
Cumberland is a city in and the county seat of Allegany County, Maryland, United States. It is the primary city of the Cumberland, MD-WV Metropolitan Statistical Area. At the 2010 census, the city had a population of 20,859, and the metropolitan area had a population of 103,299. Located on the Potomac River, Cumberland is a regional business and commercial center for Western Maryland and the Potomac Highlands of West Virginia.

Point of Rocks is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Frederick County, Maryland, United States. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 1,466. It is named for the striking rock formation on the adjacent Catoctin Mountain, which was formed by the Potomac River cutting through the ridge in a water gap, a typical formation in the Appalachian Mountains. The formation is not visible from the town and can only be seen from boats on the river, or from the southern bank of the river in Virginia.

The Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park is located in the District of Columbia and the states of Maryland and West Virginia. The park was established in 1961 as a National Monument by President Dwight D. Eisenhower to preserve the neglected remains of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal and many of its original structures. The canal and towpath trail extends along the Potomac River from Georgetown, Washington, D.C., to Cumberland, Maryland, a distance of 184.5 miles (296.9 km). In 2013, the path was designated as the first section of U.S. Bicycle Route 50.

Sideling Hill is a long, steep, narrow mountain ridge in the Ridge-and-Valley physiographic province of the Appalachian Mountains, located in Washington County in western Maryland and adjacent West Virginia and Pennsylvania, USA. The highest point on the ridge is Fisher Point, at 2,310 feet (700 m) in Fulton County, Pennsylvania.

The Western Maryland Railway was an American Class I railroad (1852–1983) which operated in Maryland, West Virginia, and Pennsylvania. It was primarily a coal hauling and freight railroad, with a small passenger train operation.

The Capital Subdivision is a railroad line owned and operated by CSX Transportation in the U.S. state of Maryland and the District of Columbia. The line runs from near Baltimore, Maryland southwest to Washington, D.C. along the former Baltimore and Ohio Rail Road (B&O) Washington Branch. The subdivision's Alexandria Extension provides a connection to Virginia and points south.
The National Register of Historic Places in the United States is a register including buildings, sites, structures, districts, and objects. The Register automatically includes all National Historic Landmarks as well as all historic areas administered by the U.S. National Park Service. Since its introduction in 1966, more than 90,000 separate listings have been added to the register.

The South Branch Valley Railroad consists of a 52.4 mile (84.33 km) length of railroad in the U.S. state of West Virginia extending north along the South Branch Potomac River from Petersburg to the CSXT mainline at Green Spring adjacent to the Potomac River. At Green Spring, the CSXT mainline connects the SBVR to Cumberland, Maryland to the west and Martinsburg, West Virginia to the east. SBVR has been owned and operated by the West Virginia State Rail Authority (SRA) since it was sold by the Baltimore & Ohio Railroad on October 11, 1978. Upon purchasing the B&O's South Branch line, West Virginia became the first state in the United States to both own and operate a commercial freight railroad. In 1985, major flooding of the South Branch Valley destroyed most of the rail line, including all three bridges that crossed the South Branch Potomac River. Despite talk of shutting down the railroad after the flood, reconstruction began two years later.

Oldtown is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Allegany County, Maryland, United States, along the North Branch Potomac River. As of the 2010 census it had a population of 86.
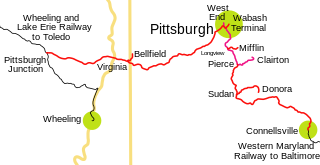
The Pittsburgh and West Virginia Railway was a railroad in the Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania and Wheeling, West Virginia, areas. Originally built as the Wabash Pittsburgh Terminal Railway, a Pittsburgh extension of George J. Gould's Wabash Railroad, the venture entered receivership in 1908 and the line was cut loose. An extension completed in 1931 connected it to the Western Maryland Railway at Connellsville, Pennsylvania, forming the Alphabet Route, an independent line between the Northeastern United States and the Midwest. It was leased by the Norfolk and Western Railway in 1964 in conjunction with the N&W acquiring several other sections of the former Alphabet Route, but was leased to the new spinoff Wheeling and Lake Erie Railway in 1990, just months before the N&W was merged into the Norfolk Southern Railway.

Magnolia is an unincorporated community northeast of Paw Paw in Morgan County in the U.S. state of West Virginia on the Potomac River. Magnolia is located along the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad mainline and east of where the Western Maryland Railway crosses the Potomac, bypassing a series of bends in the river. As a depot and water station on the B&O, Magnolia has been known by a number of names including Magnolia Dale, Magnolia Vale, and sometimes as Water Station Number 12 on the railroad.

Green Ridge is a now uninhabited railroad community in Morgan County in the U.S. state of West Virginia on the old Baltimore and Ohio Railroad mainline where the Western Maryland Railroad crosses the Potomac River from the Stickpile Tunnel in Maryland. Green Ridge was originally known as Baird and was an operating station on the B&O. Today, it is located within the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal National Historical Park. A stretch of the Western Maryland's right-of-way from Green Ridge to Jerome is listed on the National Register of Historic Places.

The North Bend Rail Trail is a 72-mile (116 km) rail trail in north-central and western West Virginia in the United States. It is operated by West Virginia State Parks and is part of the American Discovery Trail.
The Patterson Creek Cutoff is an abandoned railroad line built by the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) in northern West Virginia and Western Maryland, that served trains running on the B&O "West End" line in the Cumberland, Maryland area. The cutoff route ran from McKenzie, Maryland to Patterson Creek, West Virginia, providing a bypass of the B&O rail yard in Cumberland for coal trains moving between Keyser, West Virginia and Brunswick, Maryland.

Western Maryland Railroad Right-of-Way, Milepost 126 to Milepost 160 is a historic section of the Western Maryland Railway (WM) in Allegany County, Maryland, and in Morgan County, West Virginia. It is an abandoned 34 miles (55 km) section of the right-of-way between milepost 126 at the intersection of the Chesapeake and Ohio Canal (C&O) and Long Ridge Road, Woodmont, and milepost 160 just west of Maryland Route 51, North Branch. It closely parallels the Potomac River and the C&O Canal running along the north bank of the river. Seven miles of the roadbed are in West Virginia near Paw Paw, and include three tunnels.

Indigo Tunnel is an abandoned railroad tunnel in Allegany County, Maryland, located about 1 mile (1.6 km) east of Little Orleans. Built by the Western Maryland Railway (WM) in 1904, Indigo was the company's longest tunnel. It was part of a major WM project to extend its rail system from Hagerstown west to Cumberland. This difficult route followed the Potomac River valley and involved construction of four additional tunnels and 23 bridges. The new rail line opened for traffic in 1906. Trains ran through the tunnel until the rail line was abandoned by the newly formed Chessie System in 1975, in favor of the parallel Baltimore and Ohio railroad line on the opposite side of the Potomac River.

Kessler Tunnel is an abandoned railroad tunnel in Allegany County, Maryland, located about 8.5 miles (13.7 km) east-northeast of Oldtown. It was built by the Western Maryland Railway (WM) in 1906. It was constructed with concrete arch portals and the roof has wood planking. The tunnel was named for landowner John Kessler.

Stickpile Tunnel, also known as Greenridge Tunnel, is an abandoned railroad tunnel in Allegany County, Maryland, located about 2.5 miles (4.0 km) southwest of Little Orleans. It was built by the Western Maryland Railway (WM) in 1906. It was constructed with concrete arch portals and the roof has wood planking.
























