
Multituberculata is an extinct order of rodent-like mammals with a fossil record spanning over 130 million years. They first appeared in the Middle Jurassic, and reached a peak diversity during the Late Cretaceous and Paleocene. They eventually declined from the mid-Paleocene onwards, disappearing from the known fossil record in the late Eocene. They are the most diverse order of Mesozoic mammals with more than 200 species known, ranging from mouse-sized to beaver-sized. These species occupied a diversity of ecological niches, ranging from burrow-dwelling to squirrel-like arborealism to jerboa-like hoppers. Multituberculates are usually placed as crown mammals outside either of the two main groups of living mammals—Theria, including placentals and marsupials, and Monotremata—but usually as closer to Theria than to monotremes. They are considered to be closely related to Euharamiyida and Gondwanatheria as part of Allotheria.

Eutheria, also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of placental mammals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.

Didelphodon is a genus of stagodont metatherians from the Late Cretaceous of North America.
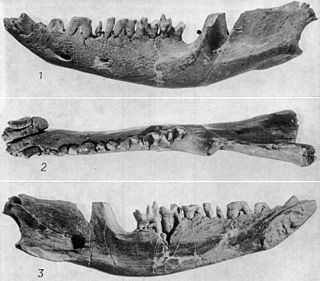
Eodelphis, from eo- (dawn) and [Di]delphis, thus meaning "dawn opossum", is a genus of stagodont metatherians from the Late Cretaceous of North America, with distinctive crushing dentition. Named species include E. browni and the more advanced E. cutleri. Both come from the Late Campanian of Dinosaur Provincial Park, Alberta. Specimens are also known from the Judith River Formation of Montana. E. cutleri is related to the Maastrichtian genus Didelphodon as indicated by its enlarged premolars and more robust jaw. Eodelphis was probably an aquatic predator like its relative Didelphodon, and may have weighed about 0.6 kg (1.3 lb), making it one of the largest mammals of its time.

Pucadelphys is an extinct genus of non-marsupial metatherian. The genus contains a single species, P. andinus. Fossils of Pucadelphys have been found in the Santa Lucía Formation in Tiupampa in Bolivia.

Sparassodonta is an extinct order of carnivorous metatherian mammals native to South America, related to modern marsupials. They were once considered to be true marsupials, but are now thought to be a separate side branch that split before the last common ancestor of all modern marsupials.
Tritylodontidae is an extinct family of small to medium-sized, highly specialized mammal-like cynodonts, with several mammalian traits including erect limbs, endothermy, and some details of the skeleton. They were the last-known family of the non-mammaliaform synapsids, persisting into the Early Cretaceous.

Deltatheroida is an extinct group of basal metatherians that were distantly related to modern marsupials. The majority of known members of the group lived in the Cretaceous; one species, Gurbanodelta kara, is known from the late Paleocene (Gashatan) of China. Their fossils are restricted to Central Asia and North America. This order can be defined as all metatherians closer to Deltatheridium than to Marsupialia.

Brachychampsa is an extinct genus of alligatorid, possibly a basal caiman. Specimens have been reported from New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, North and South Dakota, New Jersey, and Saskatchewan, though only those from Montana, Utah, and New Mexico are based on material sufficient to justify the referral. Some specimens have been reported from the Campanian-aged deposits of Central Asia, although the species status is indeterminate for these fossils. The genus first appeared during the late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous. Brachychampsa is distinguished by an enlarged fifth maxillary tooth in the upper jaw.

Acheroraptor is an extinct genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the latest Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation of Montana, United States. It contains a single species, Acheroraptor temertyorum. A. temertyorum is one of the two geologically youngest known species of dromaeosaurids, the other being Dakotaraptor steini, which is also known from Hell Creek. A basal cousin of Velociraptor, Acheroraptor is known from upper and lower jaw material.

Stagodontidae is an extinct family of carnivorous metatherian mammals that inhabited North America and Europe during the late Cretaceous, and possibly to the Eocene in South America.
Siamoperadectes is a genus of non-marsupial metatherian from the Miocene of Thailand. A member of Peradectidae, it is the first member of its clade known from South Asia, and among the last non-marsupial metatherians.
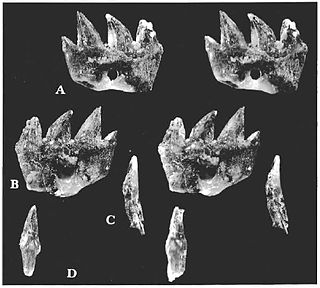
Ichthyoconodon is an extinct genus of eutriconodont mammal from the Lower Cretaceous of Morocco. It is notable for having been found in a unique marine location, and the shape of its teeth suggests an unusual, potentially fish-eating ecological niche. Analysis suggests it is part of a group of gliding mammals that includes Volaticotherium.
Groeberiidae is a family of strange non-placental mammals from the Eocene and Oligocene epochs of Patagonia, Argentina and Chile, South America. Originally classified as paucituberculate marsupials, they were suggested to be late representatives of the allothere clade Gondwanatheria. However, the relationship of the type genus, Groeberia, to Gondwanatheria has been firmly rejected by other scholars.
Patagonia is an extinct genus of non-placental mammal from the Miocene of Argentina. Traditionally considered a metatherian incertae sedis, one analysis suggested it to be a gondwanathere. However, this has been rejected by other authors.
Protalphadon is a genus of small mammal from the Late Cretaceous. Its fossils are found in Utah, Montana, New Jersey, South Dakota, Wyoming and Colorado. Originally the genus was assigned to Alphadon.

Peradectes is an extinct genus of small metatherian mammals known from the latest Cretaceous to Eocene of North and South America and Europe. The first discovered fossil of P. elegans, was one of 15 Peradectes specimens described in 1921 from the Mason pocket fossil beds in Colorado. The monophyly of the genus has been questioned.
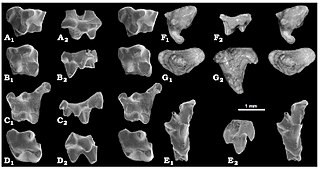
Holoclemensia is an extinct genus of mammal of uncertain phylogenetic placement. It lived during the Early Cretaceous and its fossil remains were discovered in Texas.

Asiatherium is an extinct genus of mammal, probably belonging to Metatheria. It lived during the Late Cretaceous, and its fossilized remains were discovered in Mongolia.
Albertatherium is an extinct genus of alphadontid metatherians that lived during the Late Cretaceous of North America. The genus contains two species, Albertatherium primus, and Albertatherium secundus. Fossils have been found in the Eagle Formation of Montana and the Milk River Formation of Alberta.


















