
A passerine is any bird of the order Passeriformes which includes more than half of all bird species. Sometimes known as perching birds, passerines generally have an anisodactyl arrangement of their toes, which facilitates perching.

Charadriiformes is a diverse order of small to medium-large birds. It includes about 390 species and has members in all parts of the world. Most charadriiform birds live near water and eat invertebrates or other small animals; however, some are pelagic (seabirds), others frequent deserts, and a few are found in dense forest. Members of this group can also collectively be referred to as shorebirds.

The Anatidae are the biological family of water birds that includes ducks, geese, and swans. The family has a cosmopolitan distribution, occurring on all the world's continents except Antarctica. These birds are adapted for swimming, floating on the water surface, and in some cases diving in at least shallow water. The family contains around 174 species in 43 genera.

Rails are a large, cosmopolitan family of small- to medium-sized terrestrial and/or semi-amphibious birds. The family exhibits considerable diversity in its forms, and includes such ubiquitous species as the crakes, coots, and gallinule; other rail species are extremely rare or endangered. Many are associated with wetland habitats, some being semi-aquatic like waterfowl, but many more are wading birds or shorebirds. The ideal rail habitats are marsh areas, including rice paddies, and flooded fields or open forest. They are especially fond of dense vegetation for nesting. The rail family is found in every terrestrial habitat with the exception of dry desert, polar or freezing regions, and alpine areas. Members of Rallidae occur on every continent except Antarctica. Numerous unique island species are known.

Phalacrocoracidae is a family of approximately 40 species of aquatic birds commonly known as cormorants and shags. Several different classifications of the family have been proposed, but in 2021 the International Ornithologists' Union (IOU) adopted a consensus taxonomy of seven genera. The great cormorant and the common shag are the only two species of the family commonly encountered in Britain and Ireland and "cormorant" and "shag" appellations have been later assigned to different species in the family somewhat haphazardly.

The Anserinae are a subfamily in the waterfowl family Anatidae. It includes the swans and the true geese. Under alternative systematical concepts, it is split into two subfamilies, the Anserinae contain the geese and the ducks, while the Cygninae contain the swans.

The diving petrels form a genus, Pelecanoides, of seabirds in the family Procellariidae. There are four very similar species of diving petrels, distinguished only by small differences in the coloration of their plumage, habitat, and bill construction. They are only found in the southern hemisphere. The diving petrels were formerly placed in their own family, the Pelecanoididae.

Anas is a genus of dabbling ducks. It includes the pintails, most teals, and the mallard and its close relatives. It formerly included additional species but following the publication of a molecular phylogenetic study in 2009 the genus was split into four separate genera. The genus now contains 31 living species. The name Anas is the Latin for "duck".

The adzebills, genus Aptornis, were two closely related bird species, the North Island adzebill,, and the South Island adzebill,, of the extinct family Aptornithidae. The family was endemic to New Zealand. A tentative fossil species,, is known from the Miocene Saint Bathans fauna.

The great albatrosses are seabirds in the genus Diomedea in the albatross family. The genus Diomedea formerly included all albatrosses except the sooty albatrosses, but in 1996 the genus was split, with the mollymawks and the North Pacific albatrosses both being elevated to separate genera.

The Subantarctic snipe is a species of snipe endemic to New Zealand's subantarctic islands. The Maori call it "Tutukiwi". The nominate race C. a. aucklandica is found on the Auckland Islands. Other subspecies include C. a. meinertzhagenae from the Antipodes Islands, and C. a. perseverance from Campbell Island / Motu Ihupuku. The former subspecies from the Snares Islands has been separated as a full species, the Snares snipe, as have the extinct South Island and North Island snipes.

The austral snipes, also known as the New Zealand snipes or tutukiwi, are a genus, Coenocorypha, of tiny birds in the sandpiper family, which are now only found on New Zealand's outlying islands. There are currently three living species and six known extinct species, with the Subantarctic snipe having three subspecies, including the Campbell Island snipe discovered as recently as 1997. The genus was once distributed from Fiji, New Caledonia and Norfolk Island, across New Zealand and southwards into New Zealand's subantarctic islands, but predation by introduced species, especially rats, has drastically reduced their range.

The New Zealand parrot family, Strigopidae, consists of at least three genera of parrots – Nestor, Strigops, the fossil Nelepsittacus, and probably the fossil Heracles. The genus Nestor consists of the kea, kākā, Norfolk kākā and Chatham kākā, while the genus Strigops contains the iconic kākāpō. All extant species are endemic to New Zealand. The species of the genus Nelepsittacus were endemics of the main islands, while the two extinct species of the genus Nestor were found at the nearby oceanic islands such as Chatham Island of New Zealand, and Norfolk Island and adjacent Phillip Island.

The South Island snipe, also known as the Stewart Island snipe or tutukiwi in Māori, is an extinct species of bird in the sandpiper family Scolopacidae that was endemic to New Zealand.

The Antipodes snipe, also known as the Antipodes Island snipe, is an isolated subspecies of the Subantarctic snipe that is endemic to the Antipodes Islands, a subantarctic island group south of New Zealand in the Southern Ocean.
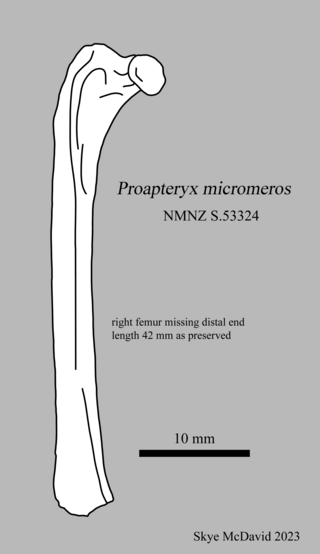
Proapteryx micromeros is an extinct kiwi known from the 16–19 million-year-old early Miocene sediments of the St Bathans Fauna of Otago, New Zealand.

The St Bathans fauna is found in the lower Bannockburn Formation of the Manuherikia Group of Central Otago, in the South Island of New Zealand. It comprises a suite of fossilised prehistoric animals from the late Early Miocene (Altonian) period, with an age range of 19–16 million years ago.
Miotadorna is a genus of extinct tadornine ducks from the Miocene of New Zealand. It contains two species, M. sanctibathansi, and M. catrionae.

The Manuherikia Group is a fluvial-lacustrine sedimentary fill in the Central Otago area of New Zealand, at the site of the prehistoric Lake Manuherikia. The area consists of a valley and ridge topography, with a series of schist-greywacke mountains at roughly ninety degrees to each other. The Manuherika Group occurs in the current basins, and occasionally on the mountains themselves.



















