Related Research Articles

The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states.

Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, are a number of conditions caused by hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermatitis, allergic asthma, and anaphylaxis. Symptoms may include red eyes, an itchy rash, sneezing, a runny nose, shortness of breath, or swelling. Food intolerances and food poisoning are separate conditions.

Mokutarō Kinoshita was the pen-name of a Japanese author, dramaturge, poet, art historian and literary critic, as well as a licensed doctor specializing in dermatology during Taishō and early Shōwa period Japan. His other pen names included Horikason (堀花村), Chikaisshakusei (地下一尺生), Sounan (葱南) and others. As professor of dermatology and a noted leprosy researcher, he served at four universities.
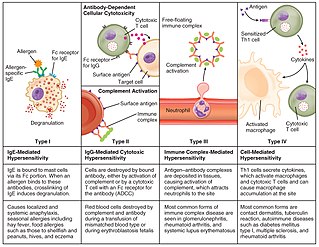
Hypersensitivity refers to undesirable reactions produced by the normal immune system, including allergies and autoimmunity. They are usually referred to as an over-reaction of the immune system and these reactions may be damaging and uncomfortable. This is an immunologic term and is not to be confused with the psychiatric term of being hypersensitive which implies to an individual who may be overly sensitive to physical and/or emotional stimuli. Although there is a relation between the two - studies have shown that those individuals that have ADHD are more likely to have hypersensitivity reactions such as allergies, asthma, eczema than those who do not have ADHD.

Mycobacterium leprae is a bacterium that causes leprosy, also known as "Hansen’s disease", which is a chronic infectious disease that damages the peripheral nerves and targets the skin, eyes, nose, and muscles. Leprosy can occur at all ages from infancy to elderly, but is curable in which treatments can avert disabilities. It was discovered in 1873 by the Norwegian physician Gerhard Armauer Hansen, who was searching for the bacteria in the skin nodules of patients with leprosy. It was the first bacterium to be identified as causing disease in humans.
The lepromin skin test is used to determine what type of leprosy a person is infected with. It involves the injection of a standardized extract of the inactivated "leprosy bacillus" under the skin. It is not recommended as a primary mode of diagnosis.

A patch test is a diagnostic method used to determine which specific substances cause allergic inflammation of a patient's skin.
Skin allergy testing comprises a range of methods for medical diagnosis of allergies that attempts to provoke a small, controlled, allergic response.

Sporothrix schenckii, a fungus that can be found worldwide in the environment, is named for medical student Benjamin Schenck who in 1896 was the first to isolate it from a human specimen. The species is present in soil as well as in and on living and decomposing plant material such as peat moss. It can infect humans as well as animals and is the causative agent of sporotrichosis, commonly known as "rose handler's disease." The most common route of infection is the introduction of spores to the body through a cut or puncture wound in the skin. Infection commonly occurs in otherwise healthy individuals but is rarely life-threatening and can be treated with antifungals. In the environment it is found growing as filamentous hyphae. In host tissue it is found as a yeast. The transition between the hyphal and yeast forms is temperature dependent making S. schenckii a thermally dimorphic fungus.

Solar urticaria (SU) is a rare condition in which exposure to ultraviolet or UV radiation, or sometimes even visible light, induces a case of urticaria or hives that can appear in both covered and uncovered areas of the skin. It is classified as a type of physical urticaria. The classification of disease types is somewhat controversial. One classification system distinguished various types of SU based on the wavelength of the radiation that causes the breakout; another classification system is based on the type of allergen that initiates a breakout.
HLA-DR2 (DR2) of the HLA-DR serotype system, is a broad antigen serotype that is now preferentially covered by HLA-DR15 and HLA-DR16 serotype group. This serotype primarily recognizes gene products of the HLA-DRB1*15 and HLA-DRB1*16 allele groups.
A leprostatic agent is a drug that interferes with proliferation of the bacterium that causes leprosy.

Lepromatous leprosy is a form of leprosy characterized by pale macules in the skin.
William Jopling was an Italian-born British leprologist who together with D. S. Ridley proposed the Ridley-Jopling classification of leprosy (1962), and wrote the widely read textbook of "Handbook of Leprosy" which had a fifth edition. He had a wide understanding of leprosy problems based on his experiences as the director of Jordan hospital, a leprosy hospital (1950–1967) in England and wrote various articles including "leprosy stigma".

Kensuke Mitsuda was a Japanese leprologist and director of the Tama Zenshoen Sanatorium (1914–1931) and the National Sanatorium Nagashima Aiseien (1931–1957). He had been at the frontier of leprosy policy of Japan. He was given the Order of Cultural Merits (1951) and Damien-Dutton Award (1961). He has been the cause of admiration from one side, and the target of criticism from the other.
As of 2009, 2,600 former leprosy patients were living in 13 national sanatoriums and 2 private hospitals in Japan. Their mean age is 80. There were no newly diagnosed Japanese leprosy patients in 2005, but one in 2006, and one in 2007.
Mosuke Murata was a Japanese dermatologist and was the designator of erythema nodosum leprosum (ENL)(1912), the type 2 lepra reaction.
Fumio Hayashi was a Japanese physician and leprologist. He worked in Tama Zenshoen Sanatorium, Nagashima Aiseien Sanatorium, Hoshizuka Keiaien Sanatorium and Ooshima Seishoen Sanatorium. He helped with Kensuke Mitsuda, and completed the first lepromin test or Mitsuda skin test.
The Prausnitz–Küstner test is an immunologic test formerly used by physicians to determine if a patient has an allergic reaction to a specific antigen. The test has been replaced by the safer skin prick test. The PK test involves transferring serum from the test subject to another healthy person, essentially using the second person as a mixing vessel for antibodies and antigen. This is a pathway for transmission of blood-borne ailments like variant Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease, AIDS, and others, which is why the test is no longer recommended. Or in simple words, a test for the presence of immediate hypersensitivity in humans; test serum from an atopic individual is injected intradermally into a normal subject; the normal subject is challenged 24–48 hours later with the antigen suspected of causing the immediate hypersensitivity reaction in the atopic individual.
The Dharmendra antigen is a test widely used in India. The antigen is a suspension of de-fatted leprosy bacilli which has been extracted with chloroform-ether and killed, either by heat, or by other effective methods. This antigen was first reported by Dharmendra in 1941–42 and later standardized in 1979 by Sangupta et al.
References
- ↑ Arruda, MS; Arruda, OS; Astolfi, CS; Opromolla, DV (1985). "Fernandez and Mitsuda reactions in patients with leprosy and their contacts". Hanseonologia Internationalis. 10 (1).
- ↑ Thomas J, Joseph M, Ramanujam K, Chacko CJ, Job CK. Histology of the Fernandez reaction. An appraisal. Int J Lepr Other Mycobact Dis. 1981 Mar;49(1):1-8. PMID 7195878.