaparsecs from Earth, and is possibly a member of the large Shapley Supercluster. With a diameter of about 540.89 kiloparsecs, it is one of the largest galaxies known.




















