The Akatsuki-class destroyer was a class of four destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. According to most sources, they are regarded as a sub-class of the Fubuki class, partly because the Imperial Japanese Navy itself kept the improvements made a secret, and did not officially designate these four destroyers as a separate class.

Natsushio was the sixth vessel to be commissioned in the 19-vessel Kagerō-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy in the late-1930s under the Circle Three Supplementary Naval Expansion Program.

The Minekaze class was a class of fifteen 1st-class destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy. Obsolete by the beginning of the Pacific War, the Minekaze-class ships were then relegated to mostly secondary roles, serving throughout the war as patrol vessels, high speed transports, target control vessels, and as kaiten carriers. Most ultimately were lost to U.S. and British submarines. The basic design of the Minekaze was used for the next three classes of Japanese destroyers, a total of 36 ships.

Ōi (大井) was the fourth of five Kuma-class light cruiser, which served in the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. She was named after the Ōi River in Shizuoka prefecture, Japan. Designed as a command vessel for a destroyer squadron, she was converted into a torpedo cruiser with forty torpedo launch tubes in a plan abandoned by the Japanese Navy in 1942. During most of the Pacific War, she was used primarily as a fast troop transport and was sunk by a United States Navy submarine in 1944.

The Kamikaze-class destroyers were a class of nine destroyers of the Imperial Japanese Navy. Some authors consider the Nokaze, Kamikaze and Mutsuki classes to be extensions of the Minekaze-class destroyers, and the Kamikaze class is sometimes referred to as the "Kiyokaze class" to distinguish it from the earlier World War I-era destroyer class of the same name. Obsolete by the beginning of the Pacific War, the Kamikazes were relegated to mostly secondary roles. Most ultimately were lost to U.S. submarines.

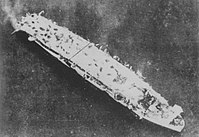
The Momo-class destroyer consisted of four destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War I. As with the previous Kaba class, all were named after trees.

Akashi was a Japanese repair ship, serving during World War II. She was the only specifically designed repair ship operated by the Imperial Japanese Navy. The navy based her design on the US Navy's USS Medusa.

The Urakaze-class destroyers were a class of two destroyers built for the Imperial Japanese Navy by Yarrow Shipbuilders of Scotland. These were the last Japanese destroyers ordered from overseas shipyards. While still under construction, one ship was transferred to Italy in 1916.

The Sokuten-class minelayer was a class of minelayers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II. The class consists of three subclasses, which this article handles collectively.

The Kamishima-class minelayer was a class of minelayers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after World War II. Nine vessels were planned under the Maru Sen Programme; however, only one vessel was completed by the end of war.

Minoo (箕面) was a minelayer of the Imperial Japanese Navy, which was in service during the final stages of World War II. She was the lead ship of what was intended to be a two-vessel class, but her sister ship, designated Vessel #1822 was not completed before the end of the war.

The Sokuten-class minelayer was a class of auxiliary minelayers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during the 1910s and World War II. They were called the Sokuten class from their nameship. They were also called the Toshima class after Sokuten was retired. In some sources Natsushima was included in this class. Their official class name was not mentioned in IJN official documents.

Ning Hai was a light cruiser in the Republic of China Navy (ROCN) before World War II and the lead ship of her class. She was sunk in the early days of the Second Sino-Japanese War by aircraft from the Imperial Japanese Navy, and her wreck was raised and repaired by the Japanese, re-entering service with the Japanese Navy in the Pacific War as the escort vessel Ioshima (五百島). She was sunk again in September 1944 by a USN submarine.

The Natsushima-class minelayer was a class of minelayers of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), serving during and after the 1930s through World War II. Their design was based on the Tsubame class, but with increased armament.

Kaibōkan or coastal defense ship was a type of naval ship used by the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II for escort duty and coastal defense. The term escort ship was used by the United States Navy to describe this category of Japanese ships.

Katsuriki (勝力) was a minelayer of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during World War I and World War II, the only ship of her class. She was the first purpose-built ocean-minelayer in the Japanese Navy.

The Ōtomari (大泊) was an icebreaker of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during the 1920s through World War II, the only ship of her class. She was the only icebreaker warship in the IJN.

The Nosaki (野埼) was a food supply ship of the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN) serving during World War II, the only ship of her class.

Chihaya (千早) was an unprotected cruiser of the Imperial Japanese Navy. The name Chihaya comes from Chihaya Castle, near Osaka, the site of one of the battles of the Genkō War of 1333.
CD-43 was a C Type class escort ship (Kaibōkan) of the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Second World War. She was laid down by Mitsubishi Heavy Industries at their Kobe Shipyard on 10 April 1944, launched on 22 June 1944, and completed and commissioned on 31 July 1944. During the war CD-43 was mostly busy on escort duties.