
Khat, also known as Bushman's tea, especially in South Africa, is a flowering plant native to eastern and southeastern Africa. It has a history of cultivation originating in the Harar area and subsequently introduced at different times to countries nearby in East Africa and Southern Arabia, most notably Yemen. Cultivated by farmers, its leaves are sold on the market to be chewed as a recreational stimulant. The world's largest consumers are Eastern Africans, particularly Somalis, and nearby Yemen, with the largest producers/exporters being Ethiopia and Kenya.

Passiflora edulis, commonly known as passion fruit, is a vine species of passion flower native to the region of southern Brazil through Paraguay to northern Argentina. It is cultivated commercially in tropical and subtropical areas for its sweet, seedy fruit.

Macrotyloma uniflorum is a legume native to tropical southern Asia, known for its distinct taste and texture, widely used legume in many cuisines. It is also known for human consumption for its rich nutrients and reputed medicinal properties. It is commonly grown for horse feed, hence the name “horse gram”. Horse gram grown in parts of India, as well as Nepal, Malaysia, Sri Lanka, and is introduced to the West Indies. It is consumed whole, sprouted, or ground. It is consumed in many parts of India and is also known as a superfood. Horse gram is also allowed to be eaten on some Hindu fasting days. Medical uses of these legumes have been discussed and is described in the Ayurveda.
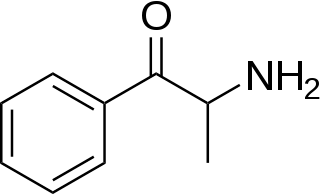
Cathinone is a monoamine alkaloid found in the shrub Catha edulis (khat) and is chemically similar to ephedrine, cathine, methcathinone and other amphetamines. It is probably the main contributor to the stimulant effect of Catha edulis, also known as khat. Cathinone differs from many other amphetamines in that it has a ketone functional group. Other phenethylamines that share this structure include the stimulants methcathinone, MDPV, mephedrone and the antidepressant bupropion.

The Pyralidae, commonly called pyralid moths, snout moths or grass moths, are a family of Lepidoptera in the ditrysian superfamily Pyraloidea. In many classifications, the grass moths (Crambidae) are included in the Pyralidae as a subfamily, making the combined group one of the largest families in the Lepidoptera. The latest review by Eugene G. Munroe and Maria Alma Solis retain the Crambidae as a full family of Pyraloidea.

Vigna aconitifolia is a drought-resistant legume, commonly grown in arid and semi-arid regions of India. It is commonly called mat bean, moth bean, matki or dew bean. The pods, sprouts and protein-rich seeds of this crop are commonly consumed in India. Moth bean can be grown on many soil types, and can also act as a pasture legume.

The cabbage moth is primarily known as a pest that is responsible for severe crop damage of a wide variety of plant species. The common name, cabbage moth, is a misnomer as the species feeds on many fruits, vegetables, and crops in the genus Brassica. Other notable host plants include tobacco, sunflower, and tomato, making this pest species particularly economically damaging.

The tropical house gecko, also called commonly the Afro-American house gecko and the cosmopolitan house gecko, is a species of house gecko, a lizard in the family Gekkonidae. The species is native to sub-Saharan Africa. However, it is also found in North, Central and South America and the Caribbean, where it has been inadvertently introduced by humans.

Orgyia antiqua, the rusty tussock moth or vapourer, is a moth in the family Erebidae.

Agrotis ipsilon, the dark sword-grass, ipsilon dart, black cutworm, greasy cutworm or floodplain cutworm, is a small noctuid moth found worldwide. The moth gets its scientific name from black markings on its forewings shaped like the letter "Y" or the Greek letter upsilon. The larvae are known as "cutworms" because they cut plants and other crops. The larvae are serious agricultural pests and feed on nearly all varieties of vegetables and many important grains.

Spodoptera littoralis, also referred to as the African cotton leafworm or Egyptian cotton leafworm or Mediterranean brocade, is a species of moth in the family Noctuidae. S. littoralis is found widely in Africa, Mediterranean Europe and Middle Eastern countries. It is a highly polyphagous organism that is a pest of many cultivated plants and crops. As a result, this species was assigned the label of A2 quarantine pest by the EPPO and was cautioned as a highly invasive species in the United States. The devastating impacts caused by these pests have led to the development of both biological and chemical control methods. This moth is often confused with Spodoptera litura.

Bunaea alcinoe, the cabbage tree emperor moth, is an African moth species belonging to the family Saturniidae. It was first described by Caspar Stoll in 1780.

Acronicta rumicis, the knot grass moth, is a species of moth which is part of the genus Acronicta and family Noctuidae. It was first described by Carl Linnaeus in his 1758 10th edition of Systema Naturae. It is found in the Palearctic region. A. rumicis lives and feeds on plants located in wide-open areas. At its larval stage, as a caterpillar, it causes such a large impact as a crop pest that it has received much attention and research. A. rumicis feeds on maize, strawberries and other herbaceous plants.

Mythimna separata, the northern armyworm, oriental armyworm or rice ear-cutting caterpillar, is a moth of the family Noctuidae. It is found in China, Japan, South-east Asia, India, eastern Australia, New Zealand, and some Pacific islands. It is one of the major pests of maize in Asia. The species was first described by Francis Walker in 1865.

Etiella behrii is a species of moth of the family Pyralidae, occurring sporadically but when present considered a serious pest of agricultural crops throughout parts of Australia.

Thaumatotibia (Cryptophlebia) leucotreta, commonly known as the false codling moth, orange moth, citrus codling moth or orange codling moth, is a moth in the family Tortricidae under the order of Lepidoptera. Larvae of the moth feed on a wide range of crops from cotton and macadamia nuts to Citrus species. The larvae have a less selective diet than the codling moth, which feeds primarily on temperate fruit crops.

Pyralis pictalis, the painted meal moth or poplar pyralis, is a snout moth. It is closely related to the family's type species the meal moth and consequently belongs to the tribe Pyralini of the snout moth subfamily Pyralinae. Its native range is tropical Asia to East Asia and to Wallacea and adjacent regions, but it has been quite widely distributed by humans. The term "Poplar" in its common name does not refer to the trees, but to Poplar, London, where the type specimen – from such an introduction – was caught. It was called scarce meal moth in the original description, which is only correct for the fringes of its range however.

Leucinodes orbonalis, the eggplant fruit and shoot borer or brinjal fruit and shoot borer, is a moth species in the genus Leucinodes described by Achille Guenée in 1854. Its native distribution is in the tropical and subtropical parts of Australia and Asia, where it is recorded from Pakistan, Nepal, India, including the Andaman Islands, Sri Lanka, Bangladesh, Myanmar, Laos, Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand, China, Taiwan, Japan, Malaysia, Singapore, Brunei, the Philippines, and Indonesia (Java). It has also been intercepted from fruit imports in the U.S.A., the Netherlands, Denmark and Great Britain, where it was also reported from the wild. A taxonomic revision of the Leucinodes species of Sub-Saharan Africa concluded that L. orbonalis is currently not present in Africa, and that previous records of this species were misidentifications of previously undescribed species.

The Phycitini are a tribe of moths of the family Pyralidae.
Aphilopota phanerostigma is a species of moth of the family Geometridae first described by Louis Beethoven Prout in 1917. It is found in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, South Africa, Zimbabwe and Ethiopia.






















