
The Mojave River is an intermittent river in the eastern San Bernardino Mountains and the Mojave Desert in San Bernardino County, California, United States. Most of its flow is underground, while its surface channels remain dry most of the time, with the exception of the headwaters and several bedrock gorges in the lower reaches.
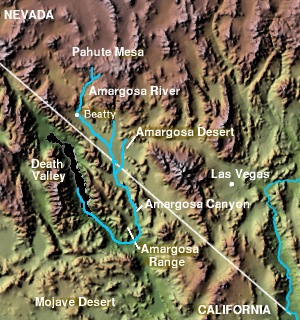
The Amargosa Valley is the valley through which the Amargosa River flows south, in Nye County, southwestern Nevada and Inyo County in the state of California. The south end is alternately called the "Amargosa River Valley'" or the "Tecopa Valley." Its northernmost point is around Beatty, Nevada and southernmost is Tecopa, California, where the Amargosa River enters into the Amargosa Canyon.

The Old Spanish Trail is a historical trade route that connected the northern New Mexico settlements of Santa Fe, New Mexico with those of Los Angeles, California and southern California. Approximately 700 mi (1,100 km) long, the trail ran through areas of high mountains, arid deserts, and deep canyons. It is considered one of the most arduous of all trade routes ever established in the United States. Explored, in part, by Spanish explorers as early as the late 16th century, the trail was extensively used by traders with pack trains from about 1830 until the mid-1850s.

The San Bernardino Valley is a valley in Southern California located at the south base of the Transverse Ranges. It is bordered on the north by the eastern San Gabriel Mountains and the San Bernardino Mountains; on the east by the San Jacinto Mountains; on the south by the Temescal Mountains and Santa Ana Mountains; and on the west by the Pomona Valley. Elevation varies from 590 feet (180 m) on valley floors near Chino, where it gradually increases to about 1,380 feet (420 m) near San Bernardino and Redlands. The valley floor is home to over 80% of the more than 4 million people of the Inland Empire region.
The Arrowhead Trail or Arrowhead Highway was the first all-weather road in the Western United States that connected Los Angeles, California to Salt Lake City, Utah by way of Las Vegas, Nevada. Built primarily during the auto trails period of the 1910s, prior to the establishment of the U.S. numbered highway system, the road was replaced in 1926 by U.S. Route 91 (US 91) and subsequently Interstate 15 (I‑15). Small portions of the route in California and Las Vegas, Las Vegas Boulevard, are sometimes still referred to by the name, or as Arrow Highway.

The Death Valley '49ers were a group of pioneers from the Eastern United States that endured a long and difficult journey during the late 1840s California Gold Rush to prospect in the Sutter's Fort area of the Central Valley and Sierra Nevada in California. Their route from Utah went through the Great Basin Desert in Nevada, and Death Valley and the Mojave Desert in Southern California, in attempting to reach the Gold Country.

Helendale or Silver Lakes is an unincorporated community and census-designated place located in the Victor Valley of the Mojave Desert, within San Bernardino County, California.

The Mojave Road, also known as Old Government Road, is a historic route and present day dirt road across what is now the Mojave National Preserve in the Mojave Desert in the United States. This rough road stretched 147 miles (237 km) from Beale's Crossing, to Fork of the Road location along the north bank of the Mojave River where the old Mojave Road split off from the route of the Old Spanish Trail/Mormon Road.

The Salt Spring Hills are a low mountain range in the Mojave Desert, in northern San Bernardino County, California. They are just outside the southeastern corner of Death Valley National Park, southeast of the Saddle Peak Hills. The road between Shoshone and Baker passes through the hills.

Glen Helen Regional Park is a county park located in San Bernardino, California, United States adjacent to the Cajon Pass. It was the site of both US Festivals of the early 1980s. It is also home to the Glen Helen Amphitheater, the largest outdoor amphitheater in the United States. The park also hosts several off-road races since 1985.
Bitter Spring is a spring within the Fort Irwin National Training Center in San Bernardino County, California. It lies at an elevation of 1355 feet and is located in a valley between the Soda Mountains to the east, the Tiefort Mountains to the northwest, Alvord Mountain to the southwest and Cronese Mountains to the south and southeast.

Monument Peak is a summit in the San Bernardino Mountains, of San Bernardino County, California. It lies at an elevation of 5272 feet.
Crowder Canyon, originally Coyote Canyon, is a valley in San Bernardino County, California. Its mouth was at an elevation of 2,999 feet / 914 meters at its confluence with Cajon Canyon. Its source was at an elevation of 4200 feet at 34°21′02″N117°26′04″W near Cajon Summit. The canyon runs southward just west of the top of Cajon Pass then turns southwestward to meet Cajon Canyon.
Lane's Crossing was a ford below the Lower Narrows of the Mojave River in San Bernardino County, California, United States. "Lane's", a ranch and store for travelers at this crossing on the Mormon Road, was established by "Captain" Aaron G. Lane the first pioneer settler on the Mojave River.

The Mohave Trail was a Native American trade route between Mohave Indian villages on the Colorado River and settlements in coastal Southern California.
Mormon Road, also known to the 49ers as the Southern Route, of the California Trail in the Western United States, was a seasonal wagon road first pioneered by a Mormon party from Salt Lake City, Utah led by Jefferson Hunt, that followed the route of Spanish explorers and the Old Spanish Trail across southwestern Utah, northwestern Arizona, southern Nevada and the Mojave Desert of California to Los Angeles in 1847. From 1855, it became a military and commercial wagon route between California and Utah, called the Los Angeles – Salt Lake Road. In later decades this route was variously called the "Old Mormon Road", the "Old Southern Road", or the "Immigrant Road" in California. In Utah, Arizona and Nevada it was known as the "California Road".

The Mojave Road Los Angeles was designated a California Historic Landmark on March 19, 1985. It runs from Drum Barracks in Los Angeles County to the Colorado River in San Bernardino County, California

The Santa Fe And Salt Lake Trail Monument was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.576) on May 17, 1957. Santa Fe And Salt Lake Trail Monument marks the place two Historic trail merged in Cajon Pass in San Bernardino County, California. The Old Spanish Trail and the Mohave Trail-Mojave Road merged in Cajon Pass. The large white marker is just off the Interstate 15 in Cajon Pass, was U.S. Route 66 in the past. It was built by the Pioneer Society of San Bernardino to remember and honor the pioneers that came west. The marker is 12 feet tall and 7 feet square at the base. Cajon Pass was home to the Serrano Indian, Native Californians that lived in the nearby Atongaibit village, in what is now Hesperia. In Summit Valley lived the Guapiabit, and in Cajon Canyon lived the Amuscopiabit. The pass was used by native in prehistory. The San Andreas Fault runs through and made the 3,777 ft (1,151 m) mountain pass between the San Bernardino Mountains and the San Gabriel Mountains in Southern California. One side in the Mojave Desert and the other the Los Angeles Basin. The Monument is specially dedicated to those that cross the pass on June 20, 1851 as part of the '49s. Sheldon Stoddard and Sydney P. Waite are two of the pioneers that crossed the pass in 1851. They were part of what is now called the Death Valley '49ers that crossed the pass after surviving a wrong detour though Death Valley in 1949. In addition to building the monument, the Pioneer Society of San Bernardino built a log cabin, picnic tables and benches in the mountains and San Bernardino for the public to use.

The Daley Toll Road Monument was designated a California Historic Landmark (No.579) on May 17, 1957. Daley Toll Road Monument marker is in the San Bernardino Mountains. The Monument is on the first wagon road built in San Bernardino Mountains. Engineer Edward Daley Sr. and his sons built and opened the toll road in 1870. They Daley family ran the toll road till 1890. The toll road ran from the city of San Bernardino to Lake Arrowhead. The road was called the Twin and City Creek Turnpike and the turnpike into the mountains. In 1890 the road became a San Bernardino County, California road called the Daley Canyon Road. The road is now a US Forest Service fire road and is closed to the public. The Monument is near the current city of Rimforest, California on California State Route 18 at Daley Canyon Rd, about 0.6 miles East of Rim Forest. The road made good money for Daley family. The road was used by lumber men, cattle men and sheep herders. Edward Daley became a San Bernardino county supervisor from January 5, 1880, to January 8, 1883. He opened a farm ranch called Dell Rosa at the entrance to the toll road. Edward Daley in Council Bluffs, Iowa, married in 1846, Nancy Ann Hunt, daughter of Capt. Jefferson Hunt. Hunt made three trips over the Cajon Pass and Mojave Desert one in 1847, second in 1849 and last in 1851. Each trip he was the leader of wagon trains, bringing pioneer west, down one of the westward Expansion Trails. Edward and Nancy came to California on the 1849 trip, together they had 11 children: Laomi, Celia, Edward Jr., Charles Jefferson, John, Grace, Annetta, Frank, Lou, May and Kate. The road he built went up Strawberry Creek, crossed over to the west fork of City Creek, passed by the east of Strawberry Peak and then dropped into Little Bear Valley. Little Bear Valley is where the towns of Blue Jay and Lake Arrowhead are located. At the end of the toll road John Commerford ran the top end of the toll road. John Commerford ran a store at the location.

Bennett-Arcane Long Camp was a 1849er camp set up in December 1849 in Death Valley as they traveled to the California Gold Rush. They were emigrants crossing the harsh Desert to get to California. The camp was located just west of valley's Badwater Basin in the Death Valley National Park Inyo County, California. Badwater Basin is lowest point in North America and the United States, at a depth of 282 ft (86 m) below sea level. The Bennett-Arcane party became known as the Death Valley '49ers. The Death Valley '49ers were pioneers from the Eastern United States travelling west to prospect in the Sutter's Fort area of the Central Valley and Sierra Nevada in California. The wagon train crossed Utah across the Great Basin Desert in Nevada. They made a wrong turn on got trapped in Death Valley. After exiting they crossed the Mojave Desert into Southern California. Still wanting to go to the California Gold Country. The group used the southern Desert part of the Old Spanish Trail, after hearing about the death of the Donner Party. Some of the party died on the near the camp and the suffering gave the place the name Death Valley. John Haney Rogers was one of the men that departed the valley on foot and came back with help.
















