Related Research Articles

In cardiac physiology, cardiac output (CO), also known as heart output and often denoted by the symbols , , or , is the volumetric flow rate of the heart's pumping output: that is, the volume of blood being pumped by a single ventricle of the heart, per unit time. Cardiac output (CO) is the product of the heart rate (HR), i.e. the number of heartbeats per minute (bpm), and the stroke volume (SV), which is the volume of blood pumped from the left ventricle per beat; thus giving the formula:

A ventricle is one of two large chambers located toward the bottom of the heart that collect and expel blood towards the peripheral beds within the body and lungs. The blood pumped by a ventricle is supplied by an atrium, an adjacent chamber in the upper heart that is smaller than a ventricle. Interventricular means between the ventricles, while intraventricular means within one ventricle.
In cardiovascular physiology, stroke volume (SV) is the volume of blood pumped from the ventricle per beat. Stroke volume is calculated using measurements of ventricle volumes from an echocardiogram and subtracting the volume of the blood in the ventricle at the end of a beat from the volume of blood just prior to the beat. The term stroke volume can apply to each of the two ventricles of the heart, although when not explicitly stated it refers to the left ventricle and should therefore be referred to as left stroke volume (LSV). The stroke volumes for each ventricle are generally equal, both being approximately 90 mL in a healthy 70-kg man. Any persistent difference between the two stroke volumes, no matter how small, would inevitably lead to venous congestion of and/or shunt between the systemic and the pulmonary circulation.
An ejection fraction (EF) is the volumetric fraction of fluid ejected from a chamber with each contraction. It can refer to the cardiac atrium, ventricle, gall bladder, or leg veins, although if unspecified it usually refers to the left ventricle of the heart. EF is widely used as a measure of the pumping efficiency of the heart and is used to classify heart failure types. It is also used as an indicator of the severity of heart failure, although it has recognized limitations.

Pulse pressure is the difference between systolic and diastolic blood pressure. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg). It represents the force that the heart generates each time it contracts. Healthy pulse pressure is around 40 mmHg. A pulse pressure that is consistently 60 mmHg or greater is likely to be associated with disease, and a pulse pressure of 50 mmHg or more increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. Pulse pressure is considered low if it is less than 25% of the systolic. A very low pulse pressure can be a symptom of disorders such as congestive heart failure.
In cardiovascular physiology, end-diastolic volume (EDV) is the volume of blood in the right or left ventricle at end of filling in diastole which is amount of blood present in ventricle at the end of diastole. Because greater EDVs cause greater distention of the ventricle, EDV is often used synonymously with preload, which refers to the length of the sarcomeres in cardiac muscle prior to contraction (systole). An increase in EDV increases the preload on the heart and, through the Frank-Starling mechanism of the heart, increases the amount of blood ejected from the ventricle during systole.

The Frank–Starling law of the heart represents the relationship between stroke volume and end diastolic volume. The law states that the stroke volume of the heart increases in response to an increase in the volume of blood in the ventricles, before contraction, when all other factors remain constant. As a larger volume of blood flows into the ventricle, the blood stretches cardiac muscle, leading to an increase in the force of contraction. The Frank-Starling mechanism allows the cardiac output to be synchronized with the venous return, arterial blood supply and humoral length, without depending upon external regulation to make alterations. The physiological importance of the mechanism lies mainly in maintaining left and right ventricular output equality.

Afterload is the pressure that the heart must work against to eject blood during systole. Afterload is proportional to the average arterial pressure. As aortic and pulmonary pressures increase, the afterload increases on the left and right ventricles respectively. Afterload changes to adapt to the continually changing demands on an animal's cardiovascular system. Afterload is proportional to mean systolic blood pressure and is measured in millimeters of mercury.

Diastole is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are refilling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricular diastole the relaxing of the ventricles.
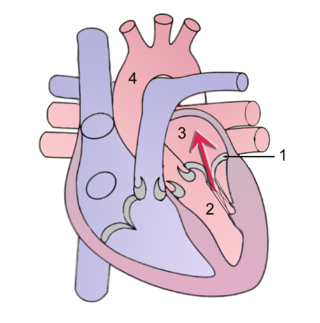
Mitral regurgitation (MR), also known as mitral insufficiency or mitral incompetence, is a form of valvular heart disease in which the mitral valve is insufficient and does not close properly when the heart pumps out blood. It is the abnormal leaking of blood backwards – regurgitation from the left ventricle, through the mitral valve, into the left atrium, when the left ventricle contracts. Mitral regurgitation is the most common form of valvular heart disease.
Pulsus paradoxus, also paradoxic pulse or paradoxical pulse, is an abnormally large decrease in stroke volume, systolic blood pressure and pulse wave amplitude during inspiration. Pulsus paradoxus is not related to pulse rate or heart rate, and it is not a paradoxical rise in systolic pressure. Normally, blood pressure drops less precipitously than 10 mmHg during inhalation. Pulsus paradoxus is a sign that is indicative of several conditions, most commonly pericardial effusion.
Tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy (TIC) is a disease where prolonged tachycardia or arrhythmia causes an impairment of the myocardium, which can result in heart failure. People with TIC may have symptoms associated with heart failure and/or symptoms related to the tachycardia or arrhythmia. Though atrial fibrillation is the most common cause of TIC, several tachycardias and arrhythmias have been associated with the disease.
Cardiovascular physiology is the study of the cardiovascular system, specifically addressing the physiology of the heart ("cardio") and blood vessels ("vascular").

Athletic heart syndrome (AHS) is a non-pathological condition commonly seen in sports medicine in which the human heart is enlarged, and the resting heart rate is lower than normal.
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to cardiology, the branch of medicine dealing with disorders of the human heart. The field includes medical diagnosis and treatment of congenital heart defects, coronary artery disease, heart failure, valvular heart disease and electrophysiology. Physicians who specialize in cardiology are called cardiologists.
The E/A ratio is a marker of the function of the left ventricle of the heart. It represents the ratio of peak velocity blood flow from left ventricular relaxation in early diastole to peak velocity flow in late diastole caused by atrial contraction. It is calculated using Doppler echocardiography, an ultrasound-based cardiac imaging modality. Abnormalities in the E/A ratio suggest that the left ventricle, which pumps blood into the systemic circulation, cannot fill with blood properly in the period between contractions. This phenomenon is referred to as diastolic dysfunction and can eventually lead to the symptoms of heart failure.
Cardiac physiology or heart function is the study of healthy, unimpaired function of the heart: involving blood flow; myocardium structure; the electrical conduction system of the heart; the cardiac cycle and cardiac output and how these interact and depend on one another.
A plot of a system's pressure versus volume has long been used to measure the work done by the system and its efficiency. This analysis can be applied to heat engines and pumps, including the heart. A considerable amount of information on cardiac performance can be determined from the pressure vs. volume plot. A number of methods have been determined for measuring PV-loop values experimentally.

Heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF) is a form of heart failure in which the ejection fraction – the percentage of the volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle with each heartbeat divided by the volume of blood when the left ventricle is maximally filled – is normal, defined as greater than 50%; this may be measured by echocardiography or cardiac catheterization. Approximately half of people with heart failure have preserved ejection fraction, while the other half have a reduction in ejection fraction, called heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF).
The main pathophysiology of heart failure is a reduction in the efficiency of the heart muscle, through damage or overloading. As such, it can be caused by a wide number of conditions, including myocardial infarction, hypertension and cardiac amyloidosis. Over time these increases in workload will produce changes to the heart itself:
References
- ↑ Boron WF, Boulpaep EL (2003). Medical physiology : a cellular and molecular approach (1st ed.). Philadelphia, Pa: Saunders. p. 521. ISBN 0-7216-3256-4.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Maceira AM, Prasad SK, Khan M, Pennell DJ (December 2006). "Reference right ventricular systolic and diastolic function normalized to age, gender and body surface area from steady-state free precession cardiovascular magnetic resonance" (PDF). European Heart Journal. 27 (23): 2879–88. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehl336. PMID 17088316.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Maceira A (2006). "Normalized Left Ventricular Systolic and Diastolic Function by Steady State Free Precession Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance". Journal of Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance. 8: 417–426. doi:10.1080/10976640600572889.(subscription required)
- 1 2 Normal ranges for heart rate are among the narrowest limits between bradycardia and tachycardia. See the Bradycardia and Tachycardia articles for more detailed limits.
- 1 2 3 "Normal Hemodynamic Parameters – Adult" (PDF). Edwards Lifesciences LLC. 2009.