Processor design is a subfield of computer engineering and electronics engineering (fabrication) that deals with creating a processor, a key component of computer hardware.

AVR is a family of microcontrollers developed since 1996 by Atmel, acquired by Microchip Technology in 2016. These are modified Harvard architecture 8-bit RISC single-chip microcontrollers. AVR was one of the first microcontroller families to use on-chip flash memory for program storage, as opposed to one-time programmable ROM, EPROM, or EEPROM used by other microcontrollers at the time.

A system on a chip or system-on-chip is an integrated circuit that integrates most or all components of a computer or other electronic system. These components almost always include on-chip central processing unit (CPU), memory interfaces, input/output devices, input/output interfaces, and secondary storage interfaces, often alongside other components such as radio modems and a graphics processing unit (GPU) – all on a single substrate or microchip. SoCs may contain digital, and also analog, mixed-signal, and often radio frequency signal processing functions.
SuperH is a 32-bit reduced instruction set computing (RISC) instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Hitachi and currently produced by Renesas. It is implemented by microcontrollers and microprocessors for embedded systems.
OpenRISC is a project to develop a series of open-source hardware based central processing units (CPUs) on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. It includes an instruction set architecture (ISA) using an open-source license. It is the original flagship project of the OpenCores community.
LEON is a radiation-tolerant 32-bit central processing unit (CPU) microprocessor core that implements the SPARC V8 instruction set architecture (ISA) developed by Sun Microsystems. It was originally designed by the European Space Research and Technology Centre (ESTEC), part of the European Space Agency (ESA), without any involvement by Sun. Later versions have been designed by Gaisler Research, under a variety of owners. It is described in synthesizable VHSIC Hardware Description Language (VHDL). LEON has a dual license model: An GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) and GNU General Public License (GPL) free and open-source software (FOSS) license that can be used without licensing fee, or a proprietary license that can be purchased for integration in a proprietary product. The core is configurable through VHDL generics, and is used in system on a chip (SOC) designs both in research and commercial settings.
The MicroBlaze is a soft microprocessor core designed for Xilinx field-programmable gate arrays (FPGA). As a soft-core processor, MicroBlaze is implemented entirely in the general-purpose memory and logic fabric of Xilinx FPGAs.
V850 is a 32-bit RISC CPU architecture produced by Renesas Electronics for embedded microcontrollers. It was designed by NEC as a replacement for their earlier NEC V60 family, and was introduced shortly before NEC sold their designs to Renesas in the early 1990s. It has continued to be developed by Renesas as of 2018.

A multi-core processor is a microprocessor on a single integrated circuit with two or more separate processing units, called cores, each of which reads and executes program instructions. The instructions are ordinary CPU instructions but the single processor can run instructions on separate cores at the same time, increasing overall speed for programs that support multithreading or other parallel computing techniques. Manufacturers typically integrate the cores onto a single integrated circuit die or onto multiple dies in a single chip package. The microprocessors currently used in almost all personal computers are multi-core.

AVR32 is a 32-bit RISC microcontroller architecture produced by Atmel. The microcontroller architecture was designed by a handful of people educated at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, including lead designer Øyvind Strøm and CPU architect Erik Renno in Atmel's Norwegian design center.

Minimig is an open source re-implementation of an Amiga 500 using a field-programmable gate array (FPGA).
A computer-on-module (COM) is a type of single-board computer (SBC), a subtype of an embedded computer system. An extension of the concept of system on chip (SoC) and system in package (SiP), COM lies between a full-up computer and a microcontroller in nature. It is very similar to a system on module (SOM).
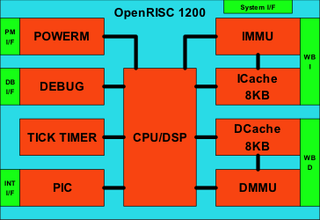
The OpenRISC 1200 (OR1200) is an implementation of the open source OpenRISC 1000 RISC architecture.
Heterogeneous computing refers to systems that use more than one kind of processor or core. These systems gain performance or energy efficiency not just by adding the same type of processors, but by adding dissimilar coprocessors, usually incorporating specialized processing capabilities to handle particular tasks.
RISC-V is an open standard instruction set architecture (ISA) based on established reduced instruction set computer (RISC) principles. Unlike most other ISA designs, RISC-V is provided under royalty-free open-source licenses. A number of companies are offering or have announced RISC-V hardware; open source operating systems with RISC-V support are available, and the instruction set is supported in several popular software toolchains.
The ZPU is a microprocessor stack machine designed by Norwegian company Zylin AS to run supervisory code in electronic systems that include a field-programmable gate array (FPGA).

SiFive, Inc. is a fabless semiconductor company and provider of commercial RISC-V processor IP and silicon chips based on the RISC-V instruction set architecture (ISA). SiFive's products include cores, SoCs, IPs, and development boards.
Since 1985, many processors implementing some version of the MIPS architecture have been designed and used widely.






