Related Research Articles

Barium is a chemical element; it has symbol Ba and atomic number 56. It is the fifth element in group 2 and is a soft, silvery alkaline earth metal. Because of its high chemical reactivity, barium is never found in nature as a free element.

The alkaline earth metals are six chemical elements in group 2 of the periodic table. They are beryllium (Be), magnesium (Mg), calcium (Ca), strontium (Sr), barium (Ba), and radium (Ra). The elements have very similar properties: they are all shiny, silvery-white, somewhat reactive metals at standard temperature and pressure.

A lower gastrointestinal series is a medical procedure used to examine and diagnose problems with the human colon of the large intestine. Radiographs are taken while barium sulfate, a radiocontrast agent, fills the colon via an enema through the rectum.

An upper gastrointestinal series, also called a barium swallow, barium study, or barium meal, is a series of radiographs used to examine the gastrointestinal tract for abnormalities. A contrast medium, usually a radiocontrast agent such as barium sulfate mixed with water, is ingested or instilled into the gastrointestinal tract, and X-rays are used to create radiographs of the regions of interest. The barium enhances the visibility of the relevant parts of the gastrointestinal tract by coating the inside wall of the tract and appearing white on the film. This in combination with other plain radiographs allows for the imaging of parts of the upper gastrointestinal tract such as the pharynx, larynx, esophagus, stomach, and small intestine such that the inside wall lining, size, shape, contour, and patency are visible to the examiner. With fluoroscopy, it is also possible to visualize the functional movement of examined organs such as swallowing, peristalsis, or sphincter closure. Depending on the organs to be examined, barium radiographs can be classified into "barium swallow", "barium meal", "barium follow-through", and "enteroclysis". To further enhance the quality of images, air or gas is sometimes introduced into the gastrointestinal tract in addition to barium, and this procedure is called double-contrast imaging. In this case the gas is referred to as the negative contrast medium. Traditionally the images produced with barium contrast are made with plain-film radiography, but computed tomography is also used in combination with barium contrast, in which case the procedure is called "CT enterography".

Barium oxide, also known as baria, is a white hygroscopic non-flammable compound with the formula BaO. It has a cubic structure and is used in cathode-ray tubes, crown glass, and catalysts. It is harmful to human skin and if swallowed in large quantity causes irritation. Excessive quantities of barium oxide may lead to death.

Barium chloride is an inorganic compound with the formula BaCl2. It is one of the most common water-soluble salts of barium. Like most other water-soluble barium salts, it is a white powder, highly toxic, and imparts a yellow-green coloration to a flame. It is also hygroscopic, converting to the dihydrate BaCl2·2H2O, which are colourless crystals with a bitter salty taste. It has limited use in the laboratory and industry.

Barium nitrate is the inorganic compound with the chemical formula Ba(NO3)2. It, like most barium salts, is colorless, toxic, and water-soluble. It burns with a green flame and is an oxidizer; the compound is commonly used in pyrotechnics.

Beta Cancri, also named Tarf, is the brightest star in the zodiacal constellation of Cancer. It has an apparent visual magnitude of +3.5 and an absolute magnitude of −1.2. Based on parallax measurements obtained during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 290 light-years distant from the Sun. An exoplanet, designated Beta Cancri b, is believed to be orbiting the star.
Zeta Ceti is a binary star in the equatorial constellation of Cetus. It has a combined apparent visual magnitude of 3.74, which is bright enough to be seen with the naked eye. Based upon parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 235 light-years from the Sun.
Eta Eridani, officially named Azha, is a giant star in the constellation of Eridanus. Based on parallax measurements taken during the Hipparcos mission, it is approximately 137 light-years from the Sun.

Zeta Capricorni, Latinised from ζ Capricorni, is a binary star system in the southern constellation of Capricornus. It is visible to the naked eye with an apparent visual magnitude of 3.77. The system is located at a distance of approximately 386 light-years from the Sun based on parallax. It is drifting further away with a radial velocity of +2 km/s. The absolute magnitude of this system is −1.59.

Barium titanate (BTO) is an inorganic compound with chemical formula BaTiO3. It is the barium salt of metatitanic acid. Barium titanate appears white as a powder and is transparent when prepared as large crystals. It is a ferroelectric, pyroelectric, and piezoelectric ceramic material that exhibits the photorefractive effect. It is used in capacitors, electromechanical transducers and nonlinear optics.

Barium iodide is an inorganic compound with the formula BaI2. The compound exists as an anhydrous and a hydrate (BaI2(H2O)2), both of which are white solids. When heated, hydrated barium iodide converts to the anhydrous salt. The hydrated form is freely soluble in water, ethanol, and acetone.
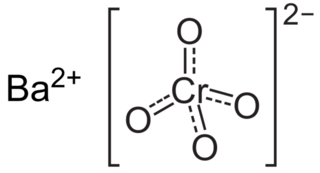
Barium chromate, is a yellow sand like powder with the formula BaCrO4. It is a known oxidizing agent and produces a green flame when heated, a result of the barium ions.
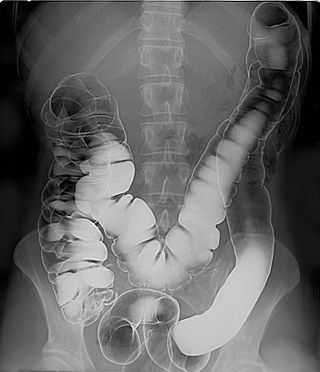
A double-contrast barium enema is a form of contrast radiography in which x-rays of the colon and rectum are taken using two forms of contrast to make the structures easier to see. A liquid containing barium is put into the rectum. Barium outlines the colon and rectum on an x-ray and helps show abnormalities. Air is also put into the rectum and colon to further enhance the x-ray.

Barium borate is an inorganic compound, a borate of barium with a chemical formula BaB2O4 or Ba(BO2)2. It is available as a hydrate or dehydrated form, as white powder or colorless crystals. The crystals exist in the high-temperature α phase and low-temperature β phase, abbreviated as BBO; both phases are birefringent, and BBO is a common nonlinear optical material.
Iota Hydrae, formally named Ukdah, is a star in the constellation of Hydra, about 8° to the north-northwest of Alphard and just to the south of the celestial equator. Visible to the naked eye, it is a suspected variable star with an apparent visual magnitude that ranges between 3.87 and 3.91. Based upon an annual parallax shift of 12.39 mas measured during the Hipparcos mission, it is located around 263 light-years from the Sun.

Barium cyanide is a chemical compound with the formula Ba(CN)2. It is synthesized by the reaction of hydrogen cyanide and barium hydroxide in water or petroleum ether. It is a white crystalline salt.
Barium permanganate is a chemical compound, with the formula Ba(MnO4)2. It forms violet to brown crystals that are sparingly soluble in water.
Barium Springs is an unincorporated community in Iredell County, North Carolina, United States. The community is located on the northern border of Troutman along U.S. Route 21. Barium Springs has a post office, with ZIP code 28010.