
The Kingdom of the West Saxons, also known as the Kingdom of Wessex, was an Anglo-Saxon kingdom in the south of Great Britain, from around 519 until Alfred the Great declared himself as King of the Anglo-Saxons in 886.

Buckinghamshire is a ceremonial county in South East England and one of the home counties. It is bordered by Northamptonshire to the north, Bedfordshire to the north-east, Hertfordshire to the east, Greater London to the south-east, Berkshire to the south, and Oxfordshire to the west. The largest settlement is the city of Milton Keynes, and the county town is Aylesbury.

Buckingham is a market town in north Buckinghamshire, England, close to the borders of Northamptonshire and Oxfordshire, which had a population of 12,890 at the 2011 Census. The town lies approximately 12 miles (19 km) west of Central Milton Keynes, 19 miles (31 km) south-east of Banbury, and 24 miles (39 km) north-east of Oxford.
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for a Brythonic kingdom that existed in Sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries CE in the more westerly parts of present-day South West England. It was centred in the area of modern Devon, but also included modern Cornwall and part of Somerset, with its eastern boundary changing over time as the gradual westward expansion of the neighbouring Anglo-Saxon kingdom of Wessex encroached on its territory. The spelling Damnonia is sometimes encountered, but that spelling is also used for the land of the Damnonii, later part of the Kingdom of Strathclyde, in present-day southern Scotland. The form Domnonia also occurs. The name of the kingdom shares a linguistic relationship with the Breton region of Domnonée.

Winslow is a market town and civil parish in north Buckinghamshire, England, within the Buckinghamshire Council unitary authority area. It has a population of just over 4,400. It is located approximately 6 miles (9.7 km) south-east of Buckingham, and 7 miles (11 km) south-west of Bletchley.

Brill is a village and civil parish in west Buckinghamshire, England, close to the border with Oxfordshire. It is about 4 miles (6 km) north-west of Long Crendon and 7 miles (11 km) south-east of Bicester. At the 2011 Census, the population of the civil parish was 1,141. Brill has a royal charter to hold a weekly market, but has not done so for many years.

Bow Brickhill is a village and civil parish in the unitary authority area of the City of Milton Keynes, Buckinghamshire, England. It is bounded to the north, west and east by the Milton Keynes urban area, approximately 2 miles (3.2 km) east of Fenny Stratford, 1.5 miles (2.4 km) west of Woburn Sands and 4 miles (6.4 km) south-east of Central Milton Keynes.
Chearsley is a village and civil parish within the Buckinghamshire district in the ceremonial county of Buckinghamshire, England. It is situated about seven miles south west of Aylesbury, and about four miles north of Thame, in Oxfordshire.
Great Brickhill is a village and civil parish in the unitary authority area of Buckinghamshire, England. It is on the border with the City of Milton Keynes, located 6 miles (9.7 km) south-east of Central Milton Keynes, and 3 miles (4.8 km) in the same direction from Fenny Stratford.

Wing, known in antiquated times as Wyng, is a village and civil parish in east Buckinghamshire, England. The village is on the main A418 road between Aylesbury and Leighton Buzzard. It is about 8 miles (13 km) north-east of Aylesbury, 3 miles (5 km) west of Leighton Buzzard, and 12 miles (19 km) south of Milton Keynes.
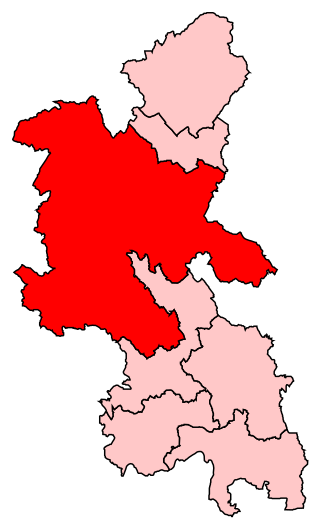
Buckingham was a constituency that was last represented in the House of Commons of the UK Parliament by Greg Smith, a Conservative.

The ceremonial county of Buckinghamshire, which includes the unitary authorities of Buckinghamshire and the City of Milton Keynes, is divided into 8 parliamentary constituencies – 1 borough constituency and 7 county constituencies. At the 2024 general election, the county returned 5 Labour MPs, 2 Conservatives and 1 Liberal Democrat.

This history of Milton Keynes details its development from the earliest human settlements, through the plans for a 'new city' for 250,000 people in northern Southeast England, its subsequent urban design and development, to the present day. Milton Keynes, founded in 1967, is the largest settlement and only city in Buckinghamshire. At the 2021 census, the population of its urban area was estimated to have exceeded 256,000.

The railway system of Buckinghamshire has a long and complex history dating back to the 1830s with the opening of sections of today's West Coast Main Line and Great Western Main Line. The development of Buckinghamshire's railway network was largely due to its position nationally as many long-distance routes chose to go through Buckinghamshire, especially between Britains two largest cities, London and Birmingham. The county had its own pulling power in addition, as produce such as the Aylesbury duck could then be easily transported to the capital.

Transport in Buckinghamshire has been shaped by its position within the United Kingdom. Most routes between the UK's two largest cities, London and Birmingham, pass through this county. The county's growing industry first brought canals to the area, then railways and then motorways.
Eadgyth of Aylesbury also known as Eadridus was a Dark Ages Catholic saint from Anglo-Saxon England.

The Aylesbury Vale is a geographical region in Buckinghamshire, England, which is bounded by the City of Milton Keynes and West Northamptonshire to the north, Central Bedfordshire and the Borough of Dacorum (Hertfordshire) to the east, the Chiltern Hills to the south and South Oxfordshire to the west. It is named after Aylesbury, the county town of Buckinghamshire. Winslow and Buckingham are among the larger towns in the vale.
The Buckinghamshire Rugby Football Union is the governing body for the sport of rugby union in the county of Buckinghamshire in England. The union is the constituent body of the Rugby Football Union (RFU) for Buckinghamshire, and administers and organises rugby union clubs and competitions in the county. It also administers the Buckinghamshire county rugby representative teams. The union was founded at a meeting at High Wycombe on 16 July 1949 during a drinking session at one of the founders house.

Buckinghamshire Council is the local authority for Buckinghamshire (district), a non-metropolitan county in England. It is a unitary authority, performing both county and district-level functions. It was created on 1 April 2020, replacing the previous Buckinghamshire County Council and the councils of the four abolished districts of Aylesbury Vale, Chiltern, South Bucks, and Wycombe. The territory of the Council is about four-fifths of Buckinghamshire and has about two-thirds of its population.














