
The metabotropic glutamate receptors, or mGluRs, are a type of glutamate receptor that are active through an indirect metabotropic process. They are members of the group C family of G-protein-coupled receptors, or GPCRs. Like all glutamate receptors, mGluRs bind with glutamate, an amino acid that functions as an excitatory neurotransmitter.
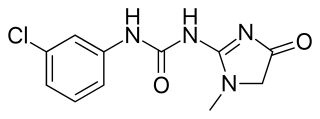
Fenobam is an imidazole derivative developed by McNeil Laboratories in the late 1970s as a novel anxiolytic drug with an at-the-time-unidentified molecular target in the brain. Subsequently, it was determined that fenobam acts as a potent and selective negative allosteric modulator of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5, and it has been used as a lead compound for the development of a range of newer mGluR5 antagonists.

The glutamate receptor, metabotropic 1, also known as GRM1, is a human gene which encodes the metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (mGluR1) protein.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 2 (mGluR2) is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the GRM2 gene. mGluR2 is a G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) that couples with the Gi alpha subunit. The receptor functions as an autoreceptor for glutamate, that upon activation, inhibits the emptying of vesicular contents at the presynaptic terminal of glutamatergic neurons.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 3 (mGluR3) is an inhibitory Gi/G0-coupled G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) generally localized to presynaptic sites of neurons in classical circuits. However, in higher cortical circuits in primates, mGluR3 are localized post-synaptically, where they strengthen rather than weaken synaptic connectivity. In humans, mGluR3 is encoded by the GRM3 gene. Deficits in mGluR3 signaling have been linked to impaired cognition in humans, and to increased risk of schizophrenia, consistent with their expanding role in cortical evolution.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM7 gene.

Metabotropic glutamate receptor 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GRM8 gene.

Eglumetad is a research drug developed by Eli Lilly and Company, which is being investigated for its potential in the treatment of anxiety and drug addiction. It is a glutamate derived compound and its mode of action implies a novel mechanism.

Tezampanel is a drug originally developed by Eli Lilly which acts as a competitive antagonist of the AMPA and kainate subtypes of the ionotropic glutamate receptor family, with selectivity for the GluR5 subtype of the kainate receptor. It has neuroprotective and anticonvulsant properties, the former of which may, at least in part, occur via blockade of calcium uptake into neurons.

AMN082 is a selective metabotropic glutamate receptor 7 (mGluR7) allosteric agonist. It mimics the effect of glutamate. AMN082 is the first selective mGluR7 agonist and has expanded the potential array of research opportunities on the effects of mGluR7 in the central nervous system.

2-Methyl-6-(phenylethynyl)pyridine (MPEP) is a research drug which was one of the first compounds found to act as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. After being originally patented as a liquid crystal for LCDs, it was developed by the pharmaceutical company Novartis in the late 1990s. It was found to produce neuroprotective effects following acute brain injury in animal studies, although it was unclear whether these results were purely from mGluR5 blockade as it also acts as a weak NMDA antagonist, and as a positive allosteric modulator of another subtype mGlu4, and there is also evidence for a functional interaction between mGluR5 and NMDA receptors in the same populations of neurons. It was also shown to produce antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animals, and to reduce the effects of morphine withdrawal, most likely due to direct interaction between mGluR5 and the μ-opioid receptor.

3-( ethynyl)pyridine (MTEP) is a research drug that was developed by Merck & Co. as a selective allosteric antagonist of the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. Identified through structure-activity relationship studies on an older mGluR5 antagonist MPEP, MTEP has subsequently itself acted as a lead compound for newer and even more improved drugs.

EGLU is a drug that is used in neuroscience research. It was one of the first compounds found that acts as a selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), and so has been useful in the characterization and study of this receptor subfamily.

SIB-1893 is a drug used in scientific research which was one of the first compounds developed that acts as a selective antagonist for the metabotropic glutamate receptor subtype mGluR5. It has anticonvulsant and neuroprotective effects, and reduces glutamate release. It has also been found to act as a positive allosteric modulator of mGluR4.

LY-379,268 is a drug that is used in neuroscience research, which acts as a potent and selective agonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3).

CECXG (3'-ethyl-LY-341,495) is a research drug which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), with reasonable selectivity for mGluR3. While it is some five times less potent than LY-341,495 at mGluR3, it has 38x higher affinity for mGluR3 over mGluR2, making it one of the few ligands available that is able to distinguish between these two closely related receptor subtypes.

PCCG-4 is a research drug which acts as a selective antagonist for the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3), with slight selectivity for mGluR2 although not sufficient to distinguish mGluR2 and mGluR3 responses from each other. It is used in research into the function of the group II metabotropic glutamate receptors.

MGS-0039 is a drug that is used in neuroscientific research, which acts as a potent and selective antagonist for group II of the metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluR2/3). It produces antidepressant and anxiolytic effects in animal studies, and has been shown to boost release of dopamine and serotonin in specific brain areas. Research has suggested this may occur through a similar mechanism as that suggested for the similarly glutamatergic drug ketamine.

CBiPES is a drug used in scientific research that acts as a selective positive allosteric modulator for the metabotropic glutamate receptor group II subtype mGluR2. It has potentially antipsychotic effects in animal models, and is used for researching the role of mGluR2 receptors in schizophrenia and related disorders.
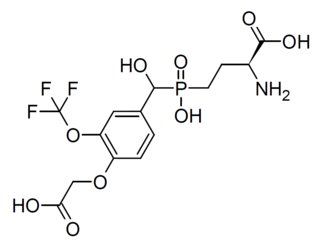
LSP2-9166 is a drug which acts as a selective agonist for the group III metabotropic glutamate receptors, with a reasonably potent EC50 of 70nM at mGluR4 and 220nM at mGluR7, and weaker activity of 1380nM at mGluR6 and 4800nM at mGluR8. It has anticonvulsant effects in animal studies, and reduces self-administration of various addictive drugs.





















