
Kamchatka Oblast was, until being incorporated into Kamchatka Krai on July 1, 2007, a federal subject of Russia. To the north, it bordered Magadan Oblast and Chukotka Autonomous Okrug. Koryak Autonomous Okrug was located in the northern part of the oblast. Including the autonomous okrug, the total area of the oblast was 472,300 square kilometres (182,400 sq mi), encompassing the southern half of the Kamchatka Peninsula. The administrative center of Kamchatka Oblast was the city of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky. Population: 358,801 (2002 Census); 466,096 (1989 Census).

The Desmostylia are an extinct order of aquatic mammals that existed from the early Oligocene (Rupelian) to the late Miocene (Tortonian).

The Kamchatka Peninsula is a 1,250-kilometre-long (777 mi) peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about 270,000 km2 (104,248 sq mi). The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively. Immediately offshore along the Pacific coast of the peninsula runs the 10,500-metre-deep (34,449 ft) Kuril–Kamchatka Trench.
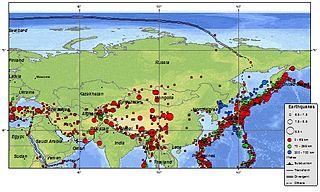
Three earthquakes, which occurred off the coast of Kamchatka Peninsula in far eastern Russia in 1737, 1923 and 1952, were megathrust earthquakes and caused tsunamis. They occurred where the Pacific Plate subducts under the Okhotsk Plate at the Kuril–Kamchatka Trench. The depth of the trench at the point of the earthquakes is 7,000–7,500 m. Northern Kamchatka lies at the western end of the Bering fault, between the Pacific Plate and North American Plate, or the Bering plate There are many more earthquakes and tsunamis originating from Kamchatka, of which the most recent was the 1997 Kamchatka earthquake and tsunami originating near the Kronotsky Peninsula.

Paleoparadoxia is a genus of large, herbivorous aquatic mammals that inhabited the northern Pacific coastal region during the Miocene epoch. It ranged from the waters of Japan, to Alaska in the north, and down to Baja California, Mexico. Paleoparadoxia was about 2.2 m long.

Kamchatka Krai is a federal subject of Russia. It is geographically located in the Far East region of the country, and it is administratively part of the Far Eastern Federal District. Kamchatka Krai has a population of 322,079 (2010).

Desmostylus is an extinct genus of herbivorous mammal of the family Desmostylidae living from the Chattian stage of the Late Oligocene subepoch through the Late Miocene subepoch and in existence for approximately 21.2 million years .
Obinautilus is an extinct genus of shelled cephalopod that has been variously identified as an argonautid octopod or a nautilid. It is known from the Late Oligocene to Pliocene of Japan. The shell is discoidal and very involute, with rapidly expanding and compressed whorls, fine radial ribs, a rounded venter with a shallow furrow, and almost closed umbilicus.
Behemotops is an extinct genus of herbivorous marine mammal. It lived from the Early Oligocene (Rupelian) through the Late Oligocene, existing for approximately 10.9 million years . It is the most primitive known desmostylian, believed to be close to the ancestry of all other desmostylians.

Prolagus is an extinct genus of pika within the order Lagomorpha. Over 20 species of Prolagus have been named, beginning in the Early Miocene in Europe 20 million years ago, where it ranged widely for most of the epoch; by the end of the Middle Pleistocene, it was confined to a single species, the Sardinian pika, on the Mediterranean islands of Corsica, Sardinia, and surrounding islands, where it survived into historical times. In Africa and Asia, the genus is known from the Miocene and Pliocene. The scientific name may mean "before hares" or "primitive hares".
Paleontology or palaeontology is the study of prehistoric life forms on Earth through the examination of plant and animal fossils. This includes the study of body fossils, tracks (ichnites), burrows, cast-off parts, fossilised feces (coprolites), palynomorphs and chemical residues. Because humans have encountered fossils for millennia, paleontology has a long history both before and after becoming formalized as a science. This article records significant discoveries and events related to paleontology that occurred or were published in the year 1999.

Ashoroa is an extinct genus of desmostylian, aquatic, herbivorous mammal. Fossils of Ashoroa have been found in the Morawan Formation on Hokkaido, Japan and were dated to the late Oligocene.
Cornwallius is an extinct herbivorous marine mammal of the family Desmostylidae. Cornwallius lived along the North American Pacific Coast from the Early Oligocene (Chattian) through the Oligocene and existing for approximately 7.8 million years .

The Kiyosu-e Formation is a Middle Jurassic (Callovian) to Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) geologic formation of the Toyonishi Group in Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan. Fossil ornithopod tracks have been reported from the formation.

The Aleutian Islands, also called the Aleut Islands or Aleutic Islands and known before 1867 as the Catherine Archipelago, are a chain of 14 large volcanic islands and 55 smaller islands. Most of the Aleutian Islands belong to the U.S. state of Alaska, but some belong to the Russian federal subject of Kamchatka Krai. They form part of the Aleutian Arc in the Northern Pacific Ocean, occupying an area of 6,821 sq mi (17,666 km2) and extending about 1,200 mi (1,900 km) westward from the Alaska Peninsula toward the Kamchatka Peninsula in Russia, and act as a border between the Bering Sea to the north and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Crossing longitude 180°, at which point east and west longitude end, the archipelago contains both the westernmost part of the United States by longitude and the easternmost by longitude. The westernmost U.S. island in real terms, however, is Attu Island, west of which runs the International Date Line. While nearly all the archipelago is part of Alaska and is usually considered as being in the "Alaskan Bush", at the extreme western end, the small, geologically related Commander Islands belong to Russia.

Plesiobalaenoptera is a genus of extinct rorqual which existed in Italy during the late Miocene epoch. The type species is P. quarantellii. It is the oldest known rorqual from the Mediterranean basin. Fossils have been found from sediments of the Stirone River in northern Italy that were deposited during the Tortonian age, around 11 to 7 million years ago.

Pappocetus is an extinct protocetid cetacean known from the Eocene of Nigeria and Togo.
Kamtschatarctos is an extinct genus of pinniped that lived approximately 15.97 to 11.608 mya during the Early Miocene in the Kavran-Ukhtolok Bay of Russia's Kamchatka Peninsula. It belonged to the family Odobenidae, the only extant species of which is the walrus.

Atlanticetus is a genus of extinct mysticete known from the Early Miocene of Italy and the US Eastern Seaboard. As of February 2021, the genus was not accepted by the Paleobiology Database.














