
The 2000 United States presidential election was the 54th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 7, 2000. Republican Texas Governor George W. Bush, the eldest son of George H. W. Bush, narrowly defeated incumbent Democratic Vice President Al Gore. It was the fourth of five U.S. presidential elections, and the first since 1888, in which the winning candidate lost the popular vote, and is considered one of the closest U.S. presidential elections, with long-standing controversy about the result. Gore conceded the election on December 13.

The Peace and Freedom Party (PFP) is a left-wing political party with ballot status in California. Its first candidates appeared on the 1966 New York ballot. The Peace and Freedom Party of California was organized in early 1967, gathering over 103,000 registrants which qualified its ballot status in January 1968 under the California Secretary of State Report of Registration.
Ballot access are rules and procedures regulating the right to candidacy, the conditions under which a candidate, political party, or ballot measure is entitled to appear on voters' ballots in elections in the United States. The jurisprudence of the right to candidacy and right to create a political party are less clear than voting rights in the United States. However, the U.S. Supreme Court has established in multiple cases that the federal constitution does not recognize a fundamental right to candidacy, and that state governments have a legitimate government interest in blocking "frivolous or fraudulent candidacies". As election processes are decentralized by Article I, Section 4, of the United States Constitution, ballot access laws are established and enforced by the states. As a result, ballot access processes may vary from one state to another. State access requirements for candidates generally pertain to personal qualities of a candidate, such as: minimum age, residency, and citizenship. Additionally, many states require prospective candidates to collect a specified number of qualified voters' signatures on petitions of support and mandate the payment of filing fees before granting access; ballot measures are similarly regulated. Each state also regulates how political parties qualify for automatic ballot access, and how those minor parties that do not can. Fundamental to democracy, topics related to ballot access are the subject of considerable debate in the United States.
The Oklahoma Libertarian Party is the state affiliate of the Libertarian Party in Oklahoma. It has been active in state politics since the 1970s, but due to Oklahoma's ballot access requirements the party has been an officially recognized party during only portions of the last twenty-five years. In 2016, The Oklahoma Libertarian Party regained ballot access. The state party has secured ballot access through at least 2024.

The Libertarian Party of New York (LPNY), is the affiliate of the Libertarian Party in the U.S. state of New York. Due to changes in New York State election law in 2020, the Libertarian Party lost its ballot status. It is the recognized affiliate of the national Libertarian Party.
A nonpartisan blanket primary is a primary election in which all candidates for the same elected office run against each other at once, regardless of the political party. Partisan elections are, on the other hand, segregated by political party. Nonpartisan blanket primaries are slightly different from most other elections systems with two rounds/a runoff, also known as "jungle primaries" , in a few ways. The first round of a nonpartisan blanket primary is officially the "primary." Round two is the "general election." Round two must be held, even if one candidate receives a majority in the first round.

Elections in California are held to fill various local, state and federal seats. In California, regular elections are held every even year ; however, some seats have terms of office that are longer than two years, so not every seat is on the ballot in every election. Special elections may be held to fill vacancies at other points in time. Recall elections can also be held. Additionally, statewide initiatives, legislative referrals and referendums may be on the ballot.

The 2008 United States presidential election in California took place on November 4, 2008, in California as part of the 2008 United States presidential election. Voters chose 55 electors, the most out of any of the 50 states, to the Electoral College, who voted for president and vice president.

The 2012 United States presidential election in California took place on November 6, 2012, as part of the 2012 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. California voters chose 55 electors, the most out of any state, to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting incumbent Democratic President Barack Obama and his running mate, Vice President Joe Biden, against Republican challenger and former Massachusetts Governor Mitt Romney and his running mate, Congressman Paul Ryan.
This article contains lists of official and potential third party and independent candidates associated with the 2016 United States presidential election.

Steven Nielson is an American statesman, small government political activist, a former Libertarian Party officer, astronautical engineer, artist, and children's author.

The 2020 United States Senate elections were held on November 3, 2020, with the 33 class 2 seats of the Senate contested in regular elections. Of these, 21 were held by Republicans, and 12 by Democrats. The winners were elected to 6-year terms from January 3, 2021, to January 3, 2027. Two special elections for seats held by Republicans were also held in conjunction with the general elections: one in Arizona, to fill the vacancy created by John McCain's death in 2018; and one in Georgia, following Johnny Isakson's resignation in 2019. These elections ran concurrently with the 2020 United States presidential election in which incumbent president Donald Trump lost to Democratic nominee Joe Biden.

The 2016 United States presidential election in California was held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016, as part of the 2016 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. California voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, businessman Donald Trump, and running mate Indiana Governor Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Secretary of State Hillary Clinton, and her running mate Virginia Senator Tim Kaine. California had 55 electoral votes in the Electoral College, the most of any state.

The 2020 Libertarian Party presidential primaries and caucuses were a series of electoral contests to indicate non-binding preferences for the Libertarian Party's presidential candidate in the 2020 United States presidential election. These differ from the Republican or Democratic presidential primaries and caucuses in that they do not appoint delegates to represent a candidate at the party's convention to select the party's presidential nominee.
This article lists third-party and independent candidates, also jointly known as minor candidates, associated with the 2020 United States presidential election.
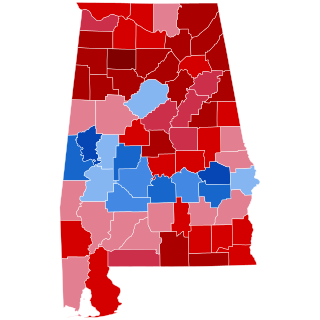
The 2020 United States presidential election in Alabama took place on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states and the District of Columbia participated. Alabama voters chose nine electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting incumbent Republican President Donald Trump and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Mike Pence, against Democratic challenger and former Vice President Joe Biden and his running mate, United States Senator Kamala Harris of California. Also on the ballot was the Libertarian nominee, psychology lecturer Jo Jorgensen and her running mate, entrepreneur and podcaster Spike Cohen. Write-in candidates were permitted without registration, and their results were not individually counted.

The 2020 United States presidential election in Alaska took place on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states and the District of Columbia participated. Alaska voters chose three electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote pitting incumbent Republican President Donald Trump and his running mate, incumbent Vice President Mike Pence, against Democratic challenger and former Vice President Joe Biden and his running mate, United States Senator Kamala Harris of California. The Libertarian, Green, Constitution, and Alliance Party nominees were also on the ballot, as was an Independent candidate.

The 2020 United States presidential election in New York was held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020, as part of the 2020 United States presidential election in which all 50 states plus the District of Columbia participated. New York voters chose electors to represent them in the Electoral College via a popular vote, pitting the Republican Party's nominee, incumbent President Donald Trump, and running mate Vice President Mike Pence against Democratic Party nominee, former Vice President Joe Biden, and his running mate California Senator Kamala Harris. New York had 29 electoral votes in the Electoral College. Trump announced that Florida would be his home state for this election, rather than New York as it had been previously. This was the first presidential election in New York to allow no-excuse absentee voting.
The Libertarian Party of Wyoming (LPWY) is the affiliate of the US Libertarian Party (LP) in Wyoming, headquartered in Riverton. As of 2021 it was the third-largest political party in Wyoming by voter registration, with a share of votes cast that has exceeded 5%.














