
Order Desmothoracida, the desmothoracids, are a group of heliozoan protists, usually sessile and found in freshwater environments. The adult is a spherical cell around 10-20 μm in diameter surrounded by a perforated organic lorica, or shell, with many radial pseudopods projecting through the holes to capture food. These are supported by small bundles of microtubules that arise near a point on the nuclear membrane. Unlike other heliozoans, the microtubules are not in any regular geometric array, there does not appear to be a microtubule organizing center, and there is no distinction between the outer and inner cytoplasm.

The chlorarachniophytes are a small group of exclusively marine algae widely distributed in tropical and temperate waters. They are typically mixotrophic, ingesting bacteria and smaller protists as well as conducting photosynthesis. Normally they have the form of small amoebae, with branching cytoplasmic extensions that capture prey and connect the cells together, forming a net. These extensions are dependent on the presence of light and polymerization of the actin cytoskeleton. They may also form flagellate zoospores, which characteristically have a single subapical flagellum that spirals backwards around the cell body, and walled coccoid cells.

Cercozoa is a phylum of diverse single-celled eukaryotes. They lack shared morphological characteristics at the microscopic level, and are instead united by molecular phylogenies of rRNA and actin or polyubiquitin. They were the first major eukaryotic group to be recognized mainly through molecular phylogenies. They are the natural predators of many species of bacteria. They are closely related to the phylum Retaria, comprising amoeboids that usually have complex shells, and together form a supergroup called Rhizaria.

The Rhizaria are a diverse and species-rich supergroup of mostly unicellular eukaryotes. Except for the Chlorarachniophytes and three species in the genus Paulinella in the phylum Cercozoa, they are all non-photosynthetic, but many Foraminifera and Radiolaria have a symbiotic relationship with unicellular algae. A multicellular form, Guttulinopsis vulgaris, a cellular slime mold, has been described. This group was used by Cavalier-Smith in 2002, although the term "Rhizaria" had been long used for clades within the currently recognized taxon.
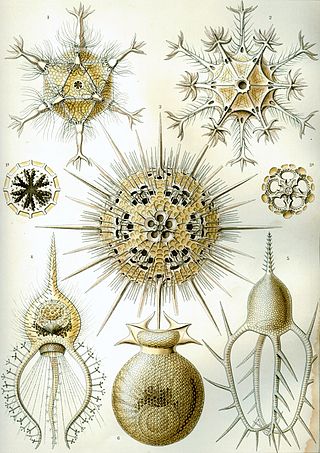
Phaeodarea or Phaeodaria is a group of amoeboid cercozoan organisms. They are traditionally considered radiolarians, but in molecular trees do not appear to be close relatives of the other groups, and are instead placed among the Cercozoa. They are distinguished by the structure of their central capsule and by the presence of a phaeodium, an aggregate of waste particles within the cell.

The euglyphids are a prominent group of filose amoebae that produce shells or tests that in most described species is reinforced by siliceous scales, plates, and sometimes spines, but this reinforcement is absent in other species.

The tectofilosids are a group of filose amoebae with shells. These are composed of organic materials and sometimes collected debris, in contrast to the euglyphids, which produce shells from siliceous scales. The shell usually has a single opening, but in Amphitrema and a few other genera it has two on opposite ends. The cell itself occupies most of the shell. They are most often found on marsh plants such as Sphagnum.
The Oxymonads are a group of flagellated protists found exclusively in the intestines of animals, mostly termites and other wood-eating insects. Along with the similar parabasalid flagellates, they harbor the symbiotic bacteria that are responsible for breaking down cellulose. There is no evidence for presence of mitochondria in oxymonads and three species have been shown to completely lack any molecular markers of mitochondria.
Gymnophryidae is a small family of amoeboids that lack shells and produce thin, reticulose pseudopods. These contain microtubules and have a granular appearance, owing to the presence of extrusomes, but are distinct from the pseudopods of Foraminifera. They are included among the Cercozoa, but differ from other cercozoans in having mitochondria with flat cristae, rather than tubular cristae.
The Ascetosporea are a group of eukaryotes that are parasites of animals, especially marine invertebrates. The two groups, the haplosporids and paramyxids, are not particularly similar morphologically, but consistently group together on molecular trees, which place them near the base of the Cercozoa. Both produce spores without the complex structures found in similar groups.
The Syndiniales are an order of early branching dinoflagellates, found as parasites of crustaceans, fish, algae, cnidarians, and protists. The trophic form is often multinucleate, and ultimately divides to form motile spores, which have two flagella in typical dinoflagellate arrangement. They lack a theca and chloroplasts, and unlike all other orders, the nucleus is never a dinokaryon. A well-studied example is Amoebophrya, which is a parasite of other dinoflagellates and may play a part in ending red tides. Several MALV groups have been assigned to Syndiniales; recent studies, however, show paraphyly of MALVs suggesting that only those groups that branch as sister to dinokaryotes belong to Syndiniales.

Monadofilosa is a grouping of Cercozoa. These organisms are single-celled amoeboid protists.

Thaumatomonadida is an order of flagellates.
Cryomonadida is a group of heterotrophic Rhizaria, that belong to the Cercozoa.

Thecofilosea is a class of unicellular testate amoebae belonging to the phylum Cercozoa. They are amoeboflagellates, organisms with flagella and pseudopodia, distinguished from other cercozoa by their scale-lacking test composed of organic material. They are closely related to the Imbricatea, a group of testate amoebae with tests composed of inorganic silica scales.
Ebria is a genus of rhizaria.

A protist is any eukaryotic organism that is not an animal, plant, or fungus. The protists do not form a natural group, or clade, since they exclude certain eukaryotes with whom they share a common ancestor; but, like algae or invertebrates, the grouping is used for convenience. In some systems of biological classification, such as the popular five-kingdom scheme proposed by Robert Whittaker in 1969, the protists make up a kingdom called Protista, composed of "organisms which are unicellular or unicellular-colonial and which form no tissues". In the 21st century, the classification shifted toward a two-kingdom system of protists: Chromista and Protozoa.

Granofilosea is a class of cercozoan protists in the subphylum Reticulofilosa. Out of the three groups that were traditionally considered heliozoans: the heliomonads, gymnosphaerids and desmothoracids, the latter were recently grouped into this new class.

Ventrifilosa is a highly diverse group of phagotrophic protists that glide through their flagella and emit filose pseudopods from their ventral side for feeding. Because of their mixture of amoeba and flagellate characteristics, they are amoeboflagellates. Members of this group are the Imbricatea, Sarcomonadea and Thecofilosea.

Euglyphia is a group of imbricate protists in the phylum Cercozoa. They are unicellular eukaryotes characterized by a cell body covered in large imbricate scales, and an apical aperture through which they extend either filose pseudopodia or two cilia of different sizes that are not used for gliding.










