
The molars or molar teeth are large, flat teeth at the back of the mouth. They are more developed in mammals. They are used primarily to grind food during chewing. The name molar derives from Latin, molaris dens, meaning "millstone tooth", from mola, millstone and dens, tooth. Molars show a great deal of diversity in size and shape across the mammal groups. The third molar of humans is sometimes vestigial.

Eutheria, also called Pan-Placentalia, is the clade consisting of placentals and all therian mammals that are more closely related to placentals than to marsupials.

Metatheria is a mammalian clade that includes all mammals more closely related to marsupials than to placentals. First proposed by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1880, it is a more inclusive group than the marsupials; it contains all marsupials as well as many extinct non-marsupial relatives. It is one of two groups placed in the clade Theria alongside Eutheria, which contains the placentals. Remains of metatherians have been found on all of Earths continents.

Theria is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians and the metatherians but excludes the egg-laying monotremes and various extinct mammals evolving prior to the common ancestor of placentals and marsupials.

Didelphodon is a genus of stagodont metatherians from the Late Cretaceous of North America.

Tribosphenida is a group (infralegion) of mammals that includes the ancestor of Hypomylos, Aegialodontia and Theria. It belongs to the group Zatheria. The current definition of Tribosphenida is more or less synonymous with Boreosphenida.

The Australosphenida are a clade of mammals, containing mammals with tribosphenic molars, known from the Jurassic to Mid-Cretaceous of Gondwana. Although they have often been suggested to have acquired tribosphenic molars independently from those of Tribosphenida, this has been disputed. Fossils of australosphenidans have been found from the Jurassic of Madagascar and Argentina, and Cretaceous of Australia and Argentina. Monotremes have also been considered a part of this group in its original definition and in many subsequent studies, but its relationship with other members has been disputed by some scholars.
Shuotherium is a fossil mammaliaform known from Middle-Late Jurassic of the Forest Marble Formation of England, and the Shaximiao Formation of Sichuan, China.

Cladotheria is a clade of mammals. It contains modern therian mammals and several extinct groups, such as the "dryolestoids", amphitheriids and peramurids. The clade was named in 1975 by Malcolm McKenna. In 2002, it was defined as a node-based taxon containing "the common ancestor of dryolestids and living therians, plus all its descendants". A different, stem-based definition was given in 2013, in which Cladotheria contains all taxa that are closer to Mus musculus than to the "symmetrodont" Spalacotherium tricuspidens.

Kuehneotherium is an early mammaliaform genus, previously considered a holothere, that lived during the Late Triassic-Early Jurassic Epochs and is characterized by reversed-triangle pattern of molar cusps. Although many fossils have been found, the fossils are limited to teeth, dental fragments, and mandible fragments. The genus includes Kuehneotherium praecursoris and all related species. It was first named and described by Doris M. Kermack, K. A. Kermack, and Frances Mussett in November 1967. The family Kuehneotheriidae and the genus Kuehneotherium were created to house the single species Kuehneotherium praecursoris. Modeling based upon a comparison of the Kuehneotherium jaw with other mammaliaforms indicates it was about the size of a modern-day shrew between 4 and 5.5 g at adulthood.

Monotremes are mammals of the order Monotremata. They are the only group of living mammals that lay eggs, rather than bearing live young. The extant monotreme species are the platypus and the four species of echidnas. Monotremes are typified by structural differences in their brains, jaws, digestive tract, reproductive tract, and other body parts, compared to the more common mammalian types. Although they are different from almost all mammals in that they lay eggs, like all mammals, the female monotremes nurse their young with milk.

Ambondro mahabo is a mammal from the Middle Jurassic (Bathonian) Isalo III Formation of Madagascar. The only described species of the genus Ambondro, it is known from a fragmentary lower jaw with three teeth, interpreted as the last premolar and the first two molars. The premolar consists of a central cusp with one or two smaller cusps and a cingulum (shelf) on the inner, or lingual, side of the tooth. The molars also have such a lingual cingulum. They consist of two groups of cusps: a trigonid of three cusps at the front and a talonid with a main cusp, a smaller cusp, and a crest at the back. Features of the talonid suggest that Ambondro had tribosphenic molars, the basic arrangement of molar features also present in marsupial and placental mammals. It is the oldest known mammal with putatively tribosphenic teeth; at the time of its discovery it antedated the second oldest example by about 25 million years.
Several mammals are known from the Mesozoic of Madagascar. The Bathonian Ambondro, known from a piece of jaw with three teeth, is the earliest known mammal with molars showing the modern, tribosphenic pattern that is characteristic of marsupial and placental mammals. Interpretations of its affinities have differed; one proposal places it in a group known as Australosphenida with other Mesozoic tribosphenic mammals from the southern continents (Gondwana) as well as the monotremes, while others favor closer affinities with northern (Laurasian) tribosphenic mammals or specifically with placentals. At least five species are known from the Maastrichtian, including a yet undescribed species known from a nearly complete skeleton that may represent a completely new group of mammals. The gondwanathere Lavanify, known from two teeth, is most closely related to other gondwanatheres found in India and Argentina. Two other teeth may represent another gondwanathere or a different kind of mammal. One molar fragment is one of the few known remains of a multituberculate mammal from Gondwana and another has been interpreted as either a marsupial or a placental.

Pappotherium is an extinct genus of mammals from the Albian of Texas, US, known from a fossilized maxilla fragment bearing two tribosphenic molars, discovered within the Glen Rose Formation near Decatur, Wise County, Texas.
Astroconodon is an extinct genus of mammal from the Cretaceous of North America. Part of Eutriconodonta, it was a small sized predator, either a terrestrial insectivore and carnivore, or a semi-aquatic piscivore.

Peradectes is an extinct genus of small metatherian mammals known from the latest Cretaceous to Eocene of North and South America and Europe. The first discovered fossil of P. elegans, was one of 15 Peradectes specimens described in 1921 from the Mason pocket fossil beds in Colorado. The monophyly of the genus has been questioned.

Gypsonictops is an extinct genus of leptictidan mammals of the family Gypsonictopidae, which was described in 1927 by George Gaylord Simpson. Species in this genus were small mammals and the first representatives of the order Leptictida, that appeared during the Upper Cretaceous.

Asiatherium is an extinct genus of mammal, probably belonging to Metatheria. It lived during the Late Cretaceous, and its fossilized remains were discovered in Mongolia.
Ambolestes is an extinct genus of eutherian mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Ambolestes zhoui, known from a single complete skeleton recovered from the Yixian Formation, part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. Ambolestes is one of the most basal eutherians, presenting a combination of features from both early eutherians (stem-placentals) and early metatherians (stem-marsupials). This is responsible for the generic name of Ambolestes: "ambo" is Latin for "both", while "-lestes" is a popular suffix for fossil mammals. The species name honors influential Jehol paleontologist Zhou Zhonghe.
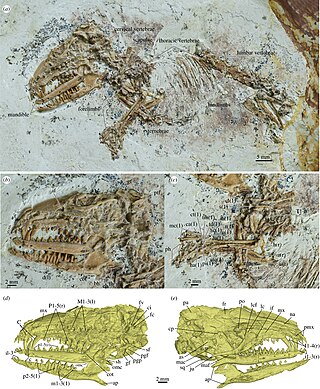
Cokotherium is an extinct genus of eutherian mammal from the Early Cretaceous of China. It includes a single species, Cokotherium jiufotangensis, known from a single partial skeleton, missing a portion of the hindlimbs and tail. It was recovered from the Jiufotang Formation, the upper part of the fossiliferous Jehol biota. The generic name of Cokotherium honors the nickname of the late paleontologist Chuan-Kui Li, a specialist on the Jiufotang Formation. The specific name refers to the formation in question. Cokotherium is one of the youngest and most well-preserved Early Cretaceous eutherians, illustrating an array of transitional conditions between Early Cretaceous and Late Cretaceous members of Eutheria.



















