Bowling Green Bay is a national park in the City of Townsville and Shire of Burdekin, Queensland, Australia, 1,103 km northwest of Brisbane, and 28 km south of Townsville and 59 km north of Ayr. It is a Ramsar Convention listed site. The park protects diverse range of habitats including the rugged, forested landscape surrounding Mount Elliot and Saddle Mountain as well as coastal estuaries between Cape Cleveland and Cape Bowling Green.

Port Broughton is a small South Australian town located at the northern extent of the Yorke Peninsula on the east coast of Spencer Gulf. It is situated about 170 km north-west of Adelaide, and 56 km south of Port Pirie. At the 2011 census, the town of Port Broughton had a population of 1,034.

Tumby Bay is a coastal town situated on the Spencer Gulf, on the eastern coast of Eyre Peninsula in South Australia, 45 kilometres (28 mi) north of Port Lincoln. The town of Tumby Bay is the major population centre of the District Council of Tumby Bay, and the centre of an agricultural district farming cereal crops and sheep, as well as having established fishing and tourism industries.

Port Neill is a small coastal town on the eastern side of the Eyre Peninsula, in South Australia about 3 km off the Lincoln Highway between the major towns of Whyalla and Port Lincoln. It is 576 km by road from Adelaide.

Cowell is a coastal town on Franklin Harbor on the eastern side of the Eyre Peninsula, in South Australia on the Lincoln Highway 111 km south of the major town of Whyalla. It is 493 km by road from Adelaide.

The yellowfin whiting, Sillago schomburgkii, is a species of inshore marine fish in the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The species is endemic to the eastern Indian Ocean, ranging from Dampier, Western Australia to Gulf St Vincent in South Australia, with an apparent division in the populations of the two states. Yellowfin whiting inhabit relatively shallow waters for their entire life, often found on tidal flats and creeks, as well as large estuaries. It is one of the largest members of the smelt-whiting family, growing to 42 cm, and can be distinguished by a number of anatomical and colour related features. Yellowfin whiting are benthic carnivores, preying predominantly on polychaete worms, with minor amounts of copepods, amphipods and bivalves also commonly taken. The species shows a change in diet with age, and also dietary differences with other sillaginids presumably to minimize competition. Reproduction occurs at different times throughout its range, generally focused around summer, with up to 217,000 eggs produced per season. Yellowfin whiting reach sexual maturity at around 20 cm, with each individual spawning more than once. The species forms the basis of major fisheries in both Shark Bay, Western Australia and the two Gulfs of South Australia, with around 260 tonnes of fish taken each year. They are also a popular target for shore based anglers, with a reputation as a very good table fish.

Pelican Lagoon is a seawater lagoon in the Australian state of South Australia located on the north coast of Kangaroo Island about 18.7 kilometres south east of Kingscote. It was named by Matthew Flinders on 4 April 1802 after the large population of pelicans present in its waters and adjoining shorelines. Its role as fishery hatchery had been identified by the early 20th century with the result that fishing in its waters has been restricted in varying degrees. Since 1971, the entire lagoon has been part of a marine protected area known as the American River Aquatic Reserve where all fishing and the collection of marine organisms is prohibited.

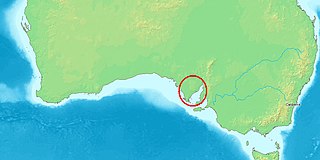
Tumby Island is a low bedrock island located 500 m east of the southern tip of Tumby Bay in Spencer Gulf, South Australia. The island is a conservation park comprising 35 hectares. The island can be accessed on foot at low tide by traversing shallow water-covered rock flats and curving sand. Visitors should request access permission from DEWNR before visiting and be mindful of the presence of Death adders.

Weeroona Island is a 77 ha island in the Australian state of South Australia located in Germein Bay, Spencer Gulf between the city of Port Pirie and town of Port Germein. It features the wreck of the York, coastal shacks, sandy beaches and is connected with the mainland by a 300m long causeway spanning mangroves and tidal flats.

Shag Island is a low island located at the mouth of Fisherman's Bay in Spencer Gulf, South Australia. It is approximately 22 ha in size with a peak elevation of approximately 4 metres. It is uninhabited by humans but is home to thousands of cormorants which roost and breed there. It is also an important nursery-ground for fish. In April 2013, the discovery of several sick and dead cormorants near Fisherman's Bay raised public concerns for the health of the Shag Island colony. The discovery coincided with significant fish and dolphin mortality events around the state, mostly concentrated in Spencer Gulf and Gulf St. Vincent.

Nepean Bay is a bay located on the north-east coast of Kangaroo Island in the Australian state of South Australia about 130 kilometres south-south-west of Adelaide. It was named by the British navigator, Matthew Flinders, after Sir Evan Nepean on 21 March 1802.

Munyaroo Conservation Park is a protected area in the Australian state of South Australia in the gazetted locality of Midgee located on the east coast of the Eyre Peninsula about 36 kilometres south south-west of Whyalla and 35 kilometres east north-east of Cowell.

Pondalowie Bay is a bay in the Australian state of South Australia located on the west coast of the south-west tip of Yorke Peninsula in Spencer Gulf about 12 kilometres west of Marion Bay. The coastline of Pondalowie Bay is both within the gazetted locality of Inneston and the Innes National Park.

Aldinga Bay is a bay located on the east coast of Gulf St Vincent in South Australia about 40 kilometres south-southwest of Adelaide city centre.

Royston Island is an island in the Australian state of South Australia at the northern end of Pondalowie Bay on the south-west extremity of Eyre Peninsula about 13 kilometres north-west of the town of Stenhouse Bay. The island has enjoyed protected area status since 1967 and since 1972, it has been part of the Innes National Park.

Coobowie Aquatic Reserve is a marine protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located in the waters of Gulf St Vincent adjoining the east coast of Yorke Peninsula. It is located partly within the locality of Coobowie and partly within a bay called Salt Creek Bay within the gulf.

Whyalla-Cowleds Landing Aquatic Reserve is a marine protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located in the waters of Spencer Gulf adjoining the east coast of Eyre Peninsula. About 20 kilometres (12 mi) south of Whyalla, it includes land in the localities of Cowleds Landing and Middleback Range which is subject to tidal inundation. It was declared in 1984 to protect "the mangrove-seagrass communities and associated fish nursery areas".

Bales Beach Aquatic Reserve is a marine protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located in waters off the south coast of Kangaroo Island immediately adjoining and including the intertidal zone within the locality of Seal Bay whose full extent is occupied by the Seal Bay Conservation Park.