
Mercer Island is a city in King County, Washington, United States, located on an island of the same name in the southern portion of Lake Washington. Mercer Island is in the Seattle metropolitan area, with Seattle to its west and Bellevue to its east.

Lake Washington is a large freshwater lake adjacent to the city of Seattle, Washington, United States. It is the largest lake in King County and the second largest natural lake in the state of Washington, after Lake Chelan. It borders the cities of Seattle on the west, Bellevue and Kirkland on the east, Renton on the south, and Kenmore on the north, and encloses Mercer Island. The lake is fed by the Sammamish River at its north end and the Cedar River at its south.

The Lake Washington Ship Canal is a canal that runs through the city of Seattle and connects the fresh water body of Lake Washington to the salt water inland sea of Puget Sound. The Hiram M. Chittenden Locks accommodate the approximately 20-foot (6.1 m) difference in water level between Lake Washington and the sound. The canal runs east–west and connects Union Bay, the Montlake Cut, Portage Bay, Lake Union, the Fremont Cut, Salmon Bay, and Shilshole Bay, which is part of the sound.

The 14th Street bridges refers to the three bridges near each other that cross the Potomac River, connecting Arlington, Virginia and Washington, D.C. Sometimes the two nearby rail bridges are included as part of the 14th Street bridge complex. A major gateway for automotive, bicycle and rail traffic, the bridge complex is named for 14th Street, which feeds automotive traffic into it on the D.C. end.

The Lacey V. Murrow Memorial Bridge is a floating bridge in the Seattle metropolitan area of the U.S. state of Washington. It is one of the Interstate 90 floating bridges that carries the eastbound lanes of Interstate 90 across Lake Washington from Seattle to Mercer Island. Westbound traffic is carried by the adjacent Homer M. Hadley Memorial Bridge.
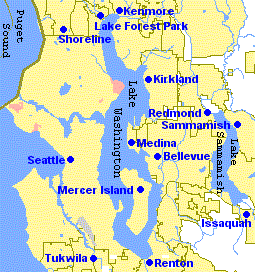
The Eastside of the King County, Washington area in the United States is a collective term for the suburbs of Seattle located on the east side of Lake Washington.

Factoria is a mixed-use suburban neighborhood in south Bellevue, Washington and is one of the city's significant commercial districts. Originally timberland from the 1890s to 1920s and later envisioned as an industrial center, Factoria has since the 1960s evolved into commercial and residential development. Factoria was annexed into Bellevue in 1993. The core neighborhood is bounded by Interstate 90 to the north, Interstate 405 to the west, Newport Way to the east, and Coal Creek Parkway to the south.

The Third Lake Washington Bridge, officially the Homer M. Hadley Memorial Bridge, is a floating bridge in the Seattle metropolitan area of the U.S. state of Washington. It is one of the Interstate 90 floating bridges, carrying the westbound lanes of Interstate 90 across Lake Washington between Mercer Island and Seattle. The floating bridge is the fifth-longest of its kind in the world, at 5,811 feet.

Transportation in Seattle is largely focused on the automobile like many other cities in western North America; however, the city is just old enough for its layout to reflect the age when railways and trolleys predominated. These older modes of transportation were made for a relatively well-defined downtown area and strong neighborhoods at the end of several former streetcar lines, now mostly bus lines.
Lake Washington Floating Bridge may refer to the following crossings of Lake Washington between Seattle and its eastern suburbs:

The Mount Baker Tunnel or Mount Baker Ridge Tunnel carries Interstate 90 under the Mount Baker neighborhood of Seattle, Washington. It is actually a group of three tubes that carry eight lanes of freeway traffic, plus a separate path for bicycles and pedestrians. The original tubes are twin tunnel bores completed in 1940 and rehabilitated in 1993. The new Mount Baker Tunnel was built north of the original tunnels and opened in June 1989. The tunnel has a double-decked roadway with the bicycle/pedestrian path above the traffic lanes.
The Interstate 90 floating bridges is the common name for the twin floating bridges that carry a section of Interstate 90 across Lake Washington between Seattle and Mercer Island in the U.S. state of Washington. They are the:

Interstate 90 (I-90), designated as the American Veterans Memorial Highway, is a transcontinental Interstate Highway that runs from Seattle, Washington, to Boston, Massachusetts. It crosses Washington state from west to east, traveling 298 miles (480 km) from Seattle across the Cascade Mountains and into Eastern Washington, reaching the Idaho state line east of Spokane. I-90 intersects several of the state's other major highways, including I-5 in Seattle, I-82 and U.S. Route 97 (US 97) near Ellensburg, and US 395 and US 2 in Spokane.

Lake Washington steamboats and ferries operated from about 1875 to 1951, transporting passengers, vehicles and freight across Lake Washington, a large lake to the east of Seattle, Washington. Before modern highways and bridges were built, the only means of crossing the lake, other than the traditional canoe or rowboat, was by steamboat, and, later, by ferry. While there was no easily navigable connection to Puget Sound, the Lake Washington Ship Canal now connects Lake Washington to Lake Union, and from there Puget Sound is reached by way of the Hiram M. Chittenden Locks.

The Benton City – Kiona Bridge is a steel box girder and cable-stayed bridge carrying two lanes of Washington State Route 225 over the Yakima River in Benton City, Benton County, Washington. The current span was opened to traffic on July 4, 1957 and measures 400-foot-long (121.9 m) by 26-foot (7.8 m) wide. Two bridges had previously connected the cities of Benton City and Kiona before and were located 300 feet (91 m) downstream. The first bridge was open by 1901, and the immediate predecessor bridge was closed and torn down in 1964. The bridge is owned and maintained by the Washington State Department of Transportation, and was added to the Washington Heritage Register on January 25, 2002.

The US 31–Island Lake Outlet Bridge is a double-leaf bascule bridge in downtown Charlevoix in the U.S. state of Michigan. The bridge carries U.S. Highway 31 across Island Lake Outlet that ultimately connects Lake Charlevoix to Lake Michigan.

The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to infrastructure of the U.S. state of Washington.















