Gibberellins (GAs) are plant hormones that regulate various developmental processes, including stem elongation, germination, dormancy, flowering, flower development, and leaf and fruit senescence. GAs are one of the longest-known classes of plant hormone. It is thought that the selective breeding of crop strains that were deficient in GA synthesis was one of the key drivers of the "green revolution" in the 1960s, a revolution that is credited to have saved over a billion lives worldwide.

Fusicoccins are organic compounds produced by a fungus. It has detrimental effect on plants and causes their death.
In enzymology, an ent-copalyl diphosphate synthase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction:
The enzyme ent-kaurene synthase catalyzes the chemical reaction
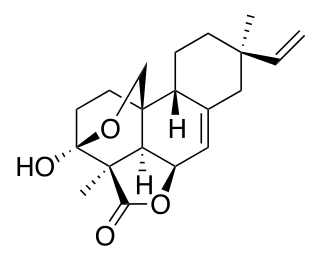
Momilactone B is an allelopathic agent produced from the roots of rice. It has been shown to be produced in high concentrations by the roots of rice seedlings. The production of momilactone B has also been induced in response to infection by blast fungus or irradiated with UV light. More recently it has been shown to be a potential chemotherapeutic agent against human colon cancer.

In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes, which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene, and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the N terminal domain of the TPS protein.
In molecular biology, this protein domain belongs to the terpene synthase family (TPS). Its role is to synthesize terpenes, which are part of primary metabolism, such as sterols and carotene, and also part of the secondary metabolism. This entry will focus on the C terminal domain of the TPS protein.
Momilactone-A synthase (EC 1.1.1.295, momilactone A synthase, OsMAS) is an enzyme with systematic name 3beta-hydroxy-9beta-pimara-7,15-diene-19,6beta-olide:NAD(P)+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ent-Cassa-12,15-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name ent-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (ent-cassa-12,15-diene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ent-Pimara-8(14),15-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name ent-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase [ent-pimara-8(14),15-diene-forming]. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
ent-Pimara-9(11),15-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name ent-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Stemar-13-ene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (stemar-13-ene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Stemod-13(17)-ene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
syn-Pimara-7,15-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (9β-pimara-7,15-diene-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Aphidicolan-16β-ol synthase (EC 4.2.3.42, PbACS) is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (aphidicolan-16β-ol-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Fusicocca-2,10(14)-diene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name geranylgeranyl diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Phyllocladan-16α-ol synthase (EC 4.2.3.45, PaDC1) is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase (phyllocladan-16α-ol-forming). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Labdatriene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9α-copalyl-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Miltiradiene synthase is an enzyme with systematic name (+)-copaly-diphosphate diphosphate-lyase . This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Syn-copalyl-diphosphate synthase is an enzyme with systematic name 9alpha-copalyl-diphosphate lyase (decyclizing). This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction




