Valladolid is a municipality in Spain and the primary seat of government and de facto capital of the autonomous community of Castile and León. It is also the capital of the province of Valladolid. It has a population of 295,639 people.

San Lorenzo de El Escorial, also known as El Escorial de Arriba, is a town and municipality in the Community of Madrid, Spain, located to the northwest of the region in the southeastern side of the Sierra de Guadarrama, at the foot of Mount Abantos and Las Machotas, 47 kilometres (29 mi) from Madrid. It is head of the eponymous judicial party. The settlement is popularly called El Escorial de Arriba, to differentiate it from the neighbouring village of El Escorial, also known as El Escorial de Abajo.

Leganés is a city in the Community of Madrid, Spain. Considered part of the Madrid metropolitan area, it is located about 11 km southwest of the centre of Madrid. As of 2018, it has a population of 188,425, making it the region's fifth most populated municipality. It covers an area of 43.09 km2 and it is located at 667 m over sea level.

The Manzanares is a river in the centre of the Iberian Peninsula, which flows from the Sierra de Guadarrama, passes through Madrid, and eventually empties into the Jarama river, which in turn is a right-bank tributary to the Tagus.

Móstoles is a municipality of Spain located in the Community of Madrid. With over 200,000 inhabitants, it is the region's second most populated municipality after Madrid. Móstoles was a small town for a long time, but expanded rapidly in the second half of the 20th century.
Pinto is a municipality in the Community of Madrid, Spain. It is located in the central area of the Iberian Peninsula at an altitude of 604 meters, 20 kilometers south of Madrid, and covers 62.7 square kilometers. In 2018, Pinto had a population of 51,541. It is home to the Torre de Pinto, the Pinto Castle, and the Éboli Tower, which is a 14th-century tower used as a prison for nobles who fell out of favor with the king.

Ocaña is a municipality of Spain, in the province of Toledo, Castilla–La Mancha.

Torrejón de Ardoz is a municipality of Spain belonging to the Community of Madrid.

Alcobendas is a municipality of Spain located in the Community of Madrid.

San Sebastián de los Reyes is a municipality in the Community of Madrid, Spain. Founded in 1492, it is located 20 kilometres (12 mi) north of Madrid.

Fuenlabrada is a city and municipality of Spain located in the Community of Madrid. As of 2018, it has a population of 193,586, making it the region's fourth most populated municipality.

Alcorcón is a city and municipality of Spain located in the Community of Madrid. As of 2022, it had a population of 170,296.

Ciempozuelos is a municipality in Spain located in the Community of Madrid. The municipality spans across a total area of 49.64 km2 and, as of 1 January 2020, it has a registered population of 25,383 (2022).

Paseo de la Castellana, commonly known as La Castellana, is a major thoroughfare in Madrid, Spain. Cutting across the city from south to north, it has been described as the "true structuring axis" of the city.
Carlos Arroyo Zapatero is a contemporary architect, urbanist and critic from Madrid, Spain. His work claims to set the frame for a new architectural culture, language and aesthetics, through the ethics, technology and parameters of sustainability. He claims that his architecture is not designed to be photographed, but to be lived-in and enjoyed through time. He has developed a diagrammatic graphic style for his presentations which is inspirational for a whole generation of architects. In contrast, his built work is often portrayed by photographer-artists, producing innovative formats like photo-novellas, gif's, or video. His work has been exhibited in internationally renowned venues like the Venice Biennale, the Institut Français d'Architecture, presented in referential publications like El Croquis, and quoted by many bloggers in the sphere.

La Blanca is a Maya pre-Columbian Mesoamerican archaeological site in the municipality of Melchor de Mencos in the northern Petén Department of Guatemala. It has an occupation dating predominantly from the Middle Preclassic period of Mesoamerican chronology. This site belongs to the later period of the Mokaya culture. The site is located in the lower reaches of the Mopan River valley and features a large acropolis complex. Activity at the site has been dated as far back as the Early Classic, with principal occupation of the site occurring in the Late Classic period, although some level of occupation continued into the Early Postclassic.

The Sierra del Ocejón or Sierra del Robledal is a mountain range located in the central part of the Iberian Peninsula.
Emilio Blanco Izaga (1892–1949) was a Spanish military comptroller, ethnographer and architect, who developed his career in the Spanish protectorate in Morocco. He published a number of ethnographic and architectural essays on the Rif region.
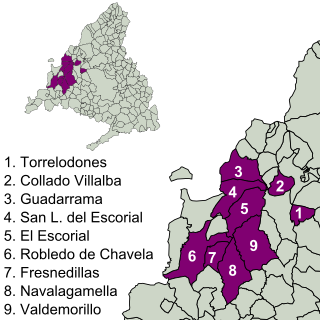
The Imperial Route of the Community of Madrid is the tourist itinerary promoted by the Ministry of Culture and Tourism of this Spanish region, which runs through several municipalities in the Sierra de Guadarrama. It partially follows the historical road that led to the Monastery of El Escorial, used in the 16th century by King Philip II in his travels from the city of Madrid to the Royal Site.
Art Nouveau in Madrid is the historiographic term given to the artistic style Art Nouveau as it developed in and around Madrid, the capital of Spain, around 1900, permeating architecture, design, the decorative arts, graphic arts, and broader culture. There is also a "Modernismo madrileño" in the field of literature, likewise situated in the capital and considered to be the nucleus of the origins of the modern movement of Spanish literature.