
Devon is a ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by the Bristol Channel to the north, Somerset and Dorset to the east, the English Channel to the south, and Cornwall to the west. The city of Plymouth is the largest settlement, and the city of Exeter is the county town.

The Quantock Hills west of Bridgwater in Somerset, England, consist of heathland, oak woodlands, ancient parklands and agricultural land. They were England's first Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty, designated in 1956.

Exmoor is loosely defined as an area of hilly open moorland in west Somerset and north Devon in South West England. It is named after the River Exe, the source of which is situated in the centre of the area, two miles north-west of Simonsbath. Exmoor is more precisely defined as the area of the former ancient royal hunting forest, also called Exmoor, which was officially surveyed 1815–1818 as 18,810 acres (7,610 ha) in extent. The moor has given its name to a National Park, which includes the Brendon Hills, the East Lyn Valley, the Vale of Porlock and 55 km (34 mi) of the Bristol Channel coast. The total area of the Exmoor National Park is 692.8 km2 (267.5 sq mi), of which 71% is in Somerset and 29% in Devon.

Porlock is a coastal village in Somerset, England, 5 miles (8 km) west of Minehead. At the 2011 census, the village had a population of 1,440.

Dunkery Beacon at the summit of Dunkery Hill is the highest point on Exmoor and in Somerset, England. It is also the highest point in southern England outside of Dartmoor.
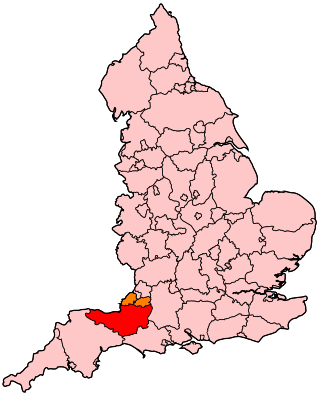
Somerset is a rural county in the southwest of England, covering 4,171 square kilometres (1,610 sq mi). It is bounded on the north-west by the Bristol Channel, on the north by Bristol and Gloucestershire, on the north-east by Wiltshire, on the south-east by Dorset, and on the south west and west by Devon. It has broad central plains with several ranges of low hills. The landscape divides into four main geological sections from the Silurian through the Devonian and Carboniferous to the Permian which influence the landscape, together with water-related features.

The River Barle runs from the Chains on northern Exmoor, in Somerset, England to join the River Exe at Exebridge, Devon. The river and the Barle Valley are both designated as biological Sites of Special Scientific Interest.

Holnicote in the parish of Selworthy, West Somerset, England, is a historic estate consisting of 12,420 acres of land, much situated within the Exmoor National Park.

Barle Valley is a 1,540 acres (620 ha) Site of Special Scientific Interest within Exmoor National Park, situated in the counties of Devon and Somerset through which the River Barle flows. It was notified in its current form under the Wildlife and Countryside Act in 1988. The site includes the Somerset Wildlife Trust's Mounsey Wood Nature Reserve and the Knaplock and North Barton SSSI which has been notified since 1954.

North Exmoor is a 12,005.3-hectare (29,666-acre) biological Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Devon and Somerset, notified in 1954.

South Exmoor is a 3132.7 hectare biological Site of Special Scientific Interest in Devon and Somerset, England, notified in 1992.

Oare is a village and civil parish on Oare Water on Exmoor in the Somerset West and Taunton district of Somerset, England. It is located 6 miles (10 km) east of Lynton and the parish includes the hamlet of Oareford and the village of Culbone which contains its own tiny church.

Simonsbath is a small village high on Exmoor in the English county of Somerset. It is the principal settlement in the Exmoor civil parish, which is the largest and most sparsely populated civil parish on Exmoor, covering nearly 32 square miles (83 km2) but with a population, at the time of the 2001 census, of 203 in 78 households, reducing to 156 at the 2011 census. The River Exe rises from a valley to the north, and the River Barle runs through the village and is crossed by a triple-arched medieval bridge that was extensively repaired after floods in 1952.

Hangman cliffs, consisting of Great Hangman and Little Hangman, are near Combe Martin on the north coast of Devon, England, where Exmoor meets the sea.
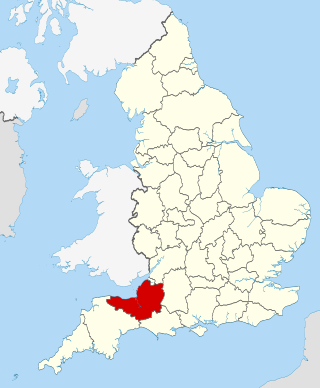
The county of Somerset is in South West England, bordered by the Bristol Channel and the counties of Bristol and Gloucestershire to the north, and Wiltshire to the east, Dorset to the south, and Devon to the west. The climate, influenced by its proximity to the Atlantic Ocean and the prevailing westerly winds, tends to be mild, damp and windy.

The Culbone Stone, an early mediaeval standing stone, is close to Culbone in the English county of Somerset. The stone is made from Hangman grit, a local sandstone, and has a wheeled ring cross carved into it. The stone has been scheduled as an ancient monument.

The Exmoor Group is a late Devonian to early Carboniferous lithostratigraphic group in southwest England whose outcrop extends from Croyde in north Devon east across Exmoor to Minehead in west Somerset. The group comprises the following formations :
The geology of Exmoor National Park in south-west England contributes significantly to the character of Exmoor, a landscape which was designated as a national park in 1954. The bedrock of the area consists almost wholly of a suite of sedimentary rocks deposited during the Devonian, a period named for the English county of Devon in which the western half of the park sits. The eastern part lies within Somerset and it is within this part of the park that limited outcrops of Triassic and Jurassic age rocks are to be found.

















