
Moreton Bay is a bay located on the eastern coast of Australia 14 kilometres (8.7 mi) from central Brisbane, Queensland. It is one of Queensland's most important coastal resources. The waters of Moreton Bay are a popular destination for recreational anglers and are used by commercial operators who provide seafood to market.

The Great Australian Bight is a large oceanic bight, or open bay, off the central and western portions of the southern coastline of mainland Australia.

Whale watching is the practice of observing whales and dolphins (cetaceans) in their natural habitat. Whale watching is mostly a recreational activity, but it can also serve scientific and/or educational purposes. A study prepared for International Fund for Animal Welfare in 2009 estimated that 13 million people went whale watching globally in 2008. Whale watching generates $2.1 billion per annum in tourism revenue worldwide, employing around 13,000 workers. The size and rapid growth of the industry has led to complex and continuing debates with the whaling industry about the best use of whales as a natural resource.

Right whales are three species of large baleen whales of the genus Eubalaena: the North Atlantic right whale, the North Pacific right whale and the Southern right whale. They are classified in the family Balaenidae with the bowhead whale. Right whales have rotund bodies with arching rostrums, V-shaped blowholes and dark gray or black skin. The most distinguishing feature of a right whale is the rough patches of skin on its head, which appear white due to parasitism by whale lice. Right whales are typically 13–17 m (43–56 ft) long and weigh up to 100 short tons or more.

The southern right whale is a baleen whale, one of three species classified as right whales belonging to the genus Eubalaena. Southern right whales inhabit oceans south of the Equator, between the latitudes of 20° and 60° south. In 2009 the global population was estimated to be approximately 13,600.

The North Atlantic right whale is a baleen whale, one of three right whale species belonging to the genus Eubalaena, all of which were formerly classified as a single species. Because of their docile nature, their slow surface-skimming feeding behaviors, their tendencies to stay close to the coast, and their high blubber content, right whales were once a preferred target for whalers. At present, they are among the most endangered whales in the world, and they are protected under the U.S. Endangered Species Act and Marine Mammal Protection Act and Canada's Species at Risk Act. There are around 356 individuals in existence in the western North Atlantic Ocean—they migrate between feeding grounds in the Labrador Sea and their winter calving areas off Georgia and Florida, an ocean area with heavy shipping traffic. In the eastern North Atlantic, on the other hand—with a total population reaching into the low teens at most—scientists believe that they may already be functionally extinct. Vessel strikes and entanglement in fixed fishing gear, which together account for nearly half of all North Atlantic right whale mortality since 1970, are their two greatest threats to recovery.

The North Pacific right whale is a very large, thickset baleen whale species that is extremely rare and endangered.
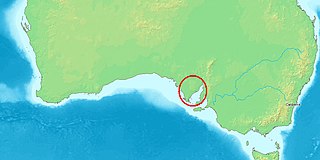
The Spencer Gulf is the westernmost and larger of two large inlets on the southern coast of Australia, in the state of South Australia, facing the Great Australian Bight. It spans from the Cape Catastrophe and Eyre Peninsula in the west to Cape Spencer and Yorke Peninsula in the east.

The Nuyts Archipelago is an island group located in South Australia in the Great Australian Bight to the south of the town of Ceduna on the west coast of the Eyre Peninsula. It consisting of mostly granitic islands and reefs that provide breeding sites for Australian sea lions and support colonies of short-tailed shearwater. It also includes the island group known as the Isles of St Francis. All the islands with exception of a part of Evans Island, are located within the following protected areas: the Nuyts Archipelago Wilderness Protection Area and the Nuyts Archipelago Conservation Park.

Whale watching in Australia is a popular recreational pursuit and a tourist activity along various coasts. In 2008, whale and dolphin watching was worth an estimated A$31 million in direct expenditure to the Australian economy with an estimated 1.6 million tourists participating in the activity. Humpback whales are the most common species seen in the waters surrounding Australia while southern right whales, minke whales and blue whales are also seen.

Whale watching in New Zealand is predominantly centred around the areas of Kaikōura and the Hauraki Gulf. Known as the 'whale capital', Kaikōura is a world-famous whale watching site, in particular for sperm whales which is currently the most abundant of large whales in New Zealand waters. The Hauraki Gulf Marine Park is also a significant whale watching area with a resident population of Bryde's Whales commonly viewed alongside other cetaceans Common Dolphins, Bottlenose Dolphins and Orca. Whale watching is also offered in other locations, often as eco-tours and in conjunction with dolphin watching. Land-based whale watching from New Zealand's last whaling station, which closed in 1964, is undertaken for scientific purposes, mostly by ex-whalers.

Great Australian Bight Marine National Park is a marine protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located 918 km (570 mi) west of the state capital of Adelaide.
In South Australia, one of the states of Australia, there are many areas which are commonly known by regional names. Regions are areas that share similar characteristics. These characteristics may be natural such as the Murray River, the coastline, desert or mountains. Alternatively, the characteristics may be cultural, such as common land use. South Australia is divided by numerous sets of regional boundaries, based on different characteristics. In many cases boundaries defined by different agencies are coterminous.

Great Australian Bight Marine Park is a marine protected area located in the Great Australian Bight south of South Australia in waters within the Australian Exclusive economic zone.

Great Australian Bight Marine Park Whale Sanctuary was a marine protected area in the Australian state of South Australia located immediately off the coastline of the Great Australian Bight in waters about 790 km (491 mi) west-northwest of the state capital of Adelaide.
Dudley West is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of Dudley Peninsula on Kangaroo Island overlooking the body of water known in Australia as the Southern Ocean and by international authorities as the Great Australian Bight. It is located about 107 kilometres south of the Adelaide city centre and about 11 kilometres south-west of Penneshaw.
D’Estrees Bay is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of Kangaroo Island overlooking the body of water known in Australia as the Southern Ocean and by international authorities as the Great Australian Bight. It is located about 145 kilometres southwest of the state capital of Adelaide and about 32 kilometres south of the municipal seat of Kingscote.

MacGillivray is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of Kangaroo Island overlooking the body of water known in Australia as the Southern Ocean and by international authorities as the Great Australian Bight. It is located about 140 kilometres southwest of the state capital of Adelaide and about 24 kilometres south of the municipal seat of Kingscote.

Seal Bay is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of Kangaroo Island overlooking the body of water known in Australia as the Southern Ocean and by international authorities as the Great Australian Bight. It is located about 164 kilometres southwest of the state capital of Adelaide and about 50 kilometres south of the municipal seat of Kingscote.
Haines is a locality in the Australian state of South Australia located on the south coast of Kangaroo Island overlooking the body of water known in Australia as the Southern Ocean and by international authorities as the Great Australian Bight. It is located about 129 kilometres south-west of the state capital of Adelaide and about 17 kilometres south of the municipal seat of Kingscote.
















