Diquat is the ISO common name for an organic dication that, as a salt with counterions such as bromide or chloride is used as a contact herbicide that produces desiccation and defoliation. Diquat is no longer approved for use in the European Union, although its registration in many other countries including the USA is still valid.

Picloram is a systemic herbicide used for general woody plant control. It also controls a wide range of broad-leaved weeds, but most grasses are resistant. A chlorinated derivative of picolinic acid, picloram is in the pyridine family of herbicides.

Glufosinate is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum herbicide produced by several species of Streptomyces soil bacteria. Glufosinate is a non-selective, contact herbicide, with some systemic action. Plants may also metabolize bialaphos, another naturally occurring herbicide, directly into glufosinate. The compound irreversibly inhibits glutamine synthetase, an enzyme necessary for the production of glutamine and for ammonia detoxification, giving it antibacterial, antifungal and herbicidal properties. Application of glufosinate to plants leads to reduced glutamine and elevated ammonia levels in tissues, halting photosynthesis and resulting in plant death.

Pendimethalin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class used in premergence and postemergence applications to control annual grasses and certain broadleaf weeds. It inhibits cell division and cell elongation. Pendimethalin is listed in the K1-group according to the Herbicide Resistance Action Committee (HRAC) classification and is approved in Europe, North America, South America, Africa, Asia and Oceania for different crops including cereals, corn, soybeans, rice, potato, legumes, fruits, vegetables, nuts as well as lawns and ornamental plants.

Mecoprop is a common general use herbicide found in many household weed killers and "weed-and-feed" type lawn fertilizers. It is primarily used to control broadleaf weeds. It is often used in combination with other chemically related herbicides such as 2,4-D, dicamba, and MCPA.
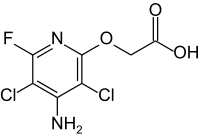
Sulfentrazone is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as a broad-spectrum herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase. It was first marketed in the US in 1997 by FMC Corporation with the brand name Authority.

MCPB, 2,4-MCPB, 4-(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)butyric acid (IUPAC), or 4-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)butanoic acid (CAS) is a phenoxybutyric herbicide. In the United States it is registered for use on pea crops before flowering, for post-emergence control of broadleaf annual and perennial weeds including Canadian thistle, buttercup, mustard, purslane, ragweed, common lambsquarters, pigweed, smartweed, sowthistle, and morning glory. It has low to moderate acute toxicity, with kidney and liver effects as the main hazard concerns. It is not volatile, persistent, or likely to bioconcentrate.

Fluvalinate is a synthetic pyrethroid chemical compound contained as an active agent in the products Apistan, Klartan, and Minadox, that is an acaricide, commonly used to control Varroa mites in honey bee colonies, infestations that constitute a significant disease of such insects.

Oryzalin is an herbicide of the dinitroaniline class. It acts through the disruption (depolymerization) of microtubules, thus blocking anisotropic growth of plant cells. It can also be used to induce polyploidy in plants as an alternative to colchicine.

Propachlor (2-chloro-N-isopropylacetanilide) is an herbicide first marketed by Monsanto. It was registered for use in the United States during 1965.

Monolinuron is a pesticide, more specifically a selective systemic herbicide and an algaecide. As an herbicide, it is used to control broad-leaved weeds and annual grasses in vegetable crops such as leeks, potatoes, and dwarf French beans. Monolinuron affects the photosynthesis in weeds. Following uptake of monolinuron through roots and leaves of weeds, monolinuron causes early symptoms of yellowing and die-back of the leaves, eventually resulting in weed death. In fishkeeping it is used to control blanketweed and hair algae.
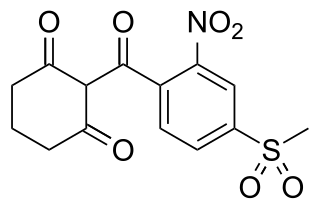
Mesotrione is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a selective herbicide, especially in maize. It inhibits the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) and is sold under brand names including Callisto and Tenacity. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2001.
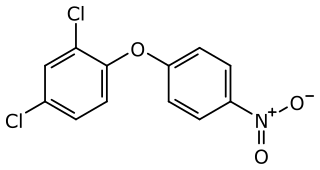
Nitrofen is an herbicide of the diphenyl ether class. Because of concerns about its carcinogenicity, the use of nitrofen has been banned in the European Union and in the United States since 1996. It has been superseded by related protoporphyrinogen oxidase enzyme inhibitors including acifluorfen and fomesafen.

Oxamyl is a chemical used as a pesticide that comes in two forms: granulated and liquid. The granulated form has been banned in the United States. It is commonly sold under the trade name Vydate.

Metribuzin is an herbicide used both pre- and post-emergence in crops including soy bean, potatoes, tomatoes and sugar cane. It acts by inhibiting photosynthesis by disrupting photosystem II. It is widely used in agriculture and has been found to contaminate groundwater.
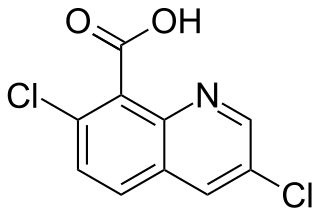
Quinclorac is a selective herbicide used primarily to control weeds in rice crops, but is also used on other agricultural crops and is found in some household herbicides for lawn use. Most lawn maintenance companies use the product for the control of annual grass weeds like crabgrass.

Prothoate is an organothiophosphate insecticide also used as an acaricide.
Hydroprene is an insect growth regulator used as an insecticide. It is used against cockroaches, beetles, and moths. Products using hydroprene include Gencor, Gentrol, and Raid Max Sterilizer Discs. Hydropene is a synthetic juvenile hormone mimic, disrupting insect larval development like molting.
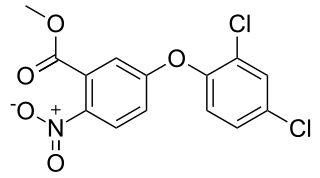
Bifenox is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase which is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis.

Isoxaben is an herbicide from the benzamide and isoxazole family.