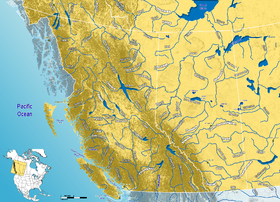
The Athabasca River is a river in Alberta, Canada, which originates at the Columbia Icefield in Jasper National Park and flows more than 1,231 km (765 mi) before emptying into Lake Athabasca. Much of the land along its banks is protected in national and provincial parks, and the river is designated a Canadian Heritage River for its historical and cultural importance. The scenic Athabasca Falls is located about 30 km (19 mi) upstream from Jasper.

Oil sands, tar sands, crude bitumen, or bituminous sands, are a type of unconventional petroleum deposit. Oil sands are either loose sands or partially consolidated sandstone containing a naturally occurring mixture of sand, clay, and water, soaked with bitumen, a dense and extremely viscous form of petroleum.

Fort McMurray is an urban service area in the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo in Alberta, Canada. It is located in northeast Alberta, in the middle of the Athabasca oil sands, surrounded by boreal forest. It has played a significant role in the development of the national petroleum industry. The 2016 Fort McMurray wildfire led to the evacuation of its residents and caused widespread damage.

The Athabasca oil sands, also known as the Athabasca tar sands, are large deposits of bitumen or extremely heavy crude oil that constitute unconventional resources, located in northeastern Alberta, Canada – roughly centred on the boomtown of Fort McMurray. These oil sands, hosted primarily in the McMurray Formation, consist of a mixture of crude bitumen, silica sand, clay minerals, and water. The Athabasca deposit is the largest known reservoir of crude bitumen in the world and the largest of three major oil sands deposits in Alberta, along with the nearby Peace River and Cold Lake deposits.

Lake Athabasca is in the north-west corner of Saskatchewan and the north-east corner of Alberta between 58° and 60° N in Canada. The lake is 26% in Alberta and 74% in Saskatchewan.

The Peace River is a 1,923-kilometre-long (1,195 mi) river in Canada that originates in the Rocky Mountains of northern British Columbia and flows to the northeast through northern Alberta. The Peace River joins the Athabasca River in the Peace-Athabasca Delta to form the Slave River, a tributary of the Mackenzie River. The Finlay River, the main headwater of the Peace River, is regarded as the ultimate source of the Mackenzie River. The combined Finlay–Peace–Slave–Mackenzie river system is the 13th longest river system in the world.
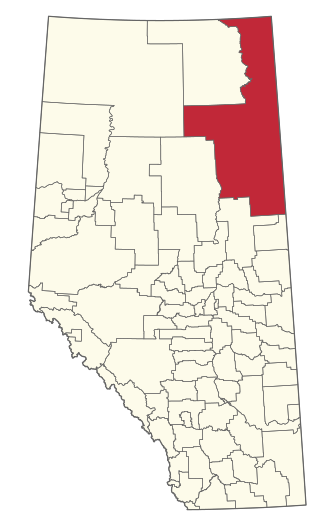
The Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo is a specialized municipality in northeast Alberta, Canada. It is the second largest municipality in Alberta by area and is home to oil sand deposits known as the Athabasca oil sands.

The Clearwater River is located in the Canadian provinces of Saskatchewan and Alberta. It rises in the northern forest region of north-western Saskatchewan and joins the Athabasca River in north-eastern Alberta. It was part of an important trade route during the fur trade era and has been designated as a Canadian Heritage River.
Syncrude Canada Ltd. is one of the world's largest producers of synthetic crude oil from oil sands and the largest single source producer in Canada. It is located just outside Fort McMurray in the Athabasca Oil Sands, and has a nameplate capacity of 350,000 barrels per day (56,000 m3/d) of oil, equivalent to about 13% of Canada's consumption. It has approximately 5.1 billion barrels (810,000,000 m3) of proven and probable reserves situated on 8 leases over 3 contiguous sites. Including fully realized prospective reserves, current production capacity could be sustained for well over 90 years.

Canada's oil sands and heavy oil resources are among the world's great petroleum deposits. They include the vast oil sands of northern Alberta, and the heavy oil reservoirs that surround the small city of Lloydminster, which sits on the border between Alberta and Saskatchewan. The extent of these resources is well known, but better technologies to produce oil from them are still being developed.

Northern Alberta is a geographic region located in the Canadian province of Alberta.

The Fort McKay First Nation (FMFN) is a First Nations government in northeast Alberta comprising five Indian reserves – Fort McKay 174, Fort McKay 174C, Fort McKay 174D, Namur Lake 174B and Namur River 174A. The FMFN, signed to Treaty 8, is affiliated with the Athabasca Tribal Council and its members are of Cree, Metis and Dene heritage. The FMFN's traditional lands include portions of the Athabasca oil sands.
The Shell Scotford Upgrader is an oilsand upgrader, a facility which processes crude bitumen from oil sands into a wide range of synthetic crude oils. The upgrader is owned by Athabasca Oil Sands Project (AOSP), a joint venture of Shell Canada Energy (60%), Marathon Oil Sands L.P. (20%) and Chevron Canada Limited (20%). The facility is located in the industrial development of Scotford, just to the northeast of Fort Saskatchewan, Alberta in the Edmonton Capital Region.

Albian Sands Energy Inc. is the operator of the Muskeg River Mine and Jack Pine Mine, an oil sands mining project located 75 kilometres (47 mi) north of Fort McMurray, Alberta, Canada. It is a joint venture between Shell Canada (10%), CNRL (70%) and Chevron Canada (20%). The company's legal headquarters are located in the Shell Centre in Calgary, Alberta. Albian Sands got its name from the Albian Boreal Sea which, during the Albian stage of the Cretaceous, moved over the McMurray sands and deposited a blanket of marine shale on its floor which trapped the hydrocarbons of the McMurray Formation. The oil sands resources of the Muskeg River Mine are a legacy of the Albian Sea.
The Clearwater Formation is a stratigraphic unit of Early Cretaceous (Albian) age in the Western Canada Sedimentary Basin in northeastern Alberta, Canada. It was first defined by R.G. McConnell in 1893 and takes its name from the Clearwater River near Fort McMurray.

The Long Lake oil sands upgrader project is an in situ oil extraction project near Anzac, Alberta, 40 km (25 mi) southeast of Fort McMurray in the Athabasca oil sands region of Alberta.

The Cold Lake oil sands are a large deposit of oil sands located near Cold Lake, Alberta. Cold Lake is east of Alberta's capital, Edmonton, near Alberta's border with Saskatchewan, and a small portion of the Cold Lake field lies in Saskatchewan.

Oil sands tailings ponds are engineered dam and dyke systems used to capture oil sand tailings. Oil sand tailings contain a mixture of salts, suspended solids and other dissolvable chemical compounds such as acids, benzene, hydrocarbons residual bitumen, fine silts and water. Large volumes of tailings are a byproduct of bitumen extraction from the oil sands and managing these tailings is one of the most difficult environmental challenges facing the oil sands industry. An October 2021 Alberta Energy Regulator (AER) report said that in 2020 the tailings ponds increased by another 90 million cubic meters and contained 1.36 billion cubic metres of fluids.
Marguerite River Wildland Provincial Park is a wildland provincial park in Wood Buffalo, northern Alberta, Canada. The park was established on 20 December 2000 and has an area of 196,301.9 hectares (757.9 sq mi). The park is part of the Lower Athabasca Regional Plan. The park was named for the Marguerite River that flows thru the park and forms a portion of the park's western boundary. The park was originally created in 1998 as Marguerite Crag and Tail Wildland Provincial Park. It was reformed and renamed in 2000.
Winagami Wildland Provincial Park is a wildland provincial park in northern Alberta, Canada. The park was established on 26 August 1998 and has an area of 17,439.886 hectares. The park is included in the Upper Athabasca Region Land Use Framework. The park is named for Winagami Lake that is adjacent to the park.