Sources
- Wixman, Ronald. The People of the USSR: An Ethnographic Handbook, (Armonk: M. E. Sharpe, 1984) p. 102
| Languages | |
|---|---|
| Forest Nenets language | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Nenets, other Samoyedic people |
The Khandeyar are one of the two groups of the Nenets. They are also known as Forest Nenets or Forest Yurak because they live in the forest region or Taiga instead of the Tundra like the other Nenets. They speak the Forest variety of Nenets.

The Nenets, also known as 'Samoyeds', are a Samoyedic ethnic group native to Arctic Russia, Russian Far North. According to the latest census in 2021, there were 49,646 Nenets in the Russian Federation, most of them living in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Nenets Autonomous Okrug and Taymyrsky Dolgano-Nenetsky District stretching along the coastline of the Arctic Ocean near the Arctic Circle between Kola and Taymyr peninsulas. The Nenets people speak either the Tundra or Forest Nenets languages. In the Russian Federation they have a status of Indigenous small-numbered peoples. Today, the Nenets people face numerous challenges from the state and oil and gas companies that threaten the environment and their way of life. As a result, many cite a rise in locally based activism.

The Samoyedic or Samoyed languages are spoken around the Ural Mountains, in northernmost Eurasia, by approximately 25,000 people altogether, accordingly called the Samoyedic peoples. They derive from a common ancestral language called Proto-Samoyedic, and form a branch of the Uralic languages. Having separated perhaps in the last centuries BC, they are not a diverse group of languages, and are traditionally considered to be an outgroup, branching off first from the other Uralic languages.

Tyumen Oblast is a federal subject of Russia. It is located in Western Siberia, and is administratively part of the Urals Federal District. The oblast has administrative jurisdiction over two autonomous okrugs: Khanty-Mansi Autonomous Okrug and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug. Tyumen Oblast, including its autonomous okrugs, is the third-largest federal subject by area, and has a population of 3,395,755 (2010).

The Nenets Autonomous Okrug is a federal subject of Russia and an autonomous okrug of Arkhangelsk Oblast. Its administrative center is the town of Naryan-Mar. It has an area of 176,700 square kilometers (68,200 sq mi) and a population of 42,090 as of the 2010 Census, making it the least populous federal subject.

The Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug or Yamalia is a federal subject of Russia and an autonomous okrug of Tyumen Oblast. Its administrative center is the town of Salekhard, and its largest city is Novy Urengoy. The 2021 Russian Census recorded its population as 510,490.

The federal subjects of Russia, also referred to as the subjects of the Russian Federation or simply as the subjects of the federation, are the constituent entities of Russia, its top-level political divisions. According to the Constitution of Russia, the federation consists of republics, krais, oblasts, cities of federal importance, an autonomous oblast, and autonomous okrugs, all of which are equal subjects of the federation.
Nenets may refer to:

The Pechora is the sixth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Northwest Russia and into the Arctic Ocean, it lies mostly in the Komi Republic but the northernmost part crosses the Nenets Autonomous Okrug.

Nenets is a pair of closely related languages spoken in northern Russia by the Nenets people. They are often treated as being two dialects of the same language, but they are very different and mutual intelligibility is low. The languages are Tundra Nenets, which has a higher number of speakers, spoken by some 30,000 to 40,000 people in an area stretching from the Kanin Peninsula to the Yenisei River, and Forest Nenets, spoken by 1,000 to 1,500 people in the area around the Agan, Pur, Lyamin and Nadym rivers.
Yurats (Yurak) was a Samoyedic language spoken in the Siberian tundra west of the Yenisei River. It became extinct in the early 19th century. Yurats was probably either a transitional variety connecting the Nenets and Enets languages of the Samoyedic family, or an archaic dialect of Enets. Some eastern dialects of Tundra Nenets may have a Yurats substrate, as the Yurats were likely absorbed by the Tundra Nenets. The uncertainty regarding the language's status is due to the scarcity of information about the language. Nevertheless, Glottolog considers it to be a dialect of Tundra Nenets.
Nenets Autonomous Okrug is a Russian federal subject. The titular ethnic group are the Nenets. Their traditional music includes epic poems comparable to the Finnish Kalevala and the Yakut Olonkho. Traditional Nenets music includes the use of neither musical instruments nor dance.
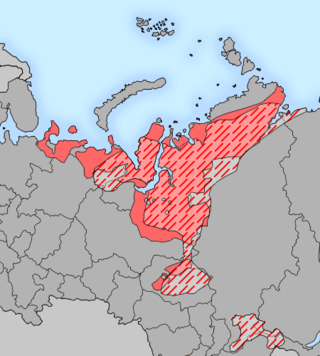
The Samoyedic peoples are a group of closely related peoples who speak Samoyedic languages, which are part of the Uralic family. They are a linguistic, ethnic, and cultural grouping. The name derives from the obsolete term Samoyed used in Russian Empire for some Indigenous people of Siberia, see Samoyedic languages#Etymology for comments of the etymology.

Noyabrsk is the second largest city in Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, Russia, located in the middle of the West Siberian oil fields, on the Tyumen–Novy Urengoy railway about 300 kilometers (190 mi) north of Surgut. Population: 110,620 (2010 Russian census).

En with hook is a letter of the Cyrillic script. Its form is derived from the Cyrillic letter En (Н н) by adding a hook to the right leg.

Forest Nenets is a Samoyedic language spoken in northern Russia, around the Agan, Pur, Lyamin and Nadym rivers, by the Nenets people. It is closely related to the Tundra Nenets language, and the two are still sometimes seen as simply being dialects of a single Nenets language, despite there being low mutual intelligibility between the two. The next closest relatives are Nganasan and Enets, after them Selkup, and even more distantly the other Uralic languages.

Tundra Nenets is a Uralic language spoken in European Russia and North-Western Siberia. It is the largest and best-preserved language in the Samoyedic group.

Dmitry Nikolaevich Kobylkin is a Russian politician who served as Governor of Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug from 4 May 2012 until 29 May 2018, and as Minister of Natural Resources of the Russian Federation from May 2018 until November 2020.

The Nenets Herding Laika is an aboriginal spitz landrace of dog originating from the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, in Russia. Unlike other laikas, Nenets Herding Laika are less commonly used for hunting. Instead they have been selected primarily for reindeer herding ability, originally by the Nenets people, and later by reindeer herders through Russia. Nenets herding laika are thought to be the progenitor of several modern breeds, the most well-documented being the Samoyed. Despite this, the breed almost died out during the Soviet era due to lack of interest in preserving genetically purebred examples. In 1994, the Russian Kynologic Federation (RKF) approved the first official standard of the breed.

Sergey Nikolaevich Kotkin is a Russian political figure and deputy of the 7th and 8th State Dumas.