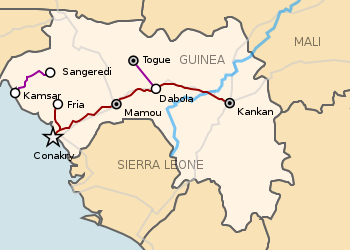
Transport in Guinea is composed by a variety of systems that people in the country use to get around as well as to and from domestic and international destinations. The railway from Conakry to Kankan ceased operating in the mid-1980s. [1] Most vehicles in Guinea are 20+ years old, and cabs are any four-door vehicle which the owner has designated as being for hire. Domestic air services are intermittent. Conakry International Airport is the largest airport in the country, with flights to other cities in Africa as well as to Europe.
Contents
- Railways
- Santou - Dapilon
- Chemin de Fer de Boké
- Chemin de fer de Conakry – Fria
- Chemin de Fer de Guinee
- Societe des Bauxites de Kindia (SBK)
- TransGuinean Railway (under construction 2025)
- Timeline
- Statistics
- Highways
- Waterways
- Ports and harbors
- Merchant marine
- Airports
- Airports - with paved runways
- Airports - with unpaved runways
- See also
- References
- External links
Locals, nearly entirely without vehicles of their own, rely upon these taxis (which charge per seat) and small buses to take them around town and across the country. There is some river traffic on the Niger and Milo rivers. Horses and donkeys pull carts, primarily to transport construction materials.
Iron mining at Simandou (North and South blocks) in the southeast is leading to the construction of a new heavy-haul standard gauge railway and deep-water port. Bauxite mining at Kalia in the east is may link to this line.