 |
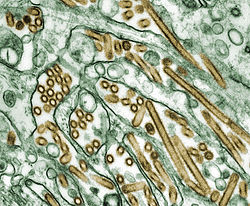
The global spread of (highly pathogenic) H5N1 in birds is considered a significant pandemic threat.
Contents
- January
- February
- March
- April
- May
- June
- July
- August
- September
- October
- November
- December
- See also
- References
While prior H5N1 strains have been known, they were significantly different from the current H5N1 strain on a genetic level, making the global spread of this new strain unprecedented. The current H5N1 strain is a fast-mutating, highly pathogenic avian influenza virus (HPAI) found in multiple bird species. It is both epizootic (an epidemic in non-humans) and panzootic (a disease affecting animals of many species especially over a wide area). Unless otherwise indicated, "H5N1" in this article refers to the recent highly pathogenic strain of H5N1.
In January 2005 an outbreak of avian influenza affected thirty three out of sixty four cities and provinces in Vietnam, leading to the forced killing of nearly 1.2 million poultry. Up to 140 million birds are believed to have died or been killed because of the outbreak. In April 2005 an unprecedented die-off began of over 6,000 migratory birds at Qinghai Lake in central China over three months. This strain of H5N1 is the same strain as is spread west by migratory birds over at least the next ten months. In August 2005 H5N1 spread to Kazakhstan, Mongolia and Russia. On September 30, 2005, David Nabarro, the newly appointed Senior United Nations System Coordinator for Avian and Human Influenza, warned the world that an outbreak of avian influenza could kill 5 to 150 million people. David Nabarro later stated that as the virus had spread to migratory birds, an outbreak could start in Africa or the Middle East. Later in 2005 H5N1 spread to Turkey, Romania, Croatia and Kuwait.
 Notes:
|
