
The Senegal River is a 1086 km (675 mi) long river in West Africa; much of its length marks part of the border between Senegal and Mauritania. It has a drainage basin of 270000 km2, a mean flow of 680 m3/s (24,000 cu ft/s), and an annual discharge of 21.5 km3 (5.2 cu mi). Important tributaries are the Falémé River, Karakoro River, and the Gorgol River. The river divides into two branches once it passes Kaédi The left branch, called the Doué, runs parallel to the main river to the north. After 200 km (120 mi) the two branches rejoin a few kilometers downstream of Podor.

The African manatee, also known as the West African manatee, is a species of manatee that inhabits much of the western region of Africa – from Senegal to Angola. It is the only manatee species to be found in the Old World.

Kayes Region is one of eight first level national subdivisions in Mali called Regions. It is the first administrative area of Mali and covers an area of 120,760 square kilometres or 46,630 square miles. Its capital is the town of Kayes. The province was historically part of the Ghana Empire and the Mali Empire.

The Bafing River is the upper course and largest tributary of the Senegal River which runs through Guinea and Mali and is about 350 miles (560 km) long.

Bafoulabé is a town and rural commune in south-western Mali. It is located in the Region of Kayes at the confluence of the Bafing and Bakoy rivers which join to become the Sénégal River. Bafoulabé is the capital of the Cercle of Bafoulabé, which in 1887 was the first Cercle to be created in Mali.
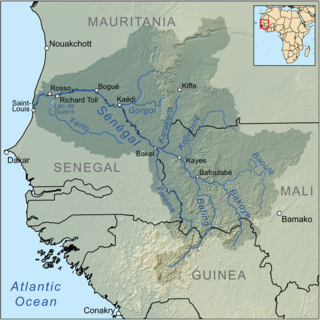
The Bakoy or Bakoye River is a river in West Africa. It runs through Guinea and Mali and joins with the Bafing River to form the Sénégal River at Bafoulabé in the Kayes Region of western Mali. In Manding languages, Bakoye signifies 'white river', Bafing 'black river' and Baloué 'red river'.
The wildlife of Mali, composed of its flora and fauna, is widely varying from the Saharan desert zone to the Sahelian east–west zone, to Mali, a landlocked francophone country in North Africa; large swathes of Mali remain unpopulated but has three sub-equal vegetation zones; the country has Sahara Desert in the north, the Niger River Basin at its center and the Senegal River on the south.
The mountain barbel is a species of fish in the genus Amphilius. Its length reaches 9.2 cm.

Lake Manantali is a large artificial lake, formed by the 1989 construction of the Manantali Dam, on the Bafing River in Mali. Its northern point is located 90 km to the south-east of the city of Bafoulabé.
The Jakhanke -- also spelled Jahanka, Jahanke, Jahanque, Jahonque, Diakkanke, Diakhanga, Diakhango, Dyakanke, Diakhanké, Diakanké, or Diakhankesare -- are a Manding-speaking ethnic group in the Senegambia region, often classified as a subgroup of the larger Soninke. The Jakhanke have historically constituted a specialized caste of professional Muslim clerics (ulema) and educators. They are centered on one larger group in Guinea, with smaller populations in the eastern region of The Gambia, Senegal, and in Mali near the Guinean border. Although generally considered a branch of the Soninke, their language is closer to Western Manding languages such as Mandinka.

The Kolenté River is a river in Guinea and Sierra Leone. The river forms a portion of the international border between the two countries. It empties into the Atlantic Ocean at Barlo Point, Sierra Leone. In Guinea, it is known as the Kolenté and in Sierra Leone, it is known as the Great Scarcies.

The Félou Falls are located on the Sénégal River 15 kilometres (9.3 mi) upstream of Kayes in western Mali. The river tumbles 13 metres (43 ft) down an irregular series of rocky steps. The waterfalls mark the furthest point from the mouth of the river that can be reached by boat. In 2009 work started on the construction of the Félou Hydroelectric Plant, a 62.3 megawatts (83,500 hp) run-of-the-river hydroelectric plant at the falls replacing a small 600 kW plant dating from the 1920s.

The Baoulé River is a river in Mali in West Africa. It flows from a source west of Bamako to the Bakoy downastream of Toukoto and forms part of the Senegal watershed.

The Guinea–Sierra Leone border is 794 km in length and runs from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the tripoint with Liberia in the east.

The Guinea–Mali border is 1,062 km in length and runs from the tripoint with Senegal in the north to the tripoint with Ivory Coast in the south.
Koukoutamba Hydroelectric Power Station is a planned 294 megawatts (394,000 hp) hydroelectric power station, across the Bafing River, a tributary of the Senegal River, in Guinea. The power station is under development by the Organisation pour la mise en valeur du fleuve Sénégal (OMVS),. OMVS will sell the electricity to the four member electricity utility companies of the organization. Sinohydro, a hydropower engineering and construction company, owned by the Chinese state, was awarded the engineering, procurement and construction (EPC) contract. The US$812 million project is funded by the Exim Bank of China.











