
Punjab, also known as the Land of the Five Rivers, is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia. It is located in the northwestern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising areas of modern-day eastern-Pakistan and northwestern-India. Punjab's major cities are Lahore, Faisalabad, Rawalpindi, Gujranwala, Multan, Ludhiana, Amritsar, Sialkot, Chandigarh, Shimla, Jalandhar, Patiala, Gurugram, and Bahawalpur.

A princely state was a nominally sovereign entity of the British Indian Empire that was not directly governed by the British, but rather by an Indian ruler under a form of indirect rule, subject to a subsidiary alliance and the suzerainty or paramountcy of the British crown.

Bundelkhand is a geographical and cultural region and a proposed state and also a mountain range in central & North India. The hilly region is now divided between the states of Uttar Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh, with the larger portion lying in the latter state.

Bamra State or Bamanda State, covering an area of 5,149 km2, was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. Its capital was in Debagarh (Deogarh). Bamra State acceded to India in 1948.

The Khanate of Kalat was a Brahui Khanate that originated in the modern-day Kalat region of Pakistan. Formed in 1666 due to the threat of Mughal expansion in the region, it controlled the wider Balochistan at its greatest extent in the mid-18th century, extending from Kerman in the west to Sindh in the east and from Helmand River in the north to the Arabian Sea in the south. The Khanate of Kalat lost considerable area to Qajar Iran and the Emirate of Afghanistan in the early 19th century, and the city of Kalat was itself sacked by the British in 1839.
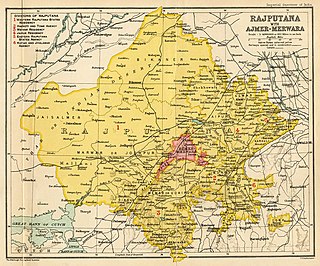
Rājputana, meaning Land of the Rajputs, was a region in the Indian subcontinent that included mainly the present-day Indian state of Rajasthan, as well as parts of Madhya Pradesh and Gujarat, and some adjoining areas of Sindh in modern-day southern Pakistan.

The Chamber of Princes was an institution established in 1920 by a royal proclamation of King-Emperor George V to provide a forum in which the rulers of the princely states of India could voice their needs and aspirations to the colonial government of British India. It survived until the end of the British Raj in 1947.

Jammu and Kashmir, also known as Kashmir and Jammu, was a princely state in a subsidiary alliance with the British East India Company from 1846 to 1858 and under the paramountcy of the British Crown, from 1858 until the Partition of India in 1947, when it became a disputed territory, now administered by three countries: China, India, and Pakistan. The princely state was created after the First Anglo-Sikh War, when the East India Company, which had annexed the Kashmir Valley, from the Sikhs as war indemnity, then sold it to the Raja of Jammu, Gulab Singh, for rupees 75 lakhs.

Patna State was a princely state in the Eastern States Agency of India during the British Raj. It had its capital at Balangir. Its area was 6,503 km2 (2,511 sq mi).

Garhwal Kingdom was an independent Himalayan kingdom in the current north-western Himalayan state of Uttarakhand, India, founded in 823 CE by Kanak Pal the progenitor of the Panwar dynasty that ruled over the kingdom uninterrupted until 1803 CE.
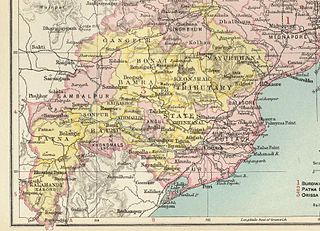
Gangpur State, also known as Gangpore State, was one of the princely states of India during the period of the British Raj. Until 1905 it was one of the Chhota Nagpur States under the Eastern States Agency.
Pal Lahara was a princely state in what is today India during the British Raj. It had its capital at Pal Lahara.

Junagarh or Junagadh was a princely state in Gujarat ruled by the Muslim Babi dynasty in India, which acceded to the Dominion of Pakistan after the Partition of British India. Subsequently, the Union of India annexed Junagadh in 1948, legitimized through a plebiscite held the same year.
Kharedi-Virpur was a third class princely state in British India under Kathiawar Agency. It was ruled by Jadeja Rajput chiefs descended from the Nawanagar ruling family.

Kalahandi State, also known as Karond State, was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. It was recognized as a state in 1874 and had its capital in Bhawanipatna. Its last ruler signed the accession to the Indian Union on 1 January 1948. The present titular head of the former state is Anant Pratap Deo who resides in the Kalahandi Palace in Bhawanipatna

Bonai State was a minor princely state during the British Raj in what is today India. It was one of the Chota Nagpur States and had its capital at Bonaigarh, located in the present-day Sundergarh district of Odisha. It had an area of 8,907 square kilometres (3,439 sq mi) and a population of 24,026 in 1892 with an average annual revenue of Rs.60,000 in 1901.

The Bhanja dynasty is a dynasty that originated in the northern and central regions of modern Odisha before the Gupta Empire became an imperial power. The dynasty, of ancient local Kshatriya lineage as documented by Hermann Kulke, succeeded the Vindhyatabi branch of the Nagas of Padmavati, who ruled from the Keonjhar district of Odisha and included Satrubhanja of the Asanpat inscription. The Bhanj later became feudatories of the Bhauma-Kara dynasty.

Mayurbhanj State was one of the princely states of India during the British Raj. It was one of the largest states of the Eastern States Agency and one of the four salute states of the Orissa States Agency. The emblem of the state was two peacocks, for according to legend the ancestors of the rulers had originated from a peafowl's eyes.
Chandel or Chandela is a Rajput clan from India. Families belonging to this clan ruled several kingdoms in north India and held various feudal estates. The most notable of these were the Chandelas of Jejakabhukti, who ruled the Bundelkhand region.















