This article needs additional citations for verification .(May 2024) |
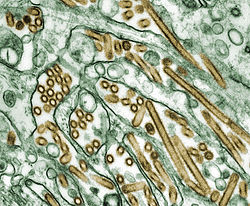 |
The global spread of (highly pathogenic) H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat.
Contents
While prior H5N1 strains have been known, they were significantly different from the current H5N1 strain on a genetic level, making the global spread of this new strain unprecedented. The current H5N1 strain is a fast-mutating, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAI) found in multiple bird species. It is both epizootic (an epidemic in non-humans) and panzootic (a disease affecting animals of many species especially over a wide area). Unless otherwise indicated, "H5N1" in this article refers to the recent highly pathogenic strain of H5N1.
H5N1 caused flu outbreaks in 1959 and in 1991 but these strains were very different from the current highly pathogenic strain of H5N1. Evolution from 1999 to 2002 created the Z genotype which became the dominant strain of highly pathogenic H5N1 in 2004.
In January 2004 a major new outbreak of H5N1 surfaced in Vietnam and Thailand's poultry industry, and within weeks spread to ten countries and regions in Asia, including Indonesia, South Korea, Japan and China. In October 2004 researchers discovered H5N1 is far more dangerous than previously believed because waterfowl were directly spreading the highly pathogenic strain of H5N1 to chickens, crows, pigeons, and other birds and that it was increasing its ability to infect mammals as well. From this point on, avian influenza experts increasingly refer to containment as a strategy that can delay but not prevent a future avian flu pandemic.
