
Daspletosaurus is a genus of tyrannosaurid dinosaur that lived in Laramidia between about 79.5 and 74 million years ago, during the Late Cretaceous Period. The genus Daspletosaurus contains two species. Fossils of the earlier type species, D. torosus, have been found in Alberta, while fossils of the later second species, D. horneri, have been found only in Montana. A possible third species, also from Alberta, awaits formal identification and another possible species D. degrootorum, also exists, but it may belong to the separate genus Thanatotheristes instead. Daspletosaurus is closely related to the much larger and more recent tyrannosaurid Tyrannosaurus rex. Like most tyrannosaurids, Daspletosaurus was a multi-tonne bipedal predator equipped with dozens of large, sharp teeth. Daspletosaurus had the small forelimbs typical of tyrannosaurids, although they were proportionately longer than in other genera.
Paracimexomys is a genus of extinct mammals in the also extinct Multituberculata order. Paracimexomys lived during the Cretaceous period. The few fossils remains come from North America. Some Romanian fossils were also tentatively assigned to this genus, though that classification now seems doubtful.
Cimolodon is a genus of the extinct mammal order of Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and the family Cimolodontidae. Specimens are known from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Didelphodon is a genus of stagodont metatherians from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Pachyrhinosaurus is an extinct genus of centrosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous period of North America. The first examples were discovered by Charles M. Sternberg in Alberta, Canada, in 1946, and named in 1950. Over a dozen partial skulls and a large assortment of other fossils from various species have been found in Alberta and Alaska. A great number were not available for study until the 1980s, resulting in a relatively recent increase of interest in Pachyrhinosaurus.

Anchiceratops is an extinct genus of chasmosaurine ceratopsid dinosaur that lived approximately 72 to 71 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Alberta, Canada. Anchiceratops was a medium-sized, heavily built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore that could grow up to an estimated 5 m (16.4 ft) long. Its skull featured two long brow horns and a short horn on the nose. The skull frill was elongated and rectangular, its edges adorned by coarse triangular projections. About a dozen skulls of the genus have been found.

Montanoceratops is an extinct genus of small ceratopsian dinosaur that lived approximately 70 million years ago during the latter part of the Cretaceous Period in what is now Montana and Alberta. Montanoceratops was a small sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could grow up to an estimated 3 m (9.8 ft) long.
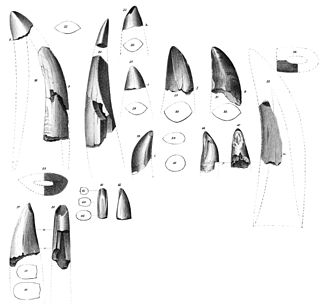
Deinodon is a dubious tyrannosaurid dinosaur genus containing a single species, Deinodon horridus. D. horridus is known only from a set of teeth found in the Late Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana and named by paleontologist Joseph Leidy in 1856. These were the first tyrannosaurid remains to be described and had been collected by Ferdinand Vandeveer Hayden. The teeth of Deinodon were slightly heterodont, and the holotype of Aublysodon can probably be assigned to Deinodon.

Anodontosaurus is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from the entire span of the Late Cretaceous Horseshoe Canyon Formation of southern Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, A. lambei and A. inceptus.

Scolosaurus is an extinct genus of ankylosaurid dinosaurs within the subfamily Ankylosaurinae. It is known from either the lower levels of the Dinosaur Park Formation or upper levels of the Oldman Formation in the Late Cretaceous of Alberta, Canada. It contains two species, S. cutleri and S. thronus.

The Oldman Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Late Cretaceous age that underlies much of southern Alberta, Canada. It consists primarily of sandstones that were deposited in fluvial channel and floodplain environments. It was named for exposures along the Oldman River between its confluence with the St. Mary River and the city of Lethbridge, and it is known primarily for its dinosaur remains and other fossils.
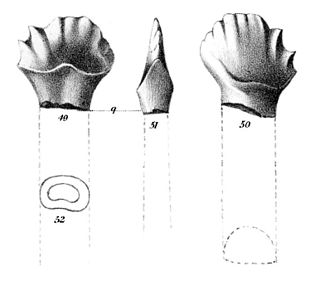
Hanssuesia is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous period. It lived in what is now Alberta and Montana, and contains the single species Hanssuesia sternbergi.
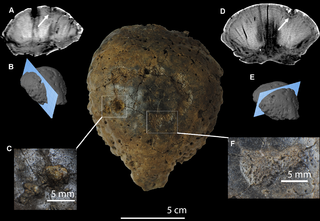
Palaeoscincus is a dubious genus of ankylosaurian dinosaur based on teeth from the mid-late Campanian-age Upper Cretaceous Judith River Formation of Montana. Like several other dinosaur genera named by Joseph Leidy, it is an historically important genus with a convoluted taxonomy that has been all but abandoned by modern dinosaur paleontologists. Because of its wide use in the early 20th century, it was somewhat well known to the general public, often through illustrations of an animal with the armor of Edmontonia and the tail club of an ankylosaurid.

The Judith River Formation is a fossil-bearing geologic formation in Montana, and is part of the Judith River Group. It dates to the Late Cretaceous, between 80 and 75 million years ago, corresponding to the "Judithian" land vertebrate age. It was laid down during the same time period as portions of the Two Medicine Formation of Montana and the Oldman Formation of Alberta. It is an historically important formation, explored by early American paleontologists such as Edward Drinker Cope, who named several dinosaurs from scrappy remains found here on his 1876 expedition. Modern work has found nearly complete skeletons of the hadrosaurid Brachylophosaurus.

The Horseshoe Canyon Formation is a stratigraphic unit of the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in southwestern Alberta. It takes its name from Horseshoe Canyon, an area of badlands near Drumheller.

The Bearpaw Formation, also called the Bearpaw Shale, is a geologic formation of Late Cretaceous (Campanian) age. It outcrops in the U.S. state of Montana, as well as the Canadian provinces of Alberta and Saskatchewan, and was named for the Bear Paw Mountains in Montana. It includes a wide range of marine fossils, as well as the remains of a few dinosaurs. It is known for its fossil ammonites, some of which are mined in Alberta to produce the organic gemstone ammolite.
William Alvin Clemens Jr. was a paleontologist at the University of California at Berkeley. He was on the faculty of the Department of Integrated Biology since 1994, and since 1967 in the Department of Paleontology and the UC Museum of Paleontology. Clemens was also director of the museum (1987–1989) and chair of the Department of Paleontology (1987–1989). He has been awarded a Guggenheim Fellowship (1974–75), a U.S. Senior Scientist Award by the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, the Romer-Simpson Medal (2006), and was made a Fellow of the California Academy of Sciences.

Kritosaurini is a tribe of saurolophine hadrosaurid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous.

Stagodontidae is an extinct family of carnivorous metatherian mammals that inhabited North America and Europe during the late Cretaceous, and possibly to the Eocene in South America.

Gypsonictops is an extinct genus of leptictidan mammals of the monotypic family Gypsonictopidae, which was described in 1927 by George Gaylord Simpson. Species in this genus were small mammals and the first representatives of the order Leptictida, that appeared during the Upper Cretaceous.





















