| Reuchenette Formation | |
|---|---|
| Stratigraphic range: Kimmeridgian, | |
 | |
| Type | Geological formation |
| Sub-units | Membre de Chevenez, Membre de Courtedoux, Marne du Banné, Membre de Vabenau |
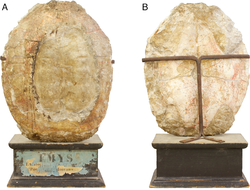
| Underlies | Twannbach Formation |
| Overlies | Formation de Court, Balsthal-Formation, Membre de Porrentruy, Verena-Member, Holzflue-Member, Formation de Courgenay |
| Thickness | 140 metres average, 160 m in type area. |
| Lithology | |
| Primary | Limestone |
| Other | Mudstone |
| Location | |
| Region | Europe |
| Country | Switzerland |
The Reuchenette Formation is a Jurassic geologic formation in Switzerland. It is Kimmeridgian in age and predominantly consists of well stratified limestone, with lithology variable both laterally and stratigraphically including wackestones, packstones and grainstones, as well as mudstone. [1] Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, including the Turiasaurian sauropod Amanzia greppini, alongside a theropod tooth belonging to Ceratosauria indet, originally assigned to Megalosaurus meriani. [2] teleosaurid crocodyliformes are also known, including Sericodon, Proexochokefalos and Machimosaurus. [3] The metriorhynchid thalatosuchians Torvoneustes [4] and Dakosaurus . The hybodontid shark Asteracanthus . [5] The thalassochelydian turtle Thalassemys [6] and Solnhofia is known from the formation, [7] as is the platychelyid turtles Platychelys, [8] and the plesiochelyid turtle Plesiochelys . [9]