Related Research Articles

The national parks of Scotland are managed areas of outstanding landscape where some forms of development are restricted to preserve the landscape and natural environment. At present, Scotland has two national parks: Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park, created in 2002, and the Cairngorms National Park, created in 2003.
The UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserves (WNBR) covers internationally designated protected areas, known as biosphere or nature reserves, which are meant to demonstrate a balanced relationship between people and nature. They are created under the Man and the Biosphere Programme (MAB).

Caerlaverock is a national nature reserve (NNR) covering parts of the mudflats and shoreline of the Solway Firth about 10 km south of Dumfries, in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. It lies between the River Nith and the Lochar Water, and consists of a variety of wetland habitats including bare mud and sand, merse and marshes, and is fringed by neutral grassland on the landward side. A nature reserve was designated in 1957 at the instigation of the Duke of Norfolk. The NNR covers an area of 82 square kilometres (32 sq mi) and is an internationally important wintering site for waterfowl and wading birds.
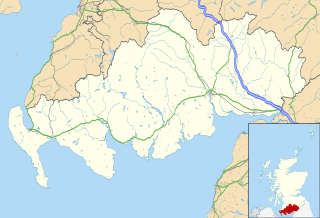
Dumfries and Galloway is one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland, located in the western part of the Southern Uplands. It is bordered by East Ayrshire, South Ayrshire, and South Lanarkshire to the north; Scottish Borders to the north-east; the English county of Cumbria, the Solway Firth, and the Irish Sea to the south, and the North Channel to the west. The administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Dumfries. The second largest town is Stranraer, located 76 miles (122 km) to the west of Dumfries on the North Channel coast.
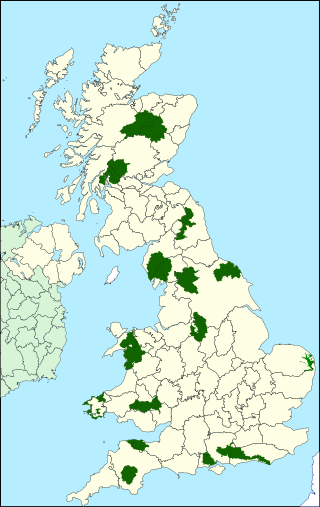
National parks of the United Kingdom are 15 areas of relatively undeveloped and scenic landscape across the country. Despite their name, they are quite different from national parks in many other countries, which are usually owned and managed by governments as protected community resources, and which do not usually include permanent human communities. In the United Kingdom, an area designated as a national park may include substantial settlements and human land uses that are often integral parts of the landscape. Land within national parks remains largely in private ownership. These parks are therefore not "national parks" according to the internationally accepted standard of the IUCN but they are areas of outstanding landscape where planning controls are a little more restrictive than elsewhere.

Beinn Eighe is a mountain massif in the Torridon area of Wester Ross in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. Lying south of Loch Maree, it forms a long ridge with many spurs and summits, two of which are classified as Munros: Ruadh-stac Mòr at 1,010 m (3,314 ft) and Spidean Coire nan Clach at 993 m (3,258 ft). Unlike most other hills in the area it has a cap of Cambrian basal quartzite which gives the peaks of Beinn Eighe a distinctive light colour. Its complex topography has made it popular with both hillwalkers and climbers and the national nature reserve on its northern side makes it an accessible mountain for all visitors.

The North Devon Coast is a designated Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty in Devon, England, designated in September 1959. The AONB contributes to a family of protected landscapes in the Southwest of England and a total of 38% of the region is classified by the International Union for Conservation of Nature as Category V Protected Landscapes. The twelve Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty extend to 30% of the region, twice the proportion covered by AONBs in England as a whole and a further two National Parks, Dartmoor and Exmoor, cover an additional 7%.

The Konza Prairie Biological Station is a 8,616-acre (3,487 ha) protected area of native tallgrass prairie in the Flint Hills of northeastern Kansas. "Konza" is an alternative name for the Kansa or Kaw Indians who inhabited this area until the mid-19th century. The Konza Prairie is owned by The Nature Conservancy and Kansas State University.

Cairnsmore of Fleet is an isolated mountain in the Southern Uplands of Scotland. The mountain forms an unafforested granite massif, whose highest point is about ten kilometres east of Newton Stewart. It is the highest of the "Solway Hills" sub-range, and the southernmost of Scotland's 219 Grahams, thus making it, or rather its subsidiary top, Knee of Cairnsmore, the most southerly mountain in Scotland. The view to the south takes in the Cree Estuary and Wigtown Bay, and extends as far as the Lake District, the Isle of Man and Snowdonia. The highest summits of the Galloway Hills can be seen to the north, and Ireland is in the view to the west.
Under UNESCO’s Man and the Biosphere Programme, there are 308 biosphere reserves recognized as part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in Europe and North America. These are distributed across 41 countries in the region.

The World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) is the largest assembly of data on the world's terrestrial and marine protected areas, containing more than 260,000 protected areas as of August 2020, with records covering 245 countries and territories throughout the world. The WDPA is a joint venture between the United Nations Environment Programme World Conservation Monitoring Centre and the International Union for Conservation of Nature World Commission on Protected Areas.

Baixa Limia – Serra do Xurés is a 209 km2 (81 sq mi) natural park in Galicia, Spain. It is located in the southern province of Ourense. The park was established in 1993. Serra do Xurés is the Galician name for a range of mountains which straddle the border between Spain and Portugal: the Portuguese variant is Gerês.
Mongol Daguur is a steppe and wetland region in Mongolia listed as a UNESCO Biosphere Reserve and Ramsar Site of International Importance. A transboundary ecoregion straddling three countries, the area is located in Dornod Province of eastern Mongolia, and is contiguous with the Daurian ecoregion in Russia and the Hulun Lake wetlands in China. The area is categorized as a Strictly Protected Area within the framework of protected areas in Mongolia.

The Fundy Biosphere Region is an area of rugged woodlands and coastline that lies along next the upper Bay of Fundy in New Brunswick, Canada. The area covers 442,250 hectares, and was named and designated as a biosphere reserve by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) in 2007.

North Devon's Biosphere Reserve is a UNESCO biosphere reserve in North Devon. It covers 55 square miles (140 km2) and is centred on Braunton Burrows, the largest sand dune system (psammosere) in England. The boundaries of the reserve follow the edges of the conjoined catchment basin of the Rivers Taw and the Torridge and stretch out to sea to include the island of Lundy. The biosphere reserve is primarily lowland farmland, and includes many protected sites including 63 Sites of Special Scientific Interest which protect habitats such as culm grassland and broadleaved woodlands. The most populous settlements in its buffer area are Barnstaple, Bideford, Northam, Ilfracombe, and Okehampton.

The Round Loch of Glenhead is a small upland single basin loch in Dumfries and Galloway. It is situated within Galloway Forest Park to the west of the hill Craiglee. It forms a pair with the nearby Long Loch of Glenhead. Both lochs are of similar sizes and each have a small island. The two lochs are separated from Loch Valley and Loch Naroch to the north by the Rig of the Jarkness. The loch is drained to the southwest by Round Loch Burn, which after joining into Glenhead Burn flows into Loch Trool.

Situated in south-west Scotland, the Silver Flowe-Merrick Kells biosphere reserve is composed of two separate sites.

Taynish National Nature Reserve is situated southwest of the village of Tayvallich in the council area of Argyll and Bute on the west coast of Scotland. The reserve encompasses almost all of the Taynish peninsula, which is around 5 km long and 1 km wide. The woodlands at Taynish are often described as a 'temperate rainforest', benefiting from the mild and moist climate brought about by the Gulf Stream. Taynish is owned and managed by NatureScot and was declared a national nature reserve (NNR) in 1977. The reserve was formerly also a biosphere reserve, but this status was withdrawn in 2014.

Hoy and West Mainland is a national scenic area (NSA) covering parts of the islands of Hoy and Mainland in the Orkney Islands of Scotland, as well as parts of the surrounding sea. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection by restricting certain forms of development. The Hoy and West Mainland NSA covers 24,407 ha in total, consisting of 16,479 ha of land with a further 7928 ha being marine.

Silver Flowe is an area of patterned blanket mire in the Galloway Hills, in Dumfries and Galloway, Scotland. Located around 16 km north northeast of Newton Stewart, it forms part of the Galloway Forest Park. An area of 620 hectares has been designated as a Ramsar Site.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 "Biosphere reserve". www.nature.scot. Nature Scotland. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ↑ "Wester Ross Biosphere Reserve". www.en.unesco.org. UNESCO. Retrieved 8 February 2024.
- ↑ "Galloway and Southern Ayrshire Biosphere Reserve". www.en.unesco.org. UNESCO. Retrieved 8 February 2024.