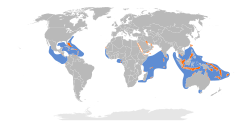
| Onychoprion | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Sooty tern Onychoprion fuscatus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Charadriiformes |
| Family: | Laridae |
| Subfamily: | Sterninae |
| Genus: | Onychoprion Wagler, 1832 |
| Type species | |
| Sterna serrata [1] | |
| Species | |
Onychoprion lunatus Contents | |
Onychoprion is a genus of four species of terns in the family Laridae. The genus name is from Ancient Greek onux, "claw" or "nail", and prion, "saw". [2] As a group, they have been variously called "brown-winged terns" [3] or "brown-backed terns", [4] though only one species is actually brown; the other three are dark grey or black.