List of thalattosuchian-bearing stratigraphic units , or geologic formations.
Thalattosuchia is the name given to a clade of marine crocodylomorphs from the Early, Middle, and Late Jurassic period eras to the Early Cretaceous period era, that had a cosmopolitan distribution.
They are colloquially referred to as 'marine crocodiles' or 'sea crocodiles' though they are not members of Crocodilia.
The Mesozoic Era is the penultimate era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about 252 to 66 million years ago, comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of gymnosperms and of archosaurian reptiles, such as the dinosaurs; a hot greenhouse climate; and the tectonic break-up of Pangaea. The Mesozoic is the middle of the three eras since complex life evolved: the Paleozoic, the Mesozoic, and the Cenozoic.

The Neogene is a geologic period and system that spans 20.45 million years from the end of the Paleogene Period 23.03 million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the present Quaternary Period 2.58 million years ago. The Neogene is sub-divided into two epochs, the earlier Miocene and the later Pliocene. Some geologists assert that the Neogene cannot be clearly delineated from the modern geological period, the Quaternary. The term "Neogene" was coined in 1853 by the Austrian palaeontologist Moritz Hörnes (1815–1868). The earlier term Tertiary Period was used to define the span of time now covered by Paleogene and Neogene and, despite no longer being recognized as a formal stratigraphic term, "Tertiary" still sometimes remains in informal use.
The PaleozoicEra is the first of three geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six geologic periods :
The Phanerozoic is the current and the latest of the four geologic eons in the Earth's geologic time scale, covering the time period from 538.8 million years ago to the present. It is the eon during which abundant animal and plant life has proliferated, diversified and colonized various niches on the Earth's surface, beginning with the Cambrian period when animals first developed hard shells that can be clearly preserved in the fossil record. The time before the Phanerozoic, collectively called the Precambrian, is now divided into the Hadean, Archaean and Proterozoic eons.

The Triassic is a geologic period and system which spans 50.5 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.4 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period of the Mesozoic Era. Both the start and end of the period are marked by major extinction events. The Triassic Period is subdivided into three epochs: Early Triassic, Middle Triassic and Late Triassic.

Crocodilia is an order of mostly large, predatory, semiaquatic reptiles known as crocodilians. They first appeared 94 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous period and are the closest living relatives of birds, as the two groups are the only known survivors of the Archosauria. Members of the order's total group, the clade Pseudosuchia, appeared about 250 million years ago in the Early Triassic period, and diversified during the Mesozoic era. The order Crocodilia includes the true crocodiles, the alligators and caimans, and the gharial and false gharial. Although the term crocodiles is sometimes used to refer to all of these, crocodilians is a less ambiguous vernacular term for members of this group.

Marine reptiles are reptiles which have become secondarily adapted for an aquatic or semiaquatic life in a marine environment. Only about 100 of the 12,000 extant reptile species and subspecies are classed as marine reptiles, including marine iguanas, sea snakes, sea turtles, and saltwater crocodiles.

The saltwater crocodile is a crocodilian native to saltwater habitats, brackish wetlands and freshwater rivers from India's east coast across Southeast Asia and the Sundaic region to northern Australia and Micronesia. It has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List since 1996. It was hunted for its skin throughout its range up to the 1970s, and is threatened by illegal killing and habitat loss. It is regarded as dangerous to humans.

The American crocodile is a species of crocodilian found in the Neotropics. It is the most widespread of the four extant species of crocodiles from the Americas, with populations present from South Florida, the Caribbean islands of Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and the coasts of Mexico to as far south as Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela.
The Early Jurassic Epoch is the earliest of three epochs of the Jurassic Period. The Early Jurassic starts immediately after the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, 201.3 Ma, and ends at the start of the Middle Jurassic 174.7 ±0.8 Ma.
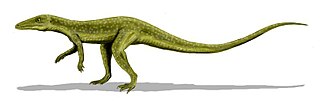
Saltoposuchus is an extinct genus of small, long-tailed crocodylomorph reptile (Sphenosuchia), from the Norian of Europe. The name translated means "leaping foot crocodile". It has been proposed that Terrestrisuchus gracilis and Saltoposuchus connectens represent different ontogenetic stages of the same genus. Saltoposuchus was commonly referred to in popular literature as the ancestor to dinosaurs; however, recent scientific research shows that this is not the case.

"Crocodile Rock" is a song written by Elton John and Bernie Taupin, and recorded in summer 1972 at the Château d'Hérouville studio in France, where John and his team had previously recorded the Honky Château album. It was released on 27 October 1972 in the UK and 20 November 1972 in the U.S., as a pre-release single from his forthcoming 1973 album Don't Shoot Me I'm Only the Piano Player, and became his first U.S. number-one single, reaching the top spot on 3 February 1973, and staying there for three consecutive weeks. In the U.S., it was certified Gold on 5 February 1973 and Platinum on 13 September 1995 by the RIAA.

Pseudosuchia is one of two major divisions of Archosauria, including living crocodilians and all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds. Pseudosuchians are also informally known as "crocodilian-line archosaurs". Despite Pseudosuchia meaning "false crocodiles", the name is a misnomer as true crocodilians are now defined as a subset of the group.

Thalattosuchia is a clade of mostly marine crocodylomorphs from the Early Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous that had a cosmopolitan distribution. They are colloquially referred to as marine crocodiles or sea crocodiles, though they are not members of Crocodilia and records from Thailand and China suggest that some members lived in freshwater. The clade contains two major subgroupings, the Teleosauroidea and Metriorhynchoidea. Teleosauroids are not greatly specialised for oceanic life, with back osteoderms similar to other crocodyliformes. Within Metriorhynchoidea, the Metriorhynchidae displayed extreme adaptions for life in the open ocean, including the transformation of limbs into flippers, the development of a tail fluke, and smooth, scaleless skin, and probably gave live birth, seemingly uniquely among archosaurs.

Hupehsuchus is an extinct genus of small marine reptiles, about 1 m (3 ft) long, found in the area of Hubei in China. This marine reptile lived in the Olenekian stage of the Early Triassic period. It was probably a filter feeder, like modern baleen whales.
Reptiles arose about 320 million years ago during the Carboniferous period. Reptiles, in the traditional sense of the term, are defined as animals that have scales or scutes, lay land-based hard-shelled eggs, and possess ectothermic metabolisms. So defined, the group is paraphyletic, excluding endothermic animals like birds that are descended from early traditionally-defined reptiles. A definition in accordance with phylogenetic nomenclature, which rejects paraphyletic groups, includes birds while excluding mammals and their synapsid ancestors. So defined, Reptilia is identical to Sauropsida.

Lolong was the largest crocodile in captivity. He was a saltwater crocodile measured at 6.17 m, and weighed 1,075 kg (2,370 lb), making him one of the largest crocodiles ever measured from snout-to-tail.
Paleontology in New Mexico refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of New Mexico. The fossil record of New Mexico is exceptionally complete and spans almost the entire stratigraphic column. More than 3,300 different kinds of fossil organisms have been found in the state. Of these more than 700 of these were new to science and more than 100 of those were type species for new genera. During the early Paleozoic, southern and western New Mexico were submerged by a warm shallow sea that would come to be home to creatures including brachiopods, bryozoans, cartilaginous fishes, corals, graptolites, nautiloids, placoderms, and trilobites. During the Ordovician the state was home to algal reefs up to 300 feet high. During the Carboniferous, a richly vegetated island chain emerged from the local sea. Coral reefs formed in the state's seas while terrestrial regions of the state dried and were home to sand dunes. Local wildlife included Edaphosaurus, Ophiacodon, and Sphenacodon.

Paleontology in Oregon refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Oregon. Oregon's geologic record extends back approximately 400 million years ago to the Devonian period, before which time the state's landmass was likely submerged under water. Sediment records show that Oregon remained mostly submerged until the Paleocene period. The state's earliest fossil record includes plants, corals, and conodonts. Oregon was covered by seaways and volcanic islands during the Mesozoic era. Fossils from this period include marine plants, invertebrates, ichthyosaurs, pterosaurs, and traces such as invertebrate burrows. During the Cenozoic, Oregon's climate gradually cooled and eventually yielded the environments now found in the state. The era's fossils include marine and terrestrial plants, invertebrates, fish, amphibians, turtles, birds, mammals, and traces such as eggs and animal tracks.

Crocodile is the provisional name of a predynastic ruler, who might have ruled during the late Naqada III epoch. The few alleged ink inscriptions showing his name are drawn very sloppily, and the reading and thus whole existence of king "Crocodile" are highly disputed. His tomb is unknown.