
Herbicides, also commonly known as weed killers, are substances used to control undesired plants, also known as weeds. Selective herbicides control specific weed species while leaving the desired crop relatively unharmed, while non-selective herbicides can be used to clear waste ground, industrial and construction sites, railways and railway embankments as they kill all plant material with which they come into contact. Apart from selective/non-selective, other important distinctions include persistence, means of uptake, and mechanism of action. Historically, products such as common salt and other metal salts were used as herbicides, however, these have gradually fallen out of favor, and in some countries, a number of these are banned due to their persistence in soil, and toxicity and groundwater contamination concerns. Herbicides have also been used in warfare and conflict.

Triclopyr is an organic compound in the pyridine group that is used as a systemic foliar herbicide and fungicide.

MCPA is a widely used phenoxy herbicide introduced in 1945. It selectively controls broad-leaf weeds in pasture and cereal crops. The mode of action of MCPA is as an auxin, which are growth hormones that naturally exist in plants.

Hexazinone is an organic compound that is used as a broad spectrum herbicide. It is a colorless solid. It exhibits some solubility in water but is highly soluble in most organic solvents except alkanes. A member of the triazine class herbicides, it is manufactured by DuPont and sold under the trade name Velpar.

Picloram is a systemic herbicide used for general woody plant control. It also controls a wide range of broad-leaved weeds, but most grasses are resistant. A chlorinated derivative of picolinic acid, picloram is in the pyridine family of herbicides.

Phenoxy herbicides are two families of chemicals that have been developed as commercially important herbicides, widely used in agriculture. They share the part structure of phenoxyacetic acid.

Glufosinate is a naturally occurring broad-spectrum herbicide produced by several species of Streptomyces soil bacteria. Glufosinate is a non-selective, contact herbicide, with some systemic action. Plants may also metabolize bialaphos and phosalacine, other naturally occurring herbicides, directly into glufosinate. The compound irreversibly inhibits glutamine synthetase, an enzyme necessary for the production of glutamine and for ammonia detoxification, giving it antibacterial, antifungal and herbicidal properties. Application of glufosinate to plants leads to reduced glutamine and elevated ammonia levels in tissues, halting photosynthesis and resulting in plant death.
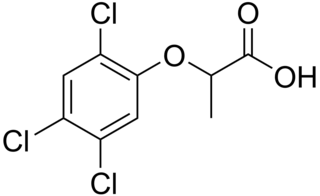
Fenoprop, also called 2,4,5-TP, is the organic compound 2-(2,4,5-trichlorophenoxy)propionic acid. It is a phenoxy herbicide and a plant growth regulator, an analog of 2,4,5-T in which the latter's acetic acid sidechain is replaced with a propionate group (with an extra CH3). The addition of this extra methyl group creates a chiral centre in the molecule and useful biological activity is found only in the (2R)-isomer. The compound's mechanism of action is to mimic the auxin growth hormone indoleacetic acid (IAA). When sprayed on plants it induces rapid, uncontrolled growth. As with 2,4,5-T, fenoprop is toxic to shrubs and trees.
Sulfentrazone is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as a broad-spectrum herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase. It was first marketed in the US in 1997 by FMC Corporation with the brand name Authority.

Bromoxynil is an organic compound with the formula HOBr2C6H2CN. It is classified as a nitrile herbicide, and as such sold under many trade names. It is a white solid. It works by inhibiting photosynthesis. It is moderately toxic to mammals.

MCPB, 2,4-MCPB, 4-(4-chloro-o-tolyloxy)butyric acid (IUPAC), or 4-(4-chloro-2-methylphenoxy)butanoic acid (CAS) is a phenoxybutyric herbicide. In the United States it is registered for use on pea crops before flowering, for post-emergence control of broadleaf annual and perennial weeds including Canadian thistle, buttercup, mustard, purslane, ragweed, common lambsquarters, pigweed, smartweed, sowthistle, and morning glory. It has low to moderate acute toxicity, with kidney and liver effects as the main hazard concerns. It is not volatile, persistent, or likely to bioconcentrate.
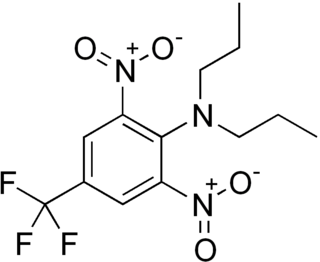
Trifluralin is a commonly used pre-emergence herbicide. With about 14 million pounds (6,400 t) used in the United States in 2001, it is one of the most widely used herbicides. Trifluralin is generally applied to the soil to provide control of a variety of annual grass and broadleaf weed species. It inhibits root development by interrupting mitosis, and thus can control weeds as they germinate.

Monolinuron is a pesticide, more specifically a selective systemic herbicide and an algaecide. As an herbicide, it is used to control broad-leaved weeds and annual grasses in vegetable crops such as leeks, potatoes, and dwarf French beans. Monolinuron affects the photosynthesis in weeds. Following uptake of monolinuron through roots and leaves of weeds, monolinuron causes early symptoms of yellowing and die-back of the leaves, eventually resulting in weed death. In fishkeeping, it is used to control blanket weed and hair algae.

Lactofen is a complex ester of acifluorfen and is a nitrophenyl ether selective herbicide and fungicide. It is used in postemergence applications to certain crops which are resistant to its action. The name "Lactofen" is approved by the American National Standards Institute and the Weed Science Society of America, and is also approved in China (乳氟禾草灵).
Mesotrione is the ISO common name for an organic compound that is used as a selective herbicide, especially in maize. A synthetic inspired by the natural substance leptospermone, it inhibits the enzyme 4-hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase (HPPD) and is sold under brand names including Callisto and Tenacity. It was first marketed by Syngenta in 2001.

2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid is an organic compound with the chemical formula C8H6Cl2O3 which is usually referred to by its ISO common name 2,4-D. It is a systemic herbicide which kills most broadleaf weeds by causing uncontrolled growth in them but most grasses such as cereals, lawn turf, and grassland are relatively unaffected.

Fluroxypyr is an herbicide in the class of synthetic auxins. It is used to control broadleaf weeds and woody brush. It is formulated as the 1-methylheptyl ester (fluroxypyr-MHE).
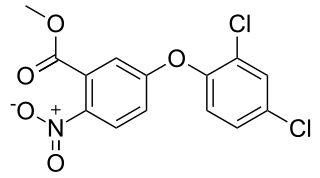
Bifenox is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase which is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis.

Cyanazine is a herbicide that belongs to the group of triazines. Cyanazine inhibits photosynthesis and is therefore used as a herbicide.

Fomesafen is the ISO common name for an organic compound used as an herbicide. It acts by inhibiting the enzyme protoporphyrinogen oxidase (PPO) which is necessary for chlorophyll synthesis. Soybeans naturally have a high tolerance to fomesafen, via metabolic disposal by glutathione S-transferase. As a result, soy is the most common crop treated with fomesafen, followed by other beans and a few other crop types. It is not safe for maize/corn or other Poaceae.






















