
The cheetah is a large cat with a tawny to creamy white or pale buff fur that is marked with evenly spaced, solid black spots. Its head is small and rounded, with a short snout and black tear-like facial streaks. It reaches 67–94 cm (26–37 in) at the shoulder, and the head-and-body length is between 1.1 and 1.5 m. Adults weigh between 21 and 72 kg. It is the fastest land animal, capable of running at 93 to 104 km/h ; it has evolved specialized adaptations for speed, including a light build, long thin legs and a long tail.

The Namib is a coastal desert in Southern Africa. According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than 2,000 kilometres (1,200 mi) along the Atlantic coasts of Angola, Namibia, and northwest South Africa, extending southward from the Carunjamba River in Angola, through Namibia and to the Olifants River in Western Cape, South Africa. The Namib's northernmost portion, which extends 450 kilometres (280 mi) from the Angola-Namibia border, is known as Moçâmedes Desert, while its southern portion approaches the neighboring Kalahari Desert. From the Atlantic coast eastward, the Namib gradually ascends in elevation, reaching up to 200 kilometres (120 mi) inland to the foot of the Great Escarpment. Annual precipitation ranges from 2 millimetres (0.079 in) in the aridest regions to 200 millimetres (7.9 in) at the escarpment, making the Namib the only true desert in southern Africa. Having endured arid or semi-arid conditions for roughly 55–80 million years, the Namib may be the oldest desert in the world and contains some of the world's driest regions, with only western South America's Atacama Desert to challenge it for age and aridity benchmarks.

The Namib-Naukluft Park is a national park in western Namibia, situated between the coast of the Atlantic Ocean and the edge of the Great Escarpment. It encompasses part of the Namib Desert, the Naukluft mountain range, and the lagoon at Sandwich Harbour. The best-known area of the park and one of the main visitor attractions in Namibia is Sossusvlei, a clay pan surrounded by dunes, and Sesriem, a small canyon of the Tsauchab. The desert research station of Gobabeb is situated within the park.

The Damara, plural Damaran are an ethnic group who make up 8.5% of Namibia's population. They speak the Khoekhoe language and the majority live in the northwestern regions of Namibia, however they are also found widely across the rest of the country.

The Etosha Pan is a large endorheic salt pan, forming part of the Cuvelai-Etosha Basin in the north of Namibia. It is a vast hollow in the ground in which water may collect or in which a deposit of salt remains after water has evaporated. The 120-kilometre-long (75-mile-long) dry lakebed and its surroundings are protected as Etosha National Park, Namibia's second-largest wildlife park, covering 22,270 square kilometres (8,600 sq mi). The pan is mostly dry but after heavy rains it is flooded with a thin layer of water, which is heavily salted by the mineral deposits on the surface.

The South West Africa Territorial Force (SWATF) was an auxiliary arm of the South African Defence Force (SADF) and comprised the armed forces of South West Africa from 1977 to 1989. It emerged as a product of South Africa's political control of the territory which was granted to the former as a League of Nations mandate following World War I.
ǃKungKUUNG (ǃXun), also known as Ju, is a dialect continuum spoken in Namibia, Botswana, and Angola by the ǃKung people, constituting two or three languages. Together with the ǂʼAmkoe language, ǃKung forms the Kxʼa language family. ǃKung constituted one of the branches of the putative Khoisan language family, and was called Northern Khoisan in that scenario, but the unity of Khoisan has never been demonstrated and is now regarded as spurious. Nonetheless, the anthropological term "Khoisan" has been retained as an umbrella term for click languages in general.
Articles related to Namibia include:
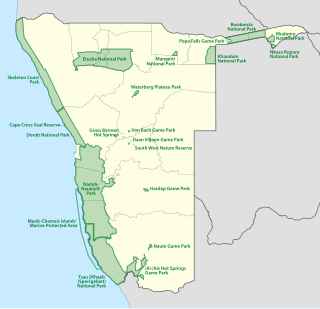
The protected areas of Namibia include its national parks and reserves. With the 2010 declaration of Dorob National Park, Namibia became the first and only country to have its entire coastline protected through a national parks network. Protected areas are subdivided into game reserves and/or nature reserves, such as special protected area, wilderness areas, natural areas, and development areas. There are also recreation reserves. Facilities in the national parks are operated by Namibia Wildlife Resorts. Over 19% of Namibia is protected, an area of some 130,000 square kilometres. However, the Ministry of Environment & Tourism auctions limited hunting rights within its protected areas. The Namibia Nature Foundation, an NGO, was established in 1987 to raise and administer funds for the conservation of wildlife and protected area management. Communal Wildlife Conservancies in Namibia help promote sustainable natural resource management by giving local communities rights to wildlife management and tourism.

The geology of Namibia encompasses rocks of Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic to Cenozoic age. About 46% of the countryʼs surface are bedrock exposure, while the remainder is covered by the young overburden sediments of the Kalahari and Namib deserts.
The following scientific events occurred in 2022.









