
Bradycardia, also called bradyarrhythmia, is a resting heart rate under 60 beats per minute (BPM). While bradycardia can result from various pathologic processes, it is commonly a physiologic response to cardiovascular conditioning or due to asymptomatic type 1 atrioventricular block.
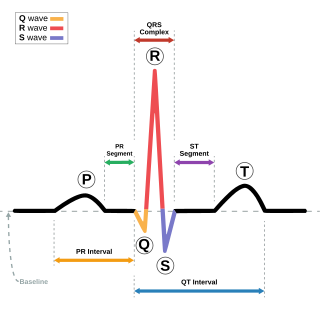
Electrocardiography is the process of producing an electrocardiogram, a recording of the heart's electrical activity through repeated cardiac cycles. It is an electrogram of the heart which is a graph of voltage versus time of the electrical activity of the heart using electrodes placed on the skin. These electrodes detect the small electrical changes that are a consequence of cardiac muscle depolarization followed by repolarization during each cardiac cycle (heartbeat). Changes in the normal ECG pattern occur in numerous cardiac abnormalities, including:

Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome (WPWS) is a disorder due to a specific type of problem with the electrical system of the heart involving an accessory pathway able to conduct electrical current between the atria and the ventricles, thus bypassing the atrioventricular node. About 60% of people with the electrical problem developed symptoms, which may include an abnormally fast heartbeat, palpitations, shortness of breath, lightheadedness, or syncope. Rarely, cardiac arrest may occur. The most common type of irregular heartbeat that occurs is known as paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia.

Sinus node dysfunction (SND), also known as sick sinus syndrome (SSS), is a group of abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) usually caused by a malfunction of the sinus node, the heart's primary pacemaker. Tachycardia-bradycardia syndrome is a variant of sick sinus syndrome in which the arrhythmia alternates between fast and slow heart rates.

The atrioventricular node or AV node electrically connects the heart's atria and ventricles to coordinate beating in the top of the heart; it is part of the electrical conduction system of the heart. The AV node lies at the lower back section of the interatrial septum near the opening of the coronary sinus, and conducts the normal electrical impulse from the atria to the ventricles. The AV node is quite compact.

Third-degree atrioventricular block is a medical condition in which the electrical impulse generated in the sinoatrial node in the atrium of the heart can not propagate to the ventricles.

The cardiac conduction system transmits the signals generated by the sinoatrial node – the heart's pacemaker, to cause the heart muscle to contract, and pump blood through the body's circulatory system. The pacemaking signal travels through the right atrium to the atrioventricular node, along the bundle of His, and through the bundle branches to Purkinje fibers in the walls of the ventricles. The Purkinje fibers transmit the signals more rapidly to stimulate contraction of the ventricles.

First-degree atrioventricular block is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart in which electrical impulses conduct from the cardiac atria to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node more slowly than normal. First degree AV block does not generally cause any symptoms, but may progress to more severe forms of heart block such as second- and third-degree atrioventricular block. It is diagnosed using an electrocardiogram, and is defined as a PR interval greater than 200 milliseconds. First degree AV block affects 0.65-1.1% of the population with 0.13 new cases per 1000 persons each year.

Second-degree atrioventricular block is a disease of the electrical conduction system of the heart. It is a conduction block between the atria and ventricles. The presence of second-degree AV block is diagnosed when one or more of the atrial impulses fail to conduct to the ventricles due to impaired conduction. It is classified as a block of the AV node, falling between first-degree and third degree blocks.

Supraventricular tachycardia (SVT) is an umbrella term for fast heart rhythms arising from the upper part of the heart. This is in contrast to the other group of fast heart rhythms – ventricular tachycardia, which start within the lower chambers of the heart. There are four main types of SVT: atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter, paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia (PSVT), and Wolff–Parkinson–White syndrome. The symptoms of SVT include palpitations, feeling of faintness, sweating, shortness of breath, and/or chest pain.

AV-nodal reentrant tachycardia (AVNRT) is a type of abnormal fast heart rhythm. It is a type of supraventricular tachycardia (SVT), meaning that it originates from a location within the heart above the bundle of His. AV nodal reentrant tachycardia is the most common regular supraventricular tachycardia. It is more common in women than men. The main symptom is palpitations. Treatment may be with specific physical maneuvers, medications, or, rarely, synchronized cardioversion. Frequent attacks may require radiofrequency ablation, in which the abnormally conducting tissue in the heart is destroyed.

Atrioventricular block is a type of heart block that occurs when the electrical signal traveling from the atria, or the upper chambers of the heart, to ventricles, or the lower chambers of the heart, is impaired. Normally, the sinoatrial node produces an electrical signal to control the heart rate. The signal travels from the SA node to the ventricles through the atrioventricular node. In an AV block, this electrical signal is either delayed or completely blocked. When the signal is completely blocked, the ventricles produce their own electrical signal to control the heart rate. The heart rate produced by the ventricles is much slower than that produced by the SA node.
Lown–Ganong–Levine syndrome (LGL) is a pre-excitation syndrome of the heart. Those with LGL syndrome have episodes of abnormal heart racing with a short PR interval and normal QRS complexes seen on their electrocardiogram when in a normal sinus rhythm. LGL syndrome was originally thought to be due to an abnormal electrical connection between the atria and the ventricles, but is now thought to be due to accelerated conduction through the atrioventricular node in the majority of cases. The syndrome is named after Bernard Lown, William Francis Ganong, Jr., and Samuel A. Levine.

Multifocal atrial tachycardia (MAT) is an abnormal heart rhythm, specifically a type of supraventricular tachycardia, that is particularly common in older people and is associated with exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Normally, the heart rate is controlled by a cluster of cells called the sinoatrial node. When a number of different clusters of cells outside the SA node take over control of the heart rate, and the rate exceeds 100 beats per minute, this is called multifocal atrial tachycardia.

Junctional rhythm also called nodal rhythm describes an abnormal heart rhythm resulting from impulses coming from a locus of tissue in the area of the atrioventricular node, the "junction" between atria and ventricles.

Junctional tachycardia is a form of supraventricular tachycardia characterized by involvement of the AV node. It can be contrasted to atrial tachycardia. It is a tachycardia associated with the generation of impulses in a focus in the region of the atrioventricular node due to an A-V disassociation. In general, the AV junction's intrinsic rate is 40-60 bpm so an accelerated junctional rhythm is from 60-100bpm and then becomes junctional tachycardia at a rate of >100 bpm.

A sinoatrial block is a disorder in the normal rhythm of the heart, known as a heart block, that is initiated in the sinoatrial node. The initial action impulse in a heart is usually formed in the sinoatrial node and carried through the atria, down the internodal atrial pathways to the atrioventricular node (AV) node. In normal conduction, the impulse would travel across the bundle of His, down the bundle branches, and into the Purkinje fibers. This would depolarize the ventricles and cause them to contract.

Junctional ectopic tachycardia (JET) is a rare syndrome of the heart that manifests in patients recovering from heart surgery. It is characterized by cardiac arrhythmia, or irregular beating of the heart, caused by abnormal conduction from or through the atrioventricular node. In newborns and infants up to 6 weeks old, the disease may also be referred to as His bundle tachycardia or congenital JET.

Arrhythmias, also known as cardiac arrhythmias, are irregularities in the heartbeat, including when it is too fast or too slow. A resting heart rate that is too fast – above 100 beats per minute in adults – is called tachycardia, and a resting heart rate that is too slow – below 60 beats per minute – is called bradycardia. Some types of arrhythmias have no symptoms. Symptoms, when present, may include palpitations or feeling a pause between heartbeats. In more serious cases, there may be lightheadedness, passing out, shortness of breath, chest pain, or decreased level of consciousness. While most cases of arrhythmia are not serious, some predispose a person to complications such as stroke or heart failure. Others may result in sudden death.

Celivarone is an experimental drug being tested for use in pharmacological antiarrhythmic therapy. Cardiac arrhythmia is any abnormality in the electrical activity of the heart. Arrhythmias range from mild to severe, sometimes causing symptoms like palpitations, dizziness, fainting, and even death. They can manifest as slow (bradycardia) or fast (tachycardia) heart rate, and may have a regular or irregular rhythm.




















