
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP).

The mevalonate pathway, also known as the isoprenoid pathway or HMG-CoA reductase pathway is an essential metabolic pathway present in eukaryotes, archaea, and some bacteria. The pathway produces two five-carbon building blocks called isopentenyl pyrophosphate (IPP) and dimethylallyl pyrophosphate (DMAPP), which are used to make isoprenoids, a diverse class of over 30,000 biomolecules such as cholesterol, vitamin K, coenzyme Q10, and all steroid hormones.
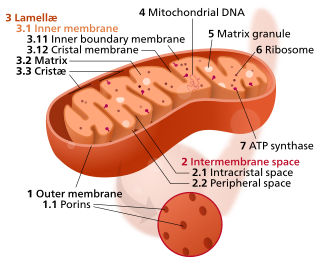
In the mitochondrion, the matrix is the space within the inner membrane. The word "matrix" stems from the fact that this space is viscous, compared to the relatively aqueous cytoplasm. The mitochondrial matrix contains the mitochondrial DNA, ribosomes, soluble enzymes, small organic molecules, nucleotide cofactors, and inorganic ions.[1] The enzymes in the matrix facilitate reactions responsible for the production of ATP, such as the citric acid cycle, oxidative phosphorylation, oxidation of pyruvate, and the beta oxidation of fatty acids.
The branched-chain α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex is a multi-subunit complex of enzymes that is found on the mitochondrial inner membrane. This enzyme complex catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of branched, short-chain alpha-ketoacids. BCKDC is a member of the mitochondrial α-ketoacid dehydrogenase complex family comprising pyruvate dehydrogenase and alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, key enzymes that function in the Krebs cycle.

ACADM is a gene that provides instructions for making an enzyme called acyl-coenzyme A dehydrogenase that is important for breaking down (degrading) a certain group of fats called medium-chain fatty acids.
Pyruvate dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the reaction of pyruvate and a lipoamide to give the acetylated dihydrolipoamide and carbon dioxide. The conversion requires the coenzyme thiamine pyrophosphate.

Glutaryl-CoA dehydrogenase (GCDH) is an enzyme encoded by the GCDH gene on chromosome 19. The protein belongs to the acyl-CoA dehydrogenase family (ACD). It catalyzes the oxidative decarboxylation of glutaryl-CoA to crotonyl-CoA and carbon dioxide in the degradative pathway of L-lysine, L-hydroxylysine, and L-tryptophan metabolism. It uses electron transfer flavoprotein as its electron acceptor. The enzyme exists in the mitochondrial matrix as a homotetramer of 45-kD subunits. Mutations in this gene result in the metabolic disorder glutaric aciduria type 1, which is also known as glutaric acidemia type I. Alternative splicing of this gene results in multiple transcript variants.

6-Phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (6PGD) is an enzyme in the pentose phosphate pathway. It forms ribulose 5-phosphate from 6-phosphogluconate:
In enzymology, a phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (decarboxylating) (EC 1.1.1.44) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.35) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-hydroxybutyryl-CoA dehydrogenase (EC 1.1.1.157) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, an isovaleryl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
In enzymology, a malonate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (acetylating) (EC 1.2.1.18) is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction

In enzymology, a 3-oxoacid CoA-transferase is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction
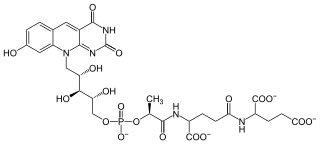
Coenzyme F420 or 8-hydroxy-5-deazaflavin is a coenzyme (sometimes called a cofactor) involved in redox reactions in methanogens, in many Actinomycetota, and sporadically in other bacterial lineages. It is a flavin derivative with an absorption maximum at 420 nm—hence its name. The coenzyme is a substrate for coenzyme F420 hydrogenase, 5,10-methylenetetrahydromethanopterin reductase and methylenetetrahydromethanopterin dehydrogenase.

Butyryl-coenzyme A is the coenzyme A-containing derivative of butyric acid. It is acted upon by butyryl-CoA dehydrogenase and an intermediary compound of ABE fermentation.
Glutaconyl-CoA is an intermediate in the metabolism of lysine. It is an organic compound containing a coenzyme substructure, which classifies it as a fatty ester lipid molecule. Being a lipid makes the molecule hydrophobic, which makes it insoluble in water. The molecule has a molecular formula of C26H40N7O19P3S, and a molecular weight 879.62 grams per mole.

Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme with systematic name short-chain acyl-CoA:electron-transfer flavoprotein 2,3-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction
Long-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase is an enzyme with systematic name long-chain acyl-CoA:electron-transfer flavoprotein 2,3-oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction

NADH:ubiquinone reductase (non-electrogenic) (EC 1.6.5.9, NDH-2, ubiquinone reductase, coenzyme Q reductase, dihydronicotinamide adenine dinucleotide-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-coenzyme Q reductase, DPNH-ubiquinone reductase, NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase, NADH-coenzyme Q reductase, NADH-CoQ oxidoreductase, NADH-CoQ reductase) is an enzyme with systematic name NADH:ubiquinone oxidoreductase. This enzyme catalyses the following chemical reaction:
















