
The Kenya Defence Forces (KDF) are the armed forces of the Republic of Kenya. They are made up of the Kenya Army, Kenya Navy, and Kenya Air Force. The current KDF was established, and its composition stipulated, in Article 241 of the 2010 Constitution of Kenya; it is governed by the KDF Act of 2012. Its main mission is the defence and protection of the sovereignty and territorial integrity of Kenya, recruitment to the KDF is done on yearly basis. The President of Kenya is the commander-in-chief of the KDF, and the Chief of Defence Forces is the highest-ranking military officer, and the principal military adviser to the President of Kenya.

Children have been recruited for participation in military operations and campaigns throughout history and in many cultures.

A human shield is a non-combatant who either volunteers or is forced to shield a legitimate military target in order to deter the enemy from attacking it.
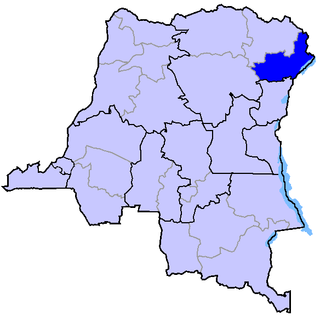
The Nationalist and Integrationist Front is a rebel group active in the Ituri conflict in Ituri, Democratic Republic of the Congo, associated with the Lendu ethnic group. The FNI has fought against ethnic Hema and is blamed for the ambush and murder of nine United Nations peacekeepers near the town of Kafe in February 2005. FNI political leader Floribert Ndjabu was arrested by Congolese authorities, while military head Etienne Lona turned himself in.
Michael Rubin is a senior fellow at the American Enterprise Institute (AEI). He previously worked as an official at the Pentagon, where he dealt with issues relating to the Middle East, and as political adviser to the Coalition Provisional Authority.

Major General Mohammed Said Hersi Morgan, also known as General Morgan or Colonel Morgan, is a Somali military and faction leader. He was the son-in-law of Siad Barre and Minister of Defence of Somalia. He hails from the Majeerteen Darood clan.
The Shifta War or Gaf Daba (1963–1967) was a secessionist conflict in which ethnic Somalis in the Northern Frontier District (NFD) of Kenya attempted to join Somalia. The Kenyan government named the conflict "shifta", after the Swahili word for "bandit", as part of a propaganda effort. The Kenyan counter-insurgency General Service Units forced civilians into "protected villages" as well as killing livestock kept by the pastoralist Somalis.

The Comprehensive Peace Agreement, also known as the Naivasha Agreement, was an accord signed on 9 January 2005, by the Sudan People's Liberation Movement (SPLM) and the Government of Sudan. The CPA was meant to end the Second Sudanese Civil War, develop democratic governance countrywide, and share oil revenues. It also set a timetable for a Southern Sudanese independence referendum.
The Sabaot Land Defence Force (SLDF) was a guerrilla militia operating in the Mount Elgon District of Kenya since 2005. It has been accused of killing more than 600 people, and of committing a variety of atrocities including murder, torture, rape, and the theft and destruction of property. More than 66,000 people had been displaced in an 18-month period.

The Mount Elgon insurgency was a conflict that started in 2005 when the Sabaot Land Defence Force militia revolted in the Mount Elgon area, Western Kenya.
Corinne Dufka is an American photojournalist, human rights researcher, criminal investigator, and social worker. She is the recipient of a MacArthur "genius grant" Fellowship.

Somalis in Kenya are citizens and residents of Kenya who are of Somali ethnic descent. They have historically inhabited the North Eastern Province, previously called the Northern Frontier District, which was carved out of the Jubaland region of present-day southern Somalia during the colonial period. Following the civil war in Somalia that broke out in 1991, many Somalis sought asylum in the Somali-inhabited enclaves of Kenya. An entrepreneurial community, they established themselves in the business sector, particularly in the Nairobi suburb of Eastleigh.

Human rights in South Sudan are a contentious issue, owing at least in part to the country's violent history.
Human rights abuses in Jammu and Kashmir range from mass killings, enforced disappearances, torture, rape and sexual abuse to political repression and suppression of freedom of speech. The Indian Army, Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF), and Border Security Personnel (BSF) have been accused of committing severe human rights abuses against Kashmiri civilians. According to Seema Kazi, militant groups have also been held responsible for similar crimes, but the vast majority of abuses have been perpetrated by the armed forces of the Indian government.
A coup d'état was carried out by the Sudanese Armed Forces on 30 June 1989 against the democratically elected government of Prime Minister Sadiq al-Mahdi and President Ahmed al-Mirghani. The coup was led by military officer Omar al-Bashir who took power in its aftermath; he ruled the country for the next 30 years until he was overthrown in 2019.

The Isaaq genocide, or Hargeisa holocaust, was the systematic, state-sponsored genocide of Isaaq civilians between 1987 and 1989 by the Somali Democratic Republic, under the dictatorship of Siad Barre, during the Somaliland War of Independence. The number of civilian deaths in this massacre is estimated to be between 50,000 and 100,000, according to various sources, whilst local reports estimate the total civilian deaths to be upwards of 200,000 Isaaq civilians. The genocide also included the levelling and complete destruction of the second and third largest cities in the Somali Republic, Hargeisa and Burao, respectively, and had caused up to 500,000 Somalis of the region, primarily of the Isaaq clan, to flee their land and cross the border to Hartasheikh in Ethiopia as refugees in what was described as "one of the fastest and largest forced movements of people recorded in Africa", which resulted in the creation of the world's largest refugee camp then (1988), with another 400,000 being displaced. The scale of destruction led to Hargeisa being known as the 'Dresden of Africa'. The killings happened during the Somali Civil War and have been referred to as a "forgotten genocide".
The Kashmir conflict has been beset by large scale usage of sexual violence by multiple belligerents since its inception.









