The following page lists all power stations in Rwanda . The country is in the midst of a rapid expansion of its electrical grid and many new plants are proposed or under construction. Rwanda is planning to expand its grid power up to 556 MW in 2024. As of December 2022 [update] , the national installed generation capacity totaled 276.068 megawatts. [1] [2] with peak demand of 140.6MW.
| Hydroelectric station | Community | Coordinates | River | Type | Name of reservoir | Capacity (MW) | Year completed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ntaruka Power Station | Ntaruka | Mukungwa River | Run of river | N/A | 11.5 MW | 1959 [3] | |
| Mukungwa Power Station | Mukungwa | Mukungwa River | Run of river | N/A | 12 MW | 1982 | |
| Mukungwa II Power Station | Mukungwa | MUkungwa River | Run of river | N/A | 2.5 MW [4] | 2010 | |
| Nyabarongo I Power Station | Nyabarongo | Nyabarongo River | Run of river | N/A | 28 MW [5] | 2014 [6] | |
| Rukarara Hydroelectric Power Station | Rukarara | River Rukarara | Run of river | N/A | 9.5 MW | 2010 [7] | |
| Rusizi I Hydroelectric Power Station | Rusizi | Rusizi River | Run of river | N/A | 30 MW | 1958 | |
| Rusizi II Hydroelectric Power Station | Rusizi | Rusizi River | Run of river | N/A | 44 MW | 1989 | |
| Hydroelectric station | Community | Coordinates | River | Type | Name of reservoir | Capacity (MW) | Year completed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Rusumo Power Station | Rusumo | Kagera River | Run of river | N/A | 80 MW [1] [8] | 2023 (expected) | |
| Nyabarongo II Power Station | Nyabarongo | Nyabarongo River | Run of river | N/A | 43 MW [1] | 2027 | |
| Rusizi III Power Station | Rusizi | Ruzizi River | Run of river | N/A | 147 MW [9] | 2023 | |
| Rusizi IV Power Station | Rusizi | Ruzizi River | Run of river | N/A | 287 MW | 2025 | |
| Thermal power station | Community | Coordinates | Fuel type | Capacity | Year completed | Name of Owner | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KivuWatt Power Station | Kibuye, Karongi District | Methane | 25 MW [10] [11] | 2015 | Contour Global | Under expansion to 100 MW [12] | |
| Kibuye Power Plant 1 [13] | Kibuye, Karongi District | Methane | 3.5MW [12] | 2012 | Government of Rwanda | ||
| Gishoma Thermal Power Station [14] | Rusizi District, Western Rwanda | Peat | 15 MW | 2016 | Shengli Energy Group and Punj Lloyd |
| Thermal power station | Community | Coordinates | Fuel type | Capacity | Year completed | Name of Owner | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gisagara Thermal Power Station [14] | Gisagara District, Southern Rwanda | Peat | 80 MW [1] | 2021 (expected) | Hakan | ||
| Symbion Thermal Power Station [15] | Nyamyumba, Gisenyi, Rubavu District | Methane | 50 MW | 2018 (expected) [12] | Symbion Power Inc. | Can be expanded to 100 MW | |
| Solar power station | Community | Coordinates | Fuel type | Capacity | Year completed | Name of Owner | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ngoma Solar Power Station | Kibungo, Ngoma District | Solar | 2.4 MW | 2011 | Government of Rwanda | [16] [17] | |
| Rwamagana Solar Power Station | Agahozo, Rwamagana District | Solar | 8.5 MW [18] | 2015 | Scatec Solar Company & Gigawatt Global Cooperatief [1] | ||
| Nasho Solar Power Plant | Rwinkwavu, Rwamagana District | Solar | 3.3 MW [19] | 2018 | Rwanda Energy Group [1] | ||
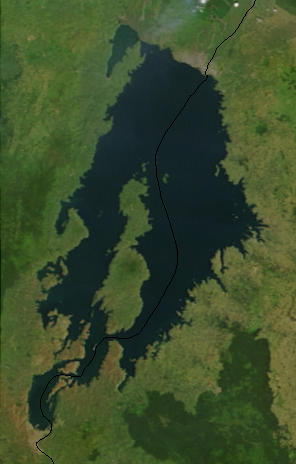
Lake Kivu is one of the African Great Lakes. It lies on the border between the Democratic Republic of the Congo and Rwanda, and is in the Albertine Rift, the western branch of the East African Rift. Lake Kivu empties into the Ruzizi River, which flows southwards into Lake Tanganyika.
Bank of Kigali (BK) is a commercial bank in Rwanda. It is licensed by the National Bank of Rwanda.

Bralirwa, also known by its French name Brasseries et Limonaderies du Rwanda, is the largest brewer and soft beverage company in Rwanda. Its shares of stock are listed on the Rwanda Stock Exchange, where they trade under the symbol:BLRW. As of December 2017, the company's total assets were valued at RWF:127.73 billion, with shareholders' equity of RWF:35.7 billion.
The Rusumo Hydroelectric Power Station, also known as the Rusumo Power Station, is a hydropower plant under construction, with initial planned capacity installation of 80 megawatts (110,000 hp) when completed. The project will involve the construction of a dam, with run of river design. A more expensive 90 megawatts (120,000 hp) reservoir design was considered before being abandoned in favor of an 80 MW project with a smaller environmental impact and an estimated cost of US$300 million compared to US$400 million for the bigger project. The World Bank announced on 6 August 2013 that it had approved loans totaling US$340 million towards the US$468.60 million needed for the project. In November 2013, the African Development Bank approved a loan of US$113 million towards completion of the project.
Nyabarongo I Hydroelectric Power Station is a 28 megawatts (38,000 hp) hydroelectric power station in Rwanda.

Energy use in Rwanda is undergoing rapid change at the beginning of the 21st century.
KivuWatt Power Station is a 26 MW (35,000 hp) methane gas-fired thermal power plant in Rwanda.
Symbion Thermal Power Station is a 56 megawatts (75,000 hp) methane gas-fired thermal power plant located at the Cape of Busororo near the town of Nyamyumba in Rubavu District, in the Western Province of Rwanda.
Gishoma Thermal Power Station is a 15 MW (20,000 hp), peat-fired thermal power plant, under construction in Gishoma, Rusizi District, in the Western Province of Rwanda.
Kibuye Power Plant 1, also Kibuye Thermal Power Station 1 (KP1), is a 3.6 megawatts (4,800 hp) methane gas-fired thermal power plant in Rwanda.
The East Africa Exchange (EAX), also, East African Commodity Exchange, is a privately funded regional, agricultural commodities exchange in East Africa. It was launched in Kigali, Rwanda, in July 2014. EAX is the third-largest agricultural commodities exchange in Africa, behind the South African Futures Exchange and the Ethiopia Commodity Exchange.
Rusumo, is a town in Kirehe District in the Eastern Province of Rwanda.
Ruzizi III Hydroelectric Power Station is a proposed hydropower plant with planned capacity installation of 206 MW when completed.
Kawanda–Birembo High Voltage Power Line is a high voltage electricity power line, under construction, connecting the high voltage substation at Kawanda, in Uganda to another high voltage substation at Birembo, in Rwanda.
The Isaka–Kigali Standard Gauge Railway is a planned railway line linking the town of Isaka in Tanzania to the city of Kigali in Rwanda.
Cimerwa Cement Limited (CCL) is a manufacturer of cement in Rwanda with capacity of approximately 600,000 tones per year.
The Rwanda Standard Gauge Railway is a railway system, under development, linking the country to the neighboring countries of Tanzania and Uganda. The system is expected to link, in the future, to Rwanda's two other neighbors, Burundi and the Democratic Republic of the Congo, as part of East African Railway Master Plan. Through Uganda, the SGR will allow faster access to the Kenyan port of Mombasa, Rwanda's primary access to the oceans. With no previously existing railway network, Rwanda is developing its railway system from scratch.
The Gasmeth Energy Gas Works (GEGW) is a planned methane gas extraction and processing plant in Rwanda.