Carinatae is the group of all birds and their extinct relatives to possess a keel, or "carina", on the underside of the breastbone used to anchor large flight muscles.

A ratite is any of a group of flightless birds within the infraclass Palaeognathae. They are mostly large, long-necked, and long-legged, the exception being the Kiwi, which is also the only nocturnal extant ratite.

Rails are a large, cosmopolitan family of small- to medium-sized terrestrial and/or semi-amphibious birds. The family exhibits considerable diversity in its forms, and includes such ubiquitous species as the crakes, coots, and gallinule; other rail species are extremely rare or endangered. Many are associated with wetland habitats, some being semi-aquatic like waterfowl, but many more are wading birds or shorebirds. The ideal rail habitats are marsh areas, including rice paddies, and flooded fields or open forest. They are especially fond of dense vegetation for nesting. The rail family is found in every terrestrial habitat with the exception of dry desert, polar or freezing regions, and alpine areas. Members of Rallidae occur on every continent except Antarctica. Numerous unique island species are known.

The Inaccessible Island rail is a small bird of the rail family, Rallidae. Endemic to Inaccessible Island in the Tristan Archipelago in the isolated south Atlantic, it is the smallest extant flightless bird in the world. The species was described by physician Percy Lowe in 1923 but had first come to the attention of scientists 50 years earlier. The Inaccessible Island rail's affinities and origin were a long-standing mystery; in 2018 its closest relative was identified as the South American dot-winged crake, and it was proposed that both species should be nested within the genus Laterallus.

Moorhens—sometimes called marsh hens—are medium-sized water birds that are members of the rail family (Rallidae). Most species are placed in the genus Gallinula, Latin for "little hen". They are close relatives of coots. They are often referred to as (black) gallinules. Recently, one of the species of Gallinula was found to have enough differences to form a new genus Paragallinula with the only species being the lesser moorhen.

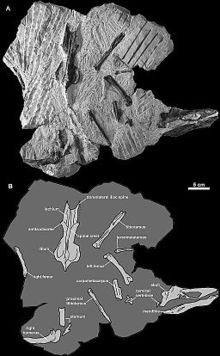
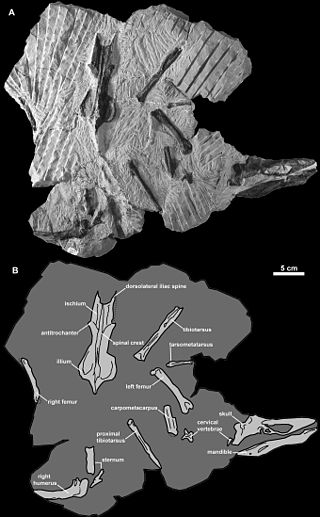
Caudipteryx is a genus of peacock-sized theropod dinosaurs that lived in the Barremian age of the early Cretaceous. They were feathered and extremely birdlike in their overall appearance, to the point that some paleontologists think it was a bird. Two species have been described: C. zoui, in 1998, and C. dongi, in 2000.

Flightless birds are birds that, through evolution, lost the ability to fly. There are over 60 extant species, including the well-known ratites and penguins. The smallest flightless bird is the Inaccessible Island rail. The largest flightless bird, which is also the largest living bird in general, is the ostrich.

The flightless cormorant, also known as the Galapagos cormorant, is a cormorant endemic to the Galapagos Islands, and an example of the highly unusual fauna there. It is unique in that it is the only known cormorant that has lost the ability to fly. It was placed in its own genus, Nannopterum, but then was later placed with most of the other cormorants in the genus Phalacrocorax. A 2014 study supported reclassifying it and two other American cormorant species back into Nannopterum. The IOC followed this classification in 2021.

The steamer ducks are a genus (Tachyeres) of ducks in the family Anatidae. All of the four species occur at the southern cone of South America in Chile and Argentina, and all except the flying steamer duck are flightless; even this one species capable of flight rarely takes to the air. They can be aggressive and are capable of chasing off predators like petrels. Bloody battles of steamer ducks with each other over territory disputes are observed in nature. They even kill waterbirds that are several times their size.

Phorusrhacos is an extinct genus of giant flightless terror birds that inhabited South America during the Miocene epoch. Phorusrhacos was one of the dominant land predators in South America at the time it existed. It is thought to have lived in woodlands and grasslands.
Mancallinae is an extinct subfamily of prehistoric flightless alcids that lived on the Pacific coast of today's California and Mexico from the late Miocene epoch to the early Pleistocene. They are sometimes collectively referred to as Lucas auks after the scientist who described the first species, Frederic Augustus Lucas.

Dromornithidae, known as mihirungs and informally as thunder birds or demon ducks, were a clade of large, flightless Australian birds of the Oligocene through Pleistocene Epochs. All are now extinct. They were long classified in Struthioniformes, but are now usually classified as galloanseres. Dromornithids were part of the Australian megafauna. One species, Dromornis stirtoni, was 3 m tall. Only a single species, Genyornis newtoni survived into the Late Pleistocene. They are thought to have been herbivorous.

Palaeognathae is an infraclass of birds, called paleognaths or palaeognaths, within the class Aves of the clade Archosauria. It is one of the two extant infraclasses of birds, the other being Neognathae, both of which form Neornithes. Palaeognathae contains five extant branches of flightless lineages, termed ratites, and one flying lineage, the Neotropic tinamous. There are 47 species of tinamous, five of kiwis (Apteryx), three of cassowaries (Casuarius), one of emus (Dromaius), two of rheas (Rhea) and two of ostriches (Struthio). Recent research has indicated that paleognaths are monophyletic but the traditional taxonomic split between flightless and flighted forms is incorrect; tinamous are within the ratite radiation, meaning flightlessness arose independently multiple times via parallel evolution.

Brontornis is an extinct genus of giant bird that inhabited Argentina during the Early to Middle Miocene. Its taxonomic position is highly controversial, with authors alternatively considering it to be a cariamiform, typically a phorusrhacid or an anserimorph.

Patagopteryx is an extinct monotypic genus of patagopterygiforms that lived during the Late Cretaceous, around 80 mya, in what is now the Sierra Barrosa in northwestern Patagonia, Argentina. About the size of a chicken, it is the earliest known unequivocal example of secondary flightlessness: its skeleton shows clear indications that the ancestors of Patagopteryx were flying birds.
Asiahesperornis is a prehistoric foot-propelled diving toothed flightless bird genus from the Late Cretaceous. The single known species is Asiahesperornis bazhanovi. It lived in what today is Kazakhstan, at its time the shores of the shallow Turgai Sea.
Dalianraptor is a dubious genus of prehistoric bird that lived in China about 120 million years ago, during the Early Cretaceous Period that was found in the Jiufotang Formation of China. It was initially believed to have been a possible dromaeosaurid before it was described in 2005.
Canadaga is a flightless bird genus from the Late Cretaceous. The single known species is Canadaga arctica. It lived in the shallow seas around what today is Bylot and Devon Islands in Nunavut, Canada. Its fossils were found in rocks dated to the Campanian to mid-Maastrichtian age, about 67 million years ago.
Long Mile Cave, sometimes known locally as Pick'ny Mama Cave or Hell's Gate Cave, is a palaeontological and palaeoanthropological site in the Cockpit Country of north-western Jamaica.
The Pindai Caves of New Caledonia are an archaeological and palaeontological site important for the study of prehistoric human settlement as well as of the Holocene fauna of the island. The Pindai area has been occupied by humans for varying periods over the last 2,800 years.